Abstract
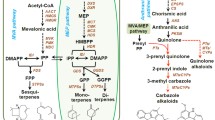
Protostane triterpenes in Alisma orientale (Sam.) Juz., because of their unique structural feature, exhibit distinctive pharmacological activities. However, the biosynthetic pathways for these compounds remain largely unknown. In this study, transcriptome analysis was performed using A. orientale tubers and leaves. We identified 101,107 unigenes, which were annotated against various databases. Importantly, 35 unigenes associated with the terpene biosynthesis pathway were identified, among which 18 encoded key enzymes catalyzing every reaction in the biosynthesis of protostane triterpenes skeleton. In addition, eight candidate transcription factor unigenes and nine candidate cytochrome P450 unigenes related to the terpene biosynthesis pathway were obtained. Moreover, the expression levels of most genes involved in protostane triterpenes biosynthesis in tubers were significantly higher than those in leaves. Furthermore, significant positive correlations were showed between the levels of key enzymes (HMGR2, SS2, SE1, SE2, OSC1, and OSC2), and the contents of the main bioactive compound at different developmental phases of A. orientale. These genes were identified first time in this study. These results provide preliminary evidence that these proteins may play crucially regulatory roles in protostane triterpenes synthesis.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TF:
-
Transcription factor
- HIV:
-
Human immunodeficiency virus
- NGS:
-
Next-generation sequencing
- bp:
-
Base pairs
- NCBI:
-
The National Center for Biotechnology Information
- Nr:
-
Non-redundant protein
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- COG:
-
Cluster of orthologous groups
- GO:
-
Gene ontology
- HPLC:
-
High performance liquid chromatography
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative real-time reverse transcription PCR
References
Aguado MT, Grande C, Gerth M, Bleidorn C, Norena C (2016) Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genomes from Polycladida (Platyhelminthes) using next-generation sequencing. Gene 575:199–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2015.08.054
Chen M et al (2017) Glandular Trichome-specific WRKY 1 promotes artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua. New Phytol 214:304–316. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14373
Fiore A, Dall’Osto L, Cazzaniga S, Diretto G, Giuliano G, Bassi R (2012) A quadruple mutant of Arabidopsis reveals a beta-carotene hydroxylation activity for LUT1/CYP97C1 and a regulatory role of xanthophylls on determination of the PSI/PSII ratio. BMC Plant Biol 12:50. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-12-50
Ghosh S (2017) Triterpene structural diversification by plant cytochrome P450 enzymes. Front Plant Sci 8:1886. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01886
Ginglinger JF et al (2013) Gene coexpression analysis reveals complex metabolism of the monoterpene alcohol linalool in Arabidopsis flowers. Plant Cell 25:4640–4657. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.113.117382
Gu W, Wu QN, Chao JG, Xi BL, Li L, Shen XY (2011) Molecular cloning of farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase from Alisma orientale (Sam) Juzep and its distribution pattern and bioinformatics analysis. Yao xue xue bao = Acta Pharm Sin 46:605–612
Gu W et al (2015) Characterization and function of the 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase gene in Alisma orientale (Sam.) Juz. and its relationship with protostane triterpene production. Plant Physiol Biochem PPB 97:378–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2015.10.031
Guleria P, Masand S, Yadav SK (2014) Overexpression of SrUGT85C2 from Stevia reduced growth and yield of transgenic Arabidopsis by influencing plastidial MEP pathway. Gene 539:250–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2014.01.071
Guo H et al (2016) Molecular characterization, expression, and regulation of Gynostemma pentaphyllum squalene epoxidase gene 1. Plant Physiol Biochem PPB 109:230–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.10.002
Guzman F, Kulcheski FR, Turchetto-Zolet AC, Margis R (2014) De novo assembly of Eugenia uniflora L. transcriptome and identification of genes from the terpenoid biosynthesis pathway. Plant Sci 229:238–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2014.10.003
Han J, Jiang DM, Du CQ, Hu SJ (2011) Alteration of enzyme expressions in mevalonate pathway: possible role for cardiovascular remodeling in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Circ J 75:1409–1417
Hansen NL, Heskes AM, Hamberger B, Olsen CE, Hallstrom BM, Andersen-Ranberg J, Hamberger B (2017) The terpene synthase gene family in Tripterygium wilfordii harbors a labdane-type diterpene synthase among the monoterpene synthase TPS-b subfamily. Plant J 89:429–441. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13410
Hong GJ, Xue XY, Mao YB, Wang LJ, Chen XY (2012) Arabidopsis MYC2 interacts with DELLA proteins in regulating sesquiterpene synthase gene expression. Plant Cell 24:2635–2648. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.098749
Huang Y, Li H, Peng D, Wang Y, Ren Q, Guo Y (2016) The production and exportation of artemisinin-derived drugs in China: current status and existing challenges. Malar J 15:365. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-016-1422-3
Jo HJ, Han JY, Hwang HS, Choi YE (2017) beta-Amyrin synthase (EsBAS) and beta-amyrin 28-oxidase (CYP716A244) in oleanane-type triterpene saponin biosynthesis in Eleutherococcus senticosus. Phytochemistry 135:53–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2016.12.011
Kanno Y et al (2017) Alisol B 23-acetate from the rhizomes of Alisma orientale is a natural agonist of the human pregnane X receptor. Phytomedicine 26:22–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2017.01.003
Leiva K, Werner N, Sepulveda D, Barahona S, Baeza M, Cifuentes V, Alcaino J (2015) Identification and functional characterization of the CYP51 gene from the yeast Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous that is involved in ergosterol biosynthesis. BMC Microbiol 15:89. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-015-0428-2
Lenka SK, Nims NE, Vongpaseuth K, Boshar RA, Roberts SC, Walker EL (2015) Jasmonate-responsive expression of paclitaxel biosynthesis genes in Taxus cuspidata cultured cells is negatively regulated by the bHLH transcription factors TcJAMYC1, TcJAMYC2, and TcJAMYC4. Front Plant Sci 6:115. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00115
Li HM et al (2017) Protostane-Type Triterpenoids from Alisma orientale. Chem Biodivers. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbdv.201700452
Liu YT, Hu TC, Chang CH, Shie WS, Wu TK (2012) Protein engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae oxidosqualene-lanosterol cyclase into parkeol synthase. Org Lett 14:5222–5225. https://doi.org/10.1021/ol302341h
Liu QZ, Gu W, Wu QN, Chao JG, Sang XH, Liu Q, Wang XH (2017) Prokaryotic expression, functional identification of squalene synthase in Alisma orientale and its immunoassay study. Zhongguo Zhong yao za zhi = Zhongguo zhongyao zazhi = China J Chin Mater Med 42:3733–3738. https://doi.org/10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.2017.0149
Lu C, Zhao S, Wei G, Zhao H, Qu Q (2017) Functional regulation of ginsenoside biosynthesis by RNA interferences of a UDP-glycosyltransferase gene in Panax ginseng and Panax quinquefolius. Plant Physiol Biochem PPB 111:67–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.11.017
Ma Q et al (2016) Structures and biological activities of the triterpenoids and sesquiterpenoids from Alisma orientale. Phytochemistry 131:150–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2016.08.015
Mai ZP et al (2015) Protostane triterpenoids from the rhizome of Alisma orientale exhibit inhibitory effects on human carboxylesterase 2. J Nat Prod 78:2372–2380. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.5b00321
Meng Q et al (2015) Alisol B 23-acetate protects against ANIT-induced hepatotoxity and cholestasis, due to FXR-mediated regulation of transporters and enzymes involved in bile acid homeostasis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 283:178–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2015.01.020
Miyazawa M, Yoshinaga S, Kashima Y, Nakahashi H, Hara N, Nakagawa H, Usami A (2016) chemical composition and characteristic odor compounds in essential oil from Alismatis Rhizoma (Tubers of Alisma orientale). J Oleo Sci 65:91–97. https://doi.org/10.5650/jos.ess15176
Moses T et al (2014a) Combinatorial biosynthesis of sapogenins and saponins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using a C-16alpha hydroxylase from Bupleurum falcatum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:1634–1639. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1323369111
Moses T, Thevelein JM, Goossens A, Pollier J (2014b) Comparative analysis of CYP93E proteins for improved microbial synthesis of plant triterpenoids. Phytochemistry 108:47–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2014.10.002
Pan WS, Zheng LP, Tian H, Li WY, Wang JW (2014) Transcriptome responses involved in artemisinin production in Artemisia annua L. under UV-B radiation. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 140:292–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2014.08.013
Pan J, Chen H, Guo B, Liu C (2017) Understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying the effects of light intensity on flavonoid production by RNA-seq analysis in Epimedium pseudowushanense B.L. Guo. PLoS ONE 12:e0182348. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0182348
Pawelkowicz M et al (2016) Next generation sequencing and omics in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) breeding directed research. Plant Sci 242:77–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.07.025
Rahimi S, Kim YJ, Sukweenadhi J, Zhang D, Yang DC (2017) PgLOX6 encoding a lipoxygenase contributes to jasmonic acid biosynthesis and ginsenoside production in Panax ginseng. J Exp Bot 68:4725. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erw413
Shu Z, Pu J, Chen L, Zhang Y, Rahman K, Qin L, Zheng C (2016) Alisma orientale: ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology of an important traditional Chinese medicine. Am J Chin Med 44:227–251. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0192415X16500142
Tamura K et al (2017) Cytochrome P450 monooxygenase CYP716A141 is a unique beta-amyrin C-16beta oxidase involved in triterpenoid saponin biosynthesis in Platycodon grandiflorus. Plant Cell Physiol 58:874–884. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcx043
Wang G, Du X, Ji J, Guan C, Li Z, Josine TL (2015) De novo characterization of the Lycium chinense Mill. leaf transcriptome and analysis of candidate genes involved in carotenoid biosynthesis. Gene 555:458–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2014.10.058
Wei YC et al (2016) Optimization of flash-type extraction technology of alisol B 23-acetate from Alismatis Rhizoma by response surface methodology. Zhongguo Zhong yao za zhi = Zhongguo zhongyao zazhi = China J Chin Mater Med 41:438–442. https://doi.org/10.4268/cjcmm20160313
Wolwer-Rieck U, May B, Lankes C, Wust M (2014) Methylerythritol and mevalonate pathway contributions to biosynthesis of mono-, sesqui-, and diterpenes in glandular trichomes and leaves of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni. J Agric Food Chem 62:2428–2435. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf500270s
Xu L et al (2015) De novo sequencing of root transcriptome reveals complex cadmium-responsive regulatory networks in radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Plant Sci 236:313–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.04.015
Yang Y, Ge F, Sun Y, Liu D, Chen C (2017) Strengthening triterpene saponins biosynthesis by over-expression of farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase gene and RNA Interference of cycloartenol synthase gene in Panax notoginseng. Cells Mol. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22040581
Yoshida I, Ito C, Matsuda S, Tsuji A, Yanaka N, Yuasa K (2017) Alisol B, a triterpene from Alismatis rhizoma (dried rhizome of Alisma orientale), inhibits melanin production in murine B16 melanoma cells. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 81:534–540. https://doi.org/10.1080/09168451.2016.1268042
Yu F, Okamoto S, Harada H, Yamasaki K, Misawa N, Utsumi R (2011) Zingiber zerumbet CYP71BA1 catalyzes the conversion of alpha-humulene to 8-hydroxy-alpha-humulene in zerumbone biosynthesis. Cell Mol Life Sci CMLS 68:1033–1040. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-010-0506-4
Zeng L, Tang W, Yin J, Feng L, Li Y, Yao X, Zhou B (2016) Alisol A 24-acetate prevents hepatic steatosis and metabolic disorders in HepG2 cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 40:453–464. https://doi.org/10.1159/000452560
Zhang LL et al (2016) Effects of alisol B 23-acetate on ovarian cancer cells: G1 phase cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, migration and invasion inhibition. Phytomedicine 23:800–809. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2016.04.003
Zhang J, Huo YB, Liu Y, Feng JT, Ma ZQ, Zhu CS, Zhang X (2017a) Differential expressed analysis of Tripterygium wilfordii unigenes involved in terpenoid backbone biosynthesis. J Asian Nat Prod Res 19:823–832. https://doi.org/10.1080/10286020.2016.1232713
Zhang LL, Xu W, Xu YL, Chen X, Huang M, Lu JJ (2017b) Therapeutic potential of Rhizoma Alismatis: a review on ethnomedicinal application, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology. Ann NY Acad Sci 1401:90–101. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.13381
Zhang X et al (2017c) Diuretic activity of compatible triterpene components of Alismatis rhizoma. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22091459
Zhao M, Godecke T, Gunn J, Duan JA, Che CT (2013) Protostane and fusidane triterpenes: a mini-review. Molecules 18:4054–4080. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18044054
Zhao H, Tang Q, Mo C, Bai L, Tu D, Ma X (2017) Cloning and characterization of squalene synthase and cycloartenol synthase from Siraitia grosvenorii. Acta Pharm Sin B 7:215–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2016.06.012
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81673534), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Grant No. BK20161576), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD-2014) and Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center of Chinese Medicinal Resources Industrialization (Grant No. ZDXM-3-24). The authors thank Prof. Jingying Chen, and Dr. Zhichao Xu for help during this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, W., Zhang, A., Jiang, L. et al. Identification of genes associated with the biosynthesis of protostane triterpenes based on the transcriptome analysis of Alisma orientale (Sam.) Juz.. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 28, 158–168 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-018-0476-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-018-0476-4