Abstract
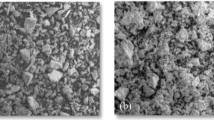
One of the key challenges in water treatment industry is the removal of organic compounds by cost-effective methods. This study evaluated the adsorptive removal of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) from reservoir water using fuller’s earth (FE) in comparison with natural (SQ) and modified quartz (MSQ) sands. The removal capacities of FE at different contact times, pH levels, adsorbent dosages and initial DOC concentrations were compared with both the quartz sands. The optimum DOC removals by FE and SQs were achieved at contact time of 60 and 30 min, pH level of 6 and 4, and at adsorbent dose of 1.5 g/150 mL and 10 g/100 mL, respectively. The adsorption capacity of FE (1.05 mg/g) was much higher compared to the MSQ (0.04 mg/g) and SQ (0.01 mg/g). Adsorption equilibrium data better fitted to the Freundlich model than to the Langmuir model, suggesting that adsorption occurred primarily through multilayer formation onto the surfaces of FE and SQ. The pseudo-second-order model described the uptake kinetics more effectively than the pseudo-first-order and intra-particle diffusion models, indicating that the mechanism was primarily governed by chemisorption. These observations were well supported by the physiochemical characteristics and charge behaviour of the adsorbents. In mass-transfer study, the results of liquid film diffusion model showed that the adsorption of DOC on FE was not controlled by film diffusion, but other mechanisms also played an essential role. This study demonstrates that FE is an effective adsorbent for the removal of DOC in surface water treatment.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arias-Paic M, Cawley KM, Byg S, Rosario-Ortiz FL (2016) Enhanced DOC removal using anion and cation ion exchange resins. Water Res 88:981–989. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2015.11.019
Atun G, Hisarli G, Sheldrick WS, Muhler M (2003) Adsorptive removal of methylene blue from colored effluents on fuller’s earth. J Colloid Interface Sci 261:32–39. doi:10.1016/S0021-9797(03)00059-6
Bajpai AK, Vishwakarma N (2003) Adsorption of polyvinylalcohol onto fuller’s earth surfaces. Colloids Surf A 220:117–130. doi:10.1016/S0927-7757(03)00073-6
Bhatt AS, Sakaria PL, Vasudevan M, Pawar RR, Sudheesh N, Bajaj HC, Mody HM (2012) Adsorption of an anionic dye from aqueous medium by organoclays: equilibrium modeling, kinetic and thermodynamic exploration. RSC Adv 2:8663–8671
Bonvin F, Jost L, Randin L, Bonvin E, Kohn T (2016) Super-fine powdered activated carbon (SPAC) for efficient removal of micropollutants from wastewater treatment plant effluent. Water Res 90:90–99. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2015.12.001
Chen W, Westerhoff P, Leenheer JA, Booksh K (2003) Fluorescence excitation–emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 37:5701–5710. doi:10.1021/es034354c
Chow CWK, Fabris R, Jv Leeuwen, Wang D, Drikas M (2008) Assessing natural organic matter treatability using high performance size exclusion chromatography. Environ Sci Technol 42:6683–6689. doi:10.1021/es800794r
Chow CWK, Majewski P, Bauer S, Fabris R, Drikas M (2009) Removal of natural organic matter using self-assembled monolayer technology. Desalin Water Treat 12:344–351
Collins MR, Amy GL, Steelink C (1986) Molecular weight distribution, carboxylic acidity, and humic substances content of aquatic organic matter: implications for removal during water treatment. Environ Sci Technol 20:1028–1032
Das P, Arias EVA, Kambala V, Mallavarapu M, Naidu R (2013) Remediation of perfluorooctane sulfonate in contaminated soils by modified clay adsorbent—a risk-based approach. Water Air Soil Pollut 224:1714
Dastgheib SA, Karanfil T, Cheng W (2004) Tailoring activated carbons for enhanced removal of natural organic matter from natural waters. Carbon 42:547–557. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2003.12.062
Deegan AM, Shaik B, Nolan K, Urell K, Oelgemöller M, Tobin J, Morrissey A (2011) Treatment options for wastewater effluents from pharmaceutical companies. Int J Environ Sci Technol 8:649–666. doi:10.1007/bf03326250
Fierro V, Torne-Fernandez V, Montane D, Celzard A (2008) Adsorption of phenol onto activated carbons having different textural and surface properties. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 111:276–284
Forsberg C (1992) Will an increased greenhouse impact in Fennoscandia give rise to more humic and coloured lakes? Hydrobiologia 229:51–58. doi:10.1007/BF00006990
Freundlich H (1926) Colloid and capillary chemistry. Methuen, London
Gone DL, Seidel J-L, Batiot C, Bamory K, Ligban R, Biemi J (2009) Using fluorescence spectroscopy EEM to evaluate the efficiency of organic matter removal during coagulation–flocculation of a tropical surface water (Agbo reservoir). J Hazard Mater 172:693–699. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.07.052
Gu L, Xu J, Lv L, Liu B, Zhang H, Yu X, Luo Z (2011) Dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) adsorption by using Al-pillared bentonite. Desalination 269(1–3):206–213
Hedegaard MJ, Albrechtsen H-J (2014) Microbial pesticide removal in rapid sand filters for drinking water treatment—potential and kinetics. Water Res 48:71–81. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2013.09.024
Ho YS, McKay G (2000) The kinetics of sorption of divalent metal ions onto sphagnum moss peat. Water Res 34:735–742. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(99)00232-8
Humbert H, Gallard H, Suty H, Croué J-P (2005) Performance of selected anion exchange resins for the treatment of a high DOC content surface water. Water Res 39:1699–1708. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2005.02.008
Hussain S, van Leeuwen J, Chow CWK, Aryal R, Beecham S, Duan J, Drikas M (2014) Comparison of the coagulation performance of tetravalent titanium and zirconium salts with alum. Chem Eng J 254:635–646. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2014.06.014
Hyung H, Kim J-H (2008) Natural organic matter (NOM) adsorption to multi-walled carbon nanotubes: effect of NOM characteristics and water quality parameters. Environ Sci Technol 42:4416–4421. doi:10.1021/es702916h
Jarvis KL, Majewski P (2012) Plasma polymerized allylamine coated quartz particles for humic acid removal. J Colloid Interface Sci 380:150–158. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2012.05.002
Kitis M, İlker Harman B, Yigit NO, Beyhan M, Nguyen H, Adams B (2007) The removal of natural organic matter from selected Turkish source waters using magnetic ion exchange resin (MIEX®). React Funct Polym 67:1495–1504. doi:10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2007.07.037
Korth A, Fiebiger C, Bornmann K, Schmidt W (2004) NOM increase in drinking water reservoirs-relevance for drinking water production. Water Supply 4:55–60
Lagergren S (1898) Zur Theorie der Sogenannten Absorption gelöster Stoffe. PA Norstedt & söner
Langmuir I (1918) The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J Am Chem Soc 40:1361–1403. doi:10.1021/ja02242a004
Mana M, Ouali MS, Lindheimer M, de Menorval LC (2008) Removal of lead from aqueous solutions with a treated spent bleaching earth. J Hazard Mater 159(2–3):358–364
Matilainen A, Vieno N, Tuhkanen T (2006) Efficiency of the activated carbon filtration in the natural organic matter removal. Environ Int 32:324–331. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2005.06.003
Matilainen A, Vepsäläinen M, Sillanpää M (2010) Natural organic matter removal by coagulation during drinking water treatment: a review. Adv Coll Interface Sci 159:189–197. doi:10.1016/j.cis.2010.06.007
Matilainen A, Gjessing ET, Lahtinen T, Hed L, Bhatnagar A, Sillanpää M (2011) An overview of the methods used in the characterisation of natural organic matter (NOM) in relation to drinking water treatment. Chemosphere 83:1431–1442. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.01.018
Oubagaranadin JUK, Sathyamurthy N, Murthy ZVP (2007) Evaluation of fuller’s earth for the adsorption of mercury from aqueous solutions: a comparative study with activated carbon. J Hazard Mater 142:165–174. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.08.001
Perelomov L, Sarkar B, Rahman MM, Goryacheva A, Naidu R (2016) Uptake of lead by Na-exchanged and Al-pillared bentonite in the presence of organic acids with different functional groups. Appl Clay Sci 119(Part 2):417–423. doi:10.1016/j.clay.2015.11.004
Rahbar MS, Alipour E, Sedighi RE (2006) Color removal from industrial wastewater with a novel coagulant flocculant formulation. Int J Environ Sci Technol 3:79–88. doi:10.1007/bf03325910
Rusmin R, Sarkar B, Liu Y, McClure S, Naidu R (2015) Structural evolution of chitosan–palygorskite composites and removal of aqueous lead by composite beads. Appl Surf Sci 353:363–375. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.06.124
Rusmin R, Sarkar B, Biswas B, Churchman J, Liu Y, Naidu R (2016) Structural, electrokinetic and surface properties of activated palygorskite for environmental application. Appl Clay Sci. doi:10.1016/j.clay.2016.07.012
Sarkar B, Xi Y, Megharaj M, Krishnamurti GS, Rajarathnam D, Naidu R (2010) Remediation of hexavalent chromium through adsorption by bentonite based Arquad® 2HT-75 organoclays. J Hazard Mater 183(1–3):87–97
Sarkar B, Megharaj M, Xi Y, Naidu R (2011) Structural characterisation of Arquad® 2HT-75 organobentonites: surface charge characteristics and environmental application. J Hazard Mater 195:155–161. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.08.016
Socrates G (2004) Infrared and raman characteristic group frequencies: tables and charts. J Raman Spectrosc 35(10):905
Tang Y, Xu Y, Li F, Jmaiff L, Hrudey SE, Li X-F (2016) Nontargeted identification of peptides and disinfection byproducts in water. J Environ Sci 42:259–266. doi:10.1016/j.jes.2015.08.007
Van der Bruggen B, Vandecasteele C, Van Gestel T, Doyen W, Leysen R (2003) A review of pressure-driven membrane processes in wastewater treatment and drinking water production. Environ Prog 22:46–56
Worrall F, Burt TP (2007) Trends in DOC concentration in Great Britain. J Hydrol 346:81–92. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2007.08.021
Yang Y, Lohwacharin J, Takizawa S (2014) Hybrid ferrihydrite-MF/UF membrane filtration for the simultaneous removal of dissolved organic matter and phosphate. Water Res 65:177–185. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2014.07.030
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Australian Research Council (ARC) for providing financial support for this research project, under Grant LP110200208. The authors would also like to thank Prof. Peter Majewski and his team of Mawson Institute, University of South Australia, for providing the natural and modified quartz sands.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Binbin Huang.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hussain, S., van Leeuwen, J., Aryal, R. et al. Removal of organic matter from reservoir water: mechanisms underpinning surface chemistry of natural adsorbents. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 15, 847–862 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1447-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1447-3