Abstract
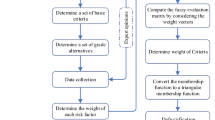
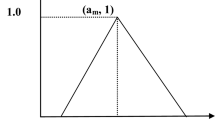
This paper is an attempt to develop and compare the risk indices developed by various methods of project risk analysis like modified expected value method, fuzzy expected value method and fuzzy analytic hierarchy process for an elevated metro rail corridor construction project in Bangalore, India. Risk management is increasingly a critical success factor for major infrastructure projects. It helps to identify, analyse, mitigate and control the risks associated with project cost, schedule and scope. Infrastructure projects are usually faced by different types of risks associated with different types of activities which finally lead to cost and time overrun. The main purpose of this work was to identify the risks and uncertainties associated with major activities of an infrastructure project like elevated metro rail corridor project and then analyse for risk severity and risk index through three different methods. It has been observed that fuzzy expected value method is more sensitive than the other two methods, and the computed values of risk indices predict risk severities which can be ranked according to criticality for almost all the identified activities. Thus, project authorities can easily take necessary mitigation measures to reduce the risk severities. Also, fuzzy expected value method gives good results for both small and large number of activities, whilst modified expected value method works well for up to 25 activities and fuzzy analytic hierarchy process works well for up to 20 activities.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Askari, H. Hokrizadeh, N. Ghane, A fuzzy AHP model in risk ranking, European. J. Bus. Manag. 6(14), 194–203 (2014)
D. Sarkar, G. Dutta, A framework of project risk management for the underground corridor construction of metro rail. Int. J. Constr. Proj. Manag. 4(1), 21–38 (2011)
H. Choi, H. Cho, J.W. Seo, Risk assessment methodology for underground construction projects. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 130(2), 258–272 (2004)
Y.C. Kuo, S.T. Lu, Using fuzzy multiple criteria decision making approach to enhance risk assessment for metropolitan construction projects. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 31, 602–614 (2013)
D. Sarkar, H.B. Raghavendra, M. Singh, P. Shah, Development of risk index through modified analytic hierarchy process (MAHP) tool for elevated corridor metro rail project. NICMAR J. Constr. Manag. 31(3), 5–18 (2016)
D. Sarkar, M. Singh, H.B. Raghavendra, Application of fuzzy analytic hierarchy process for development of risk index for elevated corridor metro rail project in Western India. Int. J. Decis. Sci. Risk Manag. 7(4), 281–298 (2017)
R.W. Saaty, The AHP—what it is and how it is used. Maths Model. 9(3–5), 161–176 (1987)
M.A. Mustafa, J.F. Al-Bahar, Project risk assessment using the analytic hierarchy process. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 38(1), 46–52 (1991)
A. Shapira, M. Simcha, AHP—based weighing of factors affecting safety on construction sites with tower cranes. J. Manag. Eng. 135(4), 307–318 (2009)
P.X.W. Zou, G. Zhang, J. Wang, Understanding the key risks in construction projects in China. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 25(6), 601–614 (2007)
A.V.O. Oliveros, A.R. Fayek, Fuzzy logic approach for activity delay analysis and scheduling updating. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 131(1), 42–51 (2005)
J. Li, P.X.W. Zou, Fuzzy AHP—based risk assessment methodology for PPP projects. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 128(6), 1205–1209 (2011)
M.V.K. Rao, V.S.S. Kumar, P.R. Kumar, Optimal contractor selection in construction industry: the fuzzy way. J. Inst. Eng. Ser. A 99(1), 67–78 (2018)
A. Majumder, T. Hazra, A. Dutta, Landfill site selection by AHP based multi-criteria decision making tool: a case study in Kolkata, India. J. Inst. Eng. Ser. A 98(3), 277–283 (2017)
V. Srinivas, S. Sasmal, R. Karusala, Fuzzy based decision support system for condition assessment and rating of bridges. J. Inst. Eng. Ser. A 97(3), 261–272 (2016)
P.K. Roy, P. Adhikary, A. Mazumdar, Preventive maintenance prioritization by fuzzy logic for seamless hydropower generation. J. Inst. Eng. Ser. A 95(2), 97–104 (2014)
C.S.J. Eom, J.H. Paek, Risk index model for minimizing environmental disputes in construction. J. Manag. Eng. 135(1), 34–41 (2009)
T.N. Mhatre, J.J. Thakkar, J. Maiti, Modelling critical risk factors for Indian construction project using interpretive ranking process (IRP) and system dynamics (SD). Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 34(9), 1451–1473 (2017)
J.M. Nicholas, Project Management for Business and Technology: Principles and Practice (Pearson Prentice Hall, New Delhi, 2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, M., Sarkar, D. & Vara, D. Comparative Study of Risk Indices for Infrastructure Transportation Project Using Different Methods. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. A 100, 275–286 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40030-018-0353-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40030-018-0353-0