Abstract
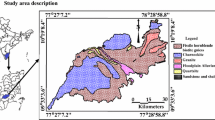
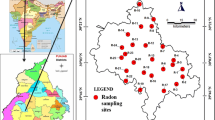
Sankarabarani river basin gains importance due to agriculture, an industrial and recreational activity that delivers large groundwater fluxes to the Bay. Attempt has been made by continuous monitoring of radon isotopes to evaluate submarine groundwater discharge with reference to groundwater and surface and pore water samples with distance perpendicular to the coast. 222Rn in groundwater samples were higher (543.0 Bq m−3) signifying major radon sources due to coastal groundwater discharge. Radon mass balance model attempted by considering fluxes like tides, atmospheric emissions, and sediment diffusion suggests higher groundwater and surface water fluxes (7.2 and 20.15 m day−1) near to the coast and higher fluxes (19.7 and 9.7 m day−1) in pore water away from the coast, suggesting influence of hydraulic gradient and radium retention in sediments. The average fresh submarine groundwater discharge calculated accounts 0.88 m day−1, higher in comparison with world studies.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SGD:
-
Submarine groundwater discharge
- RSGD:
-
Recirculated saline groundwater discharge
- SFGD:
-
Submarine fresh groundwater discharge
- AMSL:
-
Above mean sea level
- km:
-
Kilometer
- mm:
-
Millimeter
- BGL:
-
Below ground level
- LPM:
-
Liter per minute
- 222Rn:
-
Radon
References
Abraham DM, Charette MA, Allen MC, Rago A, Kroeger KD (2003) Radiochemical estimates of submarine groundwater discharge to Waquoit Bay, Massachusetts. Biol Bull 205:246–247
Barwell VK, Lee DR (1981) Determination of horizontal-to-vertical hydraulic conductivity ratios from seepage measurements on lake beds. Water Resour Res 17:65–70. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR017i003p00565
Bokuniewicz HJ (1980) Groundwater seepage into Great South Bay, New York. Estuar Coast Mar Sci 10:437–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0302-3524(80)80122-8
Burnett WC, Dulaiova H (2003) Estimating the dynamics of groundwater input into the coastal zone via continuous radon-222 measurements. J Environ Radioact 69:21–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0265-931X(03)00084-5
Burnett WC, Dulaiova H (2006) Radon as a tracer of submarine groundwater discharge into a boat basin in Donnalucata, Sicily. Cont Shelf Res 26:862–873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2005.12.003
Burnett WC, Cable JE, Corbett DR (2003a) Radon tracing of submarine groundwater discharge in coastal environments. In: Taniguchi M, Wang K, Gamo T (eds) Land and marine hydrogeology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 25–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-044451479-0/50015-7
Burnett WC, Chanton JP, Kontar E (2003b) Submarine groundwater discharge, special issue. Biogeochem 202(66):1–2
Burnett WC, Aggarwal PK, Aureli A, Bokuniewicz H, Cable JE, Charette MA, Kontar E, Krupa S, Kulkarni KM, Loveless A, Moore WS, Oberdorfer JA, Oliveira J, Ozyurt N, Povinec P, Privitera AMG, Rajar R, Ramessur RT, Scholten J, Stieglitz T, Taniguchi M, Turner JV (2006) Quantifying submarine groundwater discharge in the coastal zone via multiple methods. Sci Total Environ 367:498–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.05.009
Burnett WC, Peterson RN, Chanyotha S, Wattayakorn G, Ryan B (2013) Using high-resolution in situ radon measurements to determine groundwater discharge at a remote location: Tonle Sap Lake, Cambodia. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 296:97–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-012-1914-8
Cable JE, Burnett WC, Chanton JP, Weatherly GL (1996) Estimating groundwater discharge into the northeastern Gulf of Mexico using radon-222. Earth Planet Sci Lett 144:591–604. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0012-821X(96)00173-2
Central Groundwater board, Ground water brochure (2007) Puducherry Region Union Territory of Puducherry, technical report series, SECR/DBR/UT/12-13/01 27
Central water commission, Water year book (2017) East flowing rivers basin, volume-I, stream flow and suspended sediment data. Cauvery and southern rivers organization, Coimbatore, Unpublished report, p 488
Dulaiova H, Peterson R, Burnett WC (2005) A multi-detector continuous monitor for assessment of 222Rn in the coastal ocean. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 263:361–365
Dulaiova H, Burnett WC, Chanton JP, Moore WS, Bokuniewicz HJ (2006) Assessment of groundwater discharges into West Neck Bay, New York, via natural tracers. Cont Shelf Res 26:1971–1983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2006.07.011
Dulaiova H, Gonneea ME, Henderson PB, Charette MA (2008) Geochemical and physical sources of radon variation in a subterranean estuary—implications for groundwater radon activities in submarine groundwater discharge studies. Mar Chem 110:120–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2008.02.011
Eckerman K, Harrison J, Menzel HG, Clement CH (2012) ICRP Publication 119: compendium of dose coefficients based on ICRP Publication 60
Geng X, Boufadel MC, Xia Y, Li H, Zhao L, Jackson NL (2014) Numerical study of wave effects on groundwater flow and solute transport in a laboratory beach. J Contam Hydrol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2014.07.001
Grolander S, Kärnbränslehantering S (2009) Radon as a groundwater tracer in Forsmark and Laxemar, SKB Rapport R-09-47, 55
Happell JD, Chanton JP, Showers WJ (1995) Methane transfer across the air–water interface in stagnant wooded swamps of Florida: evaluation of mass-transfer coefficients and isotopic fractionation. Lim Oceano 40(2):290–298. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1995.40.2.0290
Hussain N, Church TM, Kim G (1999) Use of 222Rn and 226Ra to trace submarine groundwater discharge into the Chesapeake Bay. Mar Chem 65:127–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4203(99)00015-8
Jahne BKO, Munnich R, Bosinger A, Dutzi W, Huber P, Libner P (1987) On the parameters influencing air–water gas exchange. J Geophys Res 92:1937–1950
Kim G, Hwang DW (2002) Tidal pumping of groundwater into the coastal ocean revealed from submarine Rn-222 and CH4 monitoring. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002GL015093
Kim I, Kim G (2011) Large fluxes of rare earth elements through submarine groundwater discharge (SGD) from a volcanic island, Jeju, Korea. Mar Chem 127:12–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2011.07.006
Kroeger KD, Swarzenski PW, Greenwood JW, Reich C (2007) Submarine groundwater discharge to Tampa Bay: nutrient fluxes and biogeochemistry of the aquifer. Mar Chem 104:85–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2006.10.012
Lee C, Jiao JJ, Luo X (2012) Estimation of submarine groundwater discharge and associated nutrient fluxes in Tolo Harbour, Hong Kong. Sci Tot Environ 433:427–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.06.073
Macintyre S, Wanninkhof R, Chanton JP (1995) Trace gas exchange across the air–sea interface in fresh water and coastal environments. In: Harris RC, Mattson PA (eds) Biogenic trace gases: measuring emissions from soil and water. Blackwell Science Ltd, Hoboken, pp 52–77
Martens CS, Kipphut GW, Klum JV (1980) Sediment-495 water chemical exchange in the coastal zone traced by in situ radon-222 flux measurements. Science 208(4441):285–288. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.208.4441.285
Moore WS (1996) Large groundwater inputs to coastal waters revealed by 226Ra enrichments. Nature 380:612–614
Ouyang Y, Zhang JE, Parajuli P (2013) Characterization of shallow groundwater quality in the Lower St. Johns River Basin: a case study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(12):8860–8870. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1864-x
Raghavayya M, Iyengar M, Markose PM (1980) Estimation of Ra-226 by emanometry. Bull Radiat Prot 3:5
Santos IR, Eyre BD (2011) Radon tracing of groundwater discharge into an Australian estuary surrounded by coastal acid sulphate soils. J Hydrol 396:246–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.11.013
Schumann EH (1988) Physical oceanography, Natal. In: Schumann EH (ed) Coastal ocean studies, South Africa, Lecture notes on coastal and estuarine studies, vol 26. Springer, Berlin, pp 101–130
Sekulic B, Vertacnik A (1996) Balance of average annual fresh water inflow into the Adriatic Sea. Water Resour Dev 12:89–97
Slomp CP, Van Cappellen P (2004) Nutrient inputs to the coastal ocean through submarine groundwater discharge: controls and potential impact. J Hydrol 295:64–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2004.02.018
Srivastava A, Lalramengzami R, Laldawngliana C, Sinha D, Ghosh S, Dwivedi KK, Saxena A, Ramachandran TV (1996) Measurement of potential alpha energy exposure (PAEE) of radon and its progenies in dwellings in north eastern region of India. Radiat Meas 26:291–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/1350-4487(95)00295-2
Taniguchi M, Inouchi K, Tase N, Shimada J (1999) Combination of tracer and numerical simulations to evaluate the groundwater capture zone. IAHS Publ 258:207–213
Tse KC, Jiao JJ (2008) Estimation of submarine groundwater discharge in Plover Cove, Tolo Harbour, Hong Kong by 222Rn. Mar Chem 111:160–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2008.04.012
Wang X, Li H, Jinzhong Y, Zheng C, Zhang Y (2017) Nutrient inputs through submarine groundwater discharge in an embayment: a radon investigation in Daya Bay. J Hydrol, China. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.02.036
Wen T, Du J, Ji T, Wang X, Deng B (2014) Use of 222Rn to trace submarine groundwater discharge in a tidal period along the coast of Xiangshan, Zhejiang, China. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 299:53–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-013-2786-2
Wu Z, Zhou H, Zhang S, Liu Y (2013) Using 222Rn to estimate submarine groundwater discharge (SGD) and the associated nutrient fluxes into Xiangshan Bay, East China Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 73:183–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.05.024
Zektser IS, Loaiciga HA (1993) Groundwater fluxes in the global hydrologic cycle: past, present and future. J Hydrol 144:405–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(93)90182-9
Zijun WU, Zhou H, Zhang S, Liu Y (2013) Using 222Rn to estimate submarine groundwater discharge (SGD) and the associated nutrient fluxes into Xiangshan Bay, East China Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 73:183–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.05.024
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Department of Science and Technology, Science and Engineering Research board (Grant No. EMR/2015/001101), India. The authors thank their lab colleagues and students for their help during the field expeditions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Prof. M. Abbaspour.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srinivasamoorthy, K., Ponnumani, G., Prakash, R. et al. Tracing groundwater inputs to Bay of Bengal from Sankarabarani River Basin, Pondicherry, India, using continuous radon monitoring. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 5513–5524 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1938-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1938-x