Abstract
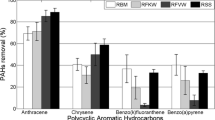
This work assesses the suitability of three commercial activated carbons (ACs) and their combination with olive mill waste compost (AC + C) as amendments for the remediation of two different contaminated soils. The treatments were applied to a mining soil, and their ability to immobilize trace elements was evaluated. Besides, the efficiency of the amendments to degrade and reduce the availability of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) was investigated in a soil from a wood creosote treatment plant. To this aim, trace elements mobility and PAH degradation and availability were evaluated. Ecotoxicological assays were performed to assess potential toxicity risks in the untreated and the amended soils. In the mining soil, the ACs were able to immobilize metals and As, but the AC + C treatments were more effective than AC. In the PAH-polluted soil, AC treatments promoted the degradation of high molecular weight PAH, but the AC + C amendments further enhanced the degradation of total PAH and reduced the availability of those with 3-rings. The ecotoxicological tests demonstrated an improvement of soil quality when AC and compost were applied together. In conclusion, the co-application of AC and compost reduces the mobility of potentially toxic elements in the polluted mine soil and enhances PAH degradation and reduces PAH availability in the creosote-contaminated soil.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alburquerque JA, de la Fuente C, Bernal MP (2011) Improvement of soil quality after “alperujo” compost application to two contaminated soils characterised by differing heavy metal solubility. J Environ Manage 92:733–741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.10.018
Alvarenga P, Palma P, Gonçalves AP et al (2009) Organic residues as immobilizing agents in aided phytostabilization: (II) effects on soil biochemical and ecotoxicological characteristics. Chemosphere 74:1301–1308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.11.006
Anyika C, Abdul Majid Z, Ibrahim Z et al (2015) The impact of biochars on sorption and biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils—a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:3314–3341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3719-5
Arco-Lázaro E, Agudo I, Clemente R, Bernal MP (2016) Arsenic (V) adsorption-desorption in agricultural and mine soils: effects of organic matter addition and phosphate competition. Environ Pollut 216:71–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.05.054
Arienzo M, Adamo P, Cozzolino V (2004) The potential of Lolium perenne for revegetation of contaminated soil from a metallurgical site. Sci Total Environ 319:13–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(03)00435-2
Bauer M, Blodau C (2006) Mobilization of arsenic by dissolved organic matter from iron oxides, soils and sediments. Sci Total Environ 354:179–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.01.027
Beesley L, Moreno-Jiménez E, Gomez-Eyles JL (2010) Effects of biochar and greenwaste compost amendments on mobility, bioavailability and toxicity of inorganic and organic contaminants in a multi-element polluted soil. Environ Pollut 158:2282–2287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2010.02.003
Beesley L, Moreno-Jiménez E, Gomez-Eyles JL et al (2011) A review of biochars’ potential role in the remediation, revegetation and restoration of contaminated soils. Environ Pollut 159:3269–3282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.07.023
Beesley L, Marmiroli M, Pagano L et al (2013) Biochar addition to an arsenic contaminated soil increases arsenic concentrations in the pore water but reduces uptake to tomato plants (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Sci Total Environ 454–455:598–603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.02.047
Beesley L, Inneh OS, Norton GJ et al (2014) Assessing the influence of compost and biochar amendments on the mobility and toxicity of metals and arsenic in a naturally contaminated mine soil. Environ Pollut 186:195–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.11.026
Brändli RC, Hartnik T, Henriksen T, Cornelissen G (2008) Sorption of native polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) to black carbon and amended activated carbon in soil. Chemosphere 73:1805–1810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.08.034
Brennan A, Moreno-Jiménez E, Alburquerque JA et al (2014) Effects of biochar and activated carbon amendment on maize growth and the uptake and measured availability of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and potentially toxic elements (PTEs). Environ Pollut 193:79–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2014.06.016
Cabal B, Ania CO, Parra JB, Pis JJ (2009) Kinetics of naphthalene adsorption on an activated carbon: comparison between aqueous and organic media. Chemosphere 76:433–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.04.002
Calvo L, Gilarranz MA, Casas JA et al (2006) Hydrodechlorination of 4-chlorophenol in aqueous phase using Pd/AC catalysts prepared with modified active carbon supports. Appl Catal B Environ 67:68–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2006.04.016
Clemente R, Walker DJ, Pardo T et al (2012) The use of a halophytic plant species and organic amendments for the remediation of a trace elements-contaminated soil under semi-arid conditions. J Hazard Mater 223–224:63–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.04.048
Clemente R, Pardo T, Madejón P et al (2015) Food byproducts as amendments in trace elements contaminated soils. Food Res Int 73:176–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2015.03.040
Denyes MJ, Rutter A, Zeeb BA (2013) In situ application of activated carbon and biochar to PCB-contaminated soil and the effects of mixing regime. Environ Pollut 182:201–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.07.016
Elouear Z, Bouhamed F, Bouzid J (2014) Evaluation of different amendments to stabilize cadmium, zinc, and copper in a contaminated soil: influence on metal leaching and phytoavailability. Soil Sediment Contam 23:628–640. https://doi.org/10.1080/15320383.2014.857640
Fresno T, Peñalosa JM, Santner J et al (2016) Iron plaque formed under aerobic conditions efficiently immobilizes arsenic in Lupinus albus L roots. Environ Pollut 2016:215–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.05.071
García-Delgado C, Yunta F, Eymar E (2013) Methodology for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons extraction from either fresh or dry spent mushroom compost and quantification by high-performance liquid chromatography–photodiode array detection. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 44:817–825. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2013.749439
García-Delgado C, Alfaro-Barta I, Eymar E (2015a) Combination of biochar amendment and mycoremediation for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons immobilization and biodegradation in creosote-contaminated soil. J Hazard Mater 285:259–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.12.002
García-Delgado C, D’Annibale A, Pesciaroli L et al (2015b) Implications of polluted soil biostimulation and bioaugmentation with spent mushroom substrate (Agaricus bisporus) on the microbial community and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons biodegradation. Sci Total Environ 508:20–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.11.046
García-Delgado C, Yunta F, Eymar E (2015c) Bioremediation of multi-polluted soil by spent mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) substrate: polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons degradation and Pb availability. J Hazard Mater 300:281–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.07.008
Gomez-Eyles JL, Sizmur T, Collins CD, Hodson ME (2011) Effects of biochar and the earthworm Eisenia fetida on the bioavailability of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and potentially toxic elements. Environ Pollut 159:616–622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2010.09.037
Hale SE, Elmquist M, Brändli R et al (2012) Activated carbon amendment to sequester PAHs in contaminated soil: a lysimeter field trial. Chemosphere 87:177–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.12.015
Herrero-Hernández E, Andrades MS, Rodríguez-Cruz MS, Sánchez-Martín MJ (2011) Effect of spent mushroom substrate applied to vineyard soil on the behaviour of copper-based fungicide residues. J Environ Manage 92:1849–1857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2011.03.011
IARC (2010) Monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. Some non-heterocyclic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and some related exposures. IARC, Lyon, France
ISO (2007) Water quality—determination of the inhibitory effect of water samples on the light emission of Vibrio fischeri (luminescent bacteria test)—part 3: method using freeze-dried bacteria. ISO 11348-3. The International Organization for Standardization
Jakob L, Hartnik T, Henriksen T et al (2012) PAH-sequestration capacity of granular and powder activated carbon amendments in soil, and their effects on earthworms and plants. Chemosphere 88:699–705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.03.080
Karami N, Clemente R, Moreno-Jiménez E et al (2011) Efficiency of green waste compost and biochar soil amendments for reducing lead and copper mobility and uptake to ryegrass. J Hazard Mater 191:41–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.04.025
Karer J, Wawra A, Zehetner F et al (2015) Effects of biochars and compost mixtures and inorganic additives on immobilisation of heavy metals in contaminated soils. Water Air Soil Pollut 226:342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2584-2
Kołtowski M, Hilber I, Bucheli TD, Oleszczuk P (2016) Effect of activated carbon and biochars on the bioavailability of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in different industrially contaminated soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:11058–11068. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6196-1
Li L, Quinlivan PA, Knappe DRU (2002) Effects of activated carbon surface chemistry and pore structure on the adsorption of organic contaminants from aqueous solution. Carbon NY 40:2085–2100. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6223(02)00069-6
Lladó S, Covino S, Solanas A et al (2015) Pyrosequencing reveals the effect of mobilizing agents and lignocellulosic substrate amendment on microbial community composition in a real industrial PAH-polluted soil. J Hazard Mater 283:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.08.065
Lukic B, Huguenot D, Panico A et al (2016) Importance of organic amendment characteristics on bioremediation of PAH-contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:15041–15052. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6635-z
Lukić B, Huguenot D, Panico A et al (2017) Influence of activated sewage sludge amendment on PAH removal efficiency from a naturally contaminated soil: application of the landfarming treatment. Environ Technol 0:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2017.1284903
Manzano R, Peñalosa JM, Esteban E (2014) Amendment application in a multicontaminated mine soil: effects on trace element mobility. Water Air Soil Pollut 225:1874–1885. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-1874-4
Marchal G, Smith KEC, Rein A et al (2013a) Comparing the desorption and biodegradation of low concentrations of phenanthrene sorbed to activated carbon, biochar and compost. Chemosphere 90:1767–1778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.07.048
Marchal G, Smith KEC, Rein A et al (2013b) Impact of activated carbon, biochar and compost on the desorption and mineralization of phenanthrene in soil. Environ Pollut 181:200–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2013.06.026
Monsalvo VM, Mohedano AF, Rodriguez JJ (2012) Adsorption of 4-chlorophenol by inexpensive sewage sludge-based adsorbents. Chem Eng Res Des 90:1807–1814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2012.03.018
Moreno-Jiménez E, Peñalosa JM, Manzano R et al (2009) Heavy metals distribution in soils surrounding an abandoned mine in NW Madrid (Spain) and their transference to wild flora. J Hazard Mater 162:854–859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.05.109
Moreno-Jiménez E, Manzano R, Esteban E, Peñalosa J (2010) The fate of arsenic in soils adjacent to an old mine site (Bustarviejo, Spain): mobility and transfer to native flora. J Soils Sediments 10:301–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-009-0099-4
Nisbet IC, LaGoy PK (1992) Toxic equivalency factors (TEFs) for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 16:290–300
Oleszczuk P, Kuśmierz M, Godlewska P et al (2016) The concentration and changes in freely dissolved polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in biochar-amended soil. Environ Pollut 214:748–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.04.064
Ouyang L, Tang Q, Yu L, Zhang R (2014) Effects of amendment of different biochars on soil enzyme activities related to carbon mineralisation. Soil Res 52:706–716. https://doi.org/10.1071/SR14075
Pardo T, Clemente R, Bernal MP (2011) Effects of compost, pig slurry and lime on trace element solubility and toxicity in two soils differently affected by mining activities. Chemosphere 84:642–650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.03.037
Pardo T, Clemente R, Epelde L et al (2014) Evaluation of the phytostabilisation efficiency in a trace elements contaminated soil using soil health indicators. J Hazard Mater 268:68–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.01.003
Pérez-Esteban J, Escolástico C, Masaguer A et al (2014) Soluble organic carbon and pH of organic amendments affect metal mobility and chemical speciation in mine soils. Chemosphere 103:164–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.11.055
Rey A, Zazo JA, Casas JA et al (2011) Influence of the structural and surface characteristics of activated carbon on the catalytic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. Appl Catal A Gen 402:146–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2011.05.040
Rodríguez-Vila A, Asensio V, Forján R, Covelo EF (2015) Chemical fractionation of Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn in a mine soil amended with compost and biochar and vegetated with Brassica juncea L. J Geochemical Explor 158:74–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.07.005
Sayara T, Sarrà M, Sánchez A (2010) Effects of compost stability and contaminant concentration on the bioremediation of PAHs-contaminated soil through composting. J Hazard Mater 179:999–1006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.03.104
Stefaniuk M, Oleszczuk P, Różyło K (2017) Co-application of sewage sludge with biochar increases disappearance of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from fertilized soil in long term field experiment. Sci Total Environ 599:854–862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.05.024
Stokes JD, Wilkinson A, Reid BJ et al (2005) Prediction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon biodegradation in contaminated soils using an aqueous hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin extraction technique. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:1325–1330. https://doi.org/10.1897/04-336R.1
Tyagi M, da Fonseca MMR, de Carvalho CCCR (2011) Bioaugmentation and biostimulation strategies to improve the effectiveness of bioremediation processes. Biodegradation 22:231–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-010-9394-4
Wu G, Kechavarzi C, Li X et al (2013) Influence of mature compost amendment on total and bioavailable polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in contaminated soils. Chemosphere 90:2240–2246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.10.003
Zhang X, Wang H, He L et al (2013) Using biochar for remediation of soils contaminated with heavy metals and organic pollutants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:8472–8483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1659-0
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness of Spain, projects CTM2013-47874-C2-R and CTM2013-48697-C2-2. CGD was supported by a postdoctoral contract (Juan de la Cierva FJCI-2015-23543) from the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness. The authors thank Dr. Rafael Clemente for providing the compost and Impregna S.A. for providing the creosote impregnated soil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Hari Pant.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
García-Delgado, C., Fresno, T., Rodríguez-Santamaría, J.J. et al. Co-application of activated carbon and compost to contaminated soils: toxic elements mobility and PAH degradation and availability. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 1057–1068 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1751-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1751-6