Abstract
Background:
Escherichia coli–derived Shiga toxin (Stx), the cause of the enteropathic hemolytic uremic syndrome, is a potent inducer of apoptotic cell death. The present study was performed to examine the hypothesis that Stx initiates apoptosis by activating the mitochondrial pathway involving mitochondrial–associated, pro–apoptotic Bcl–2 family proteins Bax and Bak.
Materials and Methods:
To determine if Stx2–mediated apoptosis is dependent on Bax or Bak, a gene–silencing approach was employed using sequence–specific small interfering (si)RNA duplexes. Silencing of Bax and Bak protein expression in human renal proximal tubular epithelial (HK–2) cells and its effect on Shiga toxicity was assessed by immunofluorescence microscopy and Western blotting.
Results:
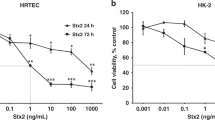
Transfection of HK–2 cells, shown to be exquisitely sensitive to Stx, with siRNA duplexes successfully diminished Bak, but not Bax protein expression. In order to determine if silencing of pro–apoptotic gene expression affects Stx–induced apoptosis, HK–2 cells were transfected with Bak–specific or control siRNA, exposed to lethal concentrations of Stx2 and assessed for cleavage of poly(ADPribose) polymerase–1 (PARP) as a marker of apoptosis, using Western blot technology. We observed that siRNA–induced reduction of Bak expression levels correlated with decreased PARP cleavage.
Conclusion:
Results suggest that Stx–induced cell death involves pro–apoptotic Bak and that silencing of Bak gene expression affords partial protection against Stx–mediated apoptosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper is dedicated to the founders of the Walter Marget Foundation, D. Adam and F. Daschner, in gratitude for their support of the training in infectious diseases.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilson, C., Foster, G.H. & Bitzan, M. Silencing of Bak Ameliorates Apoptosis of Human Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells by Escherichia coli–Derived Shiga Toxin 2. Infection 33, 362–367 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-005-5073-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-005-5073-5