Abstract
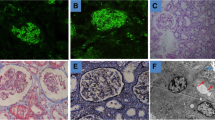
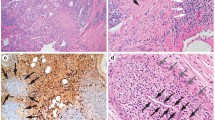
IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a newly recognized immune-mediated multisystemic disease characterized by a fibro-inflammatory condition with tissue infiltration of IgG4-positive plasma cells and often associated with elevated serum IgG4 levels. Typical renal involvement of IgG4-RD presents as tubulointerstitial nephritis (TIN), membranous or membranoproliferative nephropathy. We are presenting a case with combined IgG4 membranous nephropathy and TIN, as well as a literature review on pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment of IgG4-RD. A 62-year-old man presented with weight loss and fatigue. Labs showed significant proteinuria and hematuria with elevated serum creatinine (2.5 mg/dL). CT/PET scan found scattered lymphadenopathy without increased FDG uptake. Kidney biopsy showed glomerular lesions as well as severe interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy. Immunohistochemistry study was negative for anti-phospholipase A2 receptor antibodies and showed interstitial lymphocytic infiltration with IgG4 positive plasma cells. Patient also had elevated serum IgG4 level and IgG4 to total IgG ratio. Prednisone treatment was initiated soon after the diagnosis was made, patient responded well with proteinuria and hematuria both resolved. IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a newly increasingly recognized immune-mediated multisystemic disease; IgG4-related membranous nephropathy should be included in the differential diagnosis for patients with proteinuria.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y, et al. A new clinicopathological entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease. J Gastroenterol. 2003;38(10):982–4.
Geyer JT, Deshpande V. IgG4-associated sialadenitis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011;23(1):95–101.
Kamisawa T, Takuma K, Egawa N, et al. Autoimmune pancreatitis and IgG4-related sclerosing disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;7(7):401–9.
Tao MH, Smith RI, Morrison SL. Structural features of human immunoglobulin G that determine isotype-specific differences in complement activation. J Exp Med. 1993;178(2):661–7.
Nirula A, Glaser SM, Kalled SL, et al. What is IgG4? A review of the biology of a unique immunoglobulin subtype. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011;23(1):119–24.
Deshpande V, Zen Y, Chan JK, et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod Pathol. 2012;25(9):1181–92.
Khosroshahi A, Wallace ZS, Crowe JL, et al. International consensus guidance statement on the management and treatment of IgG4-related disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67(7):1688–99.
Dhall D, Suriawinata AA, Tang LH, et al. Use of immunohistochemistry for IgG4 in the distinction of autoimmune pancreatitis from peritumoral pancreatitis. Hum Pathol. 2010;41(5):643–52.
Chari ST. Diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis using its five cardinal features: introducing the Mayo Clinic’s HISORt criteria. J Gastroenterol. 2007;42(Suppl 18):39–41.
Beck LH Jr, Bonegio RG, Lambeau G, et al. M-type phospholipase A2 receptor as target antigen in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(1):11–21.
Alexander MP, Larsen CP, Gibson IW, et al. Membranous glomerulonephritis is a manifestation of IgG4-related disease. Kidney Int. 2013;83(3):455–62.
Kurien AA, Raychaudhury A, Walker PD. Membranous nephropathy as a rare renal manifestation of IgG4-related disease. Indian J Nephrol. 2015;25(3):164–7.
Jindal N, Yadav D, Passero C, et al. Membranous nephropathy: a rare renal manifestation of IgG4-related systemic disease. Clin Nephrol. 2012;77(4):321–8.
Stone JH, Khosroshahi A, Deshpande V, et al. Recommendations for the nomenclature of IgG4-related disease and its individual organ system manifestations. Arthritis Rheumat. 2012;64(10):3061–7.
Okazaki K, Umehara H. Are classification criteria for IgG4-RD now possible? The concept of IgG4-related disease and proposal of comprehensive diagnostic criteria in Japan. Int J Rheumatol. 2012;2012:357071.
Fervenza FC, Downer G, Beck LH Jr, et al. IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis with membranous nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis. 2011;58(2):320–4.
Kuroki A, Iyoda M, Shibata T, et al. Th2 cytokines increase and stimulate B cells to produce IgG4 in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2005;68(1):302–10.
Khosroshahi A, Stone JH. Treatment approaches to IgG4-related systemic disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011;23(1):67–71.
Kamisawa T, Okazaki K, Kawa S, et al. Japanese consensus guidelines for management of autoimmune pancreatitis: III. Treatment and prognosis of AIP. J Gastroenterol. 2010;45(5):471–7.
Khosroshahi A, Carruthers MN, Deshpande V, et al. Rituximab for the treatment of IgG4-related disease: lessons from 10 consecutive patients. Medicine. 2012;91(1):57–66.
Stone JH. IgG4-related disease: pathophysiologic insights drive emerging treatment approaches. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016;34(4 Suppl 98):66–8.
Perugino CA, Stone JH. Treatment of IgG4-related disease: current and future approaches. Z Rheumatol. 2016;75(7):681–6.
Carruthers MN, Stone JH, Deshpande V, et al. Development of an IgG4-RD responder index. Int J Rheumatol. 2012;2012:259408.
Wallace ZS, Mattoo H, Carruthers M, et al. Plasmablasts as a biomarker for IgG4-related disease, independent of serum IgG4 concentrations. Ann Rheumat Dis. 2015;74(1):190–5.
Lanzillotta M, Della-Torre E, Stone JH. Roles of plasmablasts and B cells in IgG4-related disease: implications for therapy and early treatment outcomes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2017;401:85–92.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interests to disclose. Consent, for the publication of this case report and any additional related information, was taken from the patient involved in the study. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Glaze, J.H. & Wynne, D. Combined membranous nephropathy and tubulointerstitial nephritis as a rare renal manifestation of IgG4-related disease: a case-based literature review. CEN Case Rep 7, 137–142 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13730-018-0311-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13730-018-0311-8