Abstract
Objective
Silicon, an abundant element in the earth’s crust, is a known factor in reducing the toxicity of plants. The effects of silicon were investigated to the amelioration of Zinc (Zn) toxicity on antioxidant enzyme activities (Superoxide dismutase (SOD), Catalase (CAT), and Glutathione Reductase (GR)), Hydrogen peroxide concentrations (H2O2), phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL), and soluble protein (SP) in one bamboo species (Arundinaria pygmaea).
Methods
This study was conducted in vitro condition to determine the effects of four Zn concentrations (100, 300, 500, and 1000 µmol/L) at two different concentrations of silicon (Si) (0 and 100 µmol/L) on a single bamboo species (Arundinaria pygmaea).
Results
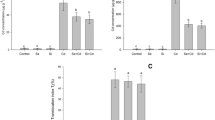
The results indicated that Si can stimulate the plant defense mechanism and ameliorate heavy metal stress caused by Zn concentrations, which can increase antioxidant enzyme and non-enzyme activity and decrease damaging effects caused by free radicals, H2O2, and soluble protein in this bamboo species.
Conclusion
Furthermore, the results indicated that the combination of 100/300 µmol/L had a considerable impact on the reduction of Zn toxicity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hartley, S. E. & DeGabri, J. L. The ecology of herbivore- induced silicon defences in grasses. Funct. Ecol. 30, 1311–1322 (2016).
Epstein, E. Silicon. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 50, 641–664 (1999).
Sommer, M., Kaczorek, D., Kuzyakov, Y. & Breuer, J. Silicon pools and fluxes in soils and landscapes-a review. J. Plant Nut. Soil Sci. 169, 310–329 (2006).
Rogalla, H. & Romheld, V. Role of leaf apoplast in silicon- mediated manganese tolerance of Cucumis stivus L. Plant Cell Environ. 25, 549–555 (2002).
Zhu, Z., Wei, G., Li, J., Qian, Q. & Yu, J. Silicon aleviated salt stress and increases antioxidant enzymes activity in leaves of salt stresses cucumber (Cucumis sativus L). Plant Sci. 167, 527–533 (2004).
Kim, Y. H., Khan, A. L., Waqas, M. & Lee, I. J. Silicon regulates Antioxidant Activities of crops plant under Abiotic-Induced Oxidative streses A review. Front. Plant Sci. 6, 510 (2017).
Alexandre, A., Meunier, J. D., Lézine, A. M., Vincens, A. & Schwartz, D. Phytoliths: indicators of grassland dynamics during the late Holocene in intertropical Africa. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 136, 213–229 (1997).
Ding, T. P. et al. Silicon isotope fractionation in bamboo and its significance to the biogeochemical cycle of silicon. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 72, 1381–1395 (2008).
Richmond, K. E. & Sussman, M. Got Silicon? The non essential benefit plant nutrreant. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 6, 268–272 (2003).
Mitani, N. & Ma, J. F. Uptake system of silicon in different plant species. J. Exp. Bot. 56, 1255–1261 (2005).
Pallavi, S., Ambuj, B. J., Rama, S. D. & Mohammad, P. Reactive Oxygen Species, Oxidative Damage, and Antioxidative Defense Mechanism in Plants under Stressful Conditions. J. Bot. 217037, doi: 10.1155/2012/217037 (2012).
Guan, F., Tang, X., Fan, S., Zhao, J. & Peng, C. Changes in soil carbon and nitrogen stocks followed the conversion from secondary forest to Chinese fir and Moso bamboo plantations. CATENA 133, 455–460 (2015).
Yang, Q. et al. Bamboo resources, utilization and exsitu conservation in Xishuangbanna, South-eastern China. J. Forest. Res. 19, 79–83 (2008).
Huang, Y. P., Hou, C. H., Hsi, H. C. & Wu, J. W. Optimization of highly microporous activated carbon preparation from Moso bamboo using central composite design approach. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 50, 266–275 (2015).
Hogarth, N. J. & Belcher, B. The contribution of bamboo to household income and rural livelihoods in a poor and mountainous county in Guangxi, China. Int. Forest. Rev. 15, 71–81 (2013).
Zhang, X., Zhong, T., Liu, L. & Ouyang, X. Impact of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution on Food Safety in China. PLoS ONE 10, e0135182 (2015).
Mittler, R. Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci. 7, 405–410 (2002).
Shi, Q. et al. Silicon-mediated alleviation of Mn toxicity in Cucumis sativus in relation to activities of superoxide dismutase and ascorbate peroxidase. Phytochemistry 66, 1551–1559 (2005).
Takahashi, M. A. & Asada, K. Superoxide anion primeability of phospholipid membranes and chloroplast thylakoides. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 226, 558–566 (1983).
Song, A. et al. The alleviation of zinc toxicity by silicon is related to zinc transport and antioxidative reactions in rice. Plant Soil 344, 319–333 (2011).
Sivanesan, I. & Jeong, B. R. Silicon promotes adventitious shoot regeneration and enhances salinity tolerance of Ajuga multiflora Bunge by altering activity of antioxidant enzyme. Sci. World J. 521703, http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/521703 (2014).
Feng, J. P., Shi, Q. H. & Wang, X. F. Effect of exogenoud silicon on photosyntesis capacity and antioxidant anzyme activity in choloroplast of cucumber seedling under excess maneges. Agric. Sci. China 8, 40–50 (2009).
Tripathi, D. K., Singh, V. P., Prasad, S. M., Chauhan, D. K. & Dubey, N. K. Silicon nanoparticles (SiNp) alleviate chromium (VI) phytotoxicity in Pisum sativum (L.) seedlings. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 96, 189–198 (2015).
Farooq, M. A. et al. Alleviation of cadmium toxicity by silicon is related to elevated photosynthesis, antioxidant enzymes; suppressed cadmium uptake and oxida tive stress in cotton. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 96, 242–249 (2013).
Song, A. et al. Silicon-enhanced resistance to cadmium toxicity in Brassica chinensis L. is attributed to Si-suppressed cadmium uptake and transport and Si-enhanced antioxidant defense capacity. J. Hazard. Mater. 172, 74–83 (2009).
Shi, G., Cai, Q., Liu, C. & Li, W. Silicon alleviates cadmium toxicity in peanut plants in relation to cadmium distribution and stimulation of antioxidative enzymes. Plant Growth Regul. 61, 45–52 (2010).
Tang, H. et al. Effects of selenium and silicon on enhancing antioxidative capacity in ramie (Boehmeria nivea (L.) Gaud.) under cadmium stress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 22, 9999–10008 (2015).
Molassiotis, A., Sotiropoulos, T., Tanou, G., Diamantidis, G. & Therios, I. Boron-induced oxidative damage and antioxidant and nucleolytic responses in shoot tips culture of the apple rootstock EM9 (Malus domestica Borkh). Environ. Exper. Bot. 56, 54–62 (2006).
Gunes, A., Inal, A., Bagci, E. G., Coban, S. & Pilbeam, D. J. Silicon mediates changes to some physiological and enzymatic parameters symptomatic for oxidative stress in spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) grown under B toxicity. Sci. Hort. 113, 113–119 (2007).
Khandekar, S. & Leisner, S. Soluble silicon modulates expression of Arabidopsis thaliana genes involved in copper stress. J. Plant Physiol. 168, 699–705 (2011).
Li, L. et al. Silicate-mediated alleviation of Pb toxicity in banana grown in Pb-contaminated soil. Biol. Trace. Elem. Res. 145, 101–108 (2012).
Miao, B. H., Han, X. G. & Zhang, W. H. The ameliorative effect of silicon on soybean seedlings grown in potassium-deficient medium. Ann. Bot. 105, 967–973 (2010).
Hall, J. L. Cellular mechanisms for heavy metal detoxification and tolerance. J. Exp. Bot. 53, 1–11 (2002).
Adrees, M. et al. Mechanisms of silicon-mediated alleviation of heavy metal toxicity in plants: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 119, 186–197 (2015).
Leyva, A., Jarillo, J. A., Salinas, J. & Martinez-Zapater, J. M. Low Temperature Induces the Accumulation of Phenylalanine Ammonia-Lyase and Chalcone Synthase mRNAs of Arabidopsis thaliana in a Light-Dependent Manner. Plant Physiol. 108, 39–46 (1995).
Sanchez-Ballesta, M. T., Zacarias, L., Granell, A. & Lafuente, M. T. Accumulation of PAL transcript and PAL activity as affected by heat-conditioning and low-temperature storage and its relation to chilling sensitivity in mandarin fruits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 48, 2726–2731 (2000).
Solecka, D. & Kacperska, A. Phenylpropanoid deficiency affects the course of plant acclimation to cold. Physiol. Plant 119, 253–262 (2003).
Sgarbi, E., Fornasiero, R. B., Lins. A. P. & Bonatti, P. M. Phenol metabolism is differentially affected by ozone in two cell lines from grape (Vitis vinifera L.) leaf. Plant Sci. 165, 951–957 (2003).
Zhang, X. The Measurement and Mechanism of Lipid Peroxidation and SOD, POD and CAT Activities in Biological System. In Research Methodology of Crop Physiology (Agriculture Press, Beijing, China, 1992).
Aebi, H. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 105, 121–126 (1984).
Bradford, M. M. A rapid sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilising the principle of protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 72, 248–254 (1976).
Zhang, Z. L. Experiment instruction of plant physiology (Higher Education Publishers, Beijing, 2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Emamverdian, A., Ding, Y. & Xie, Y. Effects of Silicon in the Amelioration of Zn Toxicity on Antioxidant Enzyme Activities. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 10, 90–96 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13530-018-0351-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13530-018-0351-7