Abstract
Purpose
Various combinations of drugs may be effective in the treatment of different types of cancer. Previously, we have shown that combinations of the histone deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat and the topoisomerase inhibitors topotecan or etoposide act synergistically, but the underlying mode of action has remained unknown. Here, we aimed at uncovering the mechanisms underlying this synergism.
Methods
The effects of (combinations of) panobinostat and topotecan or etoposide on cervical cancer-derived HeLa and SiHa cells were assessed using morphological evaluations, scratch wound healing assays, cell cycle analyses, AO/EB staining assays, Annexin V/PI staining assays, reactive oxygen species (ROS) and mitochondrial membrane potential measurements and Western blotting.
Results
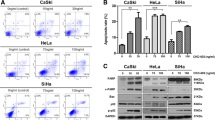
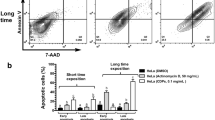
We found that combinations of panobinostat and the topoisomerase inhibitors topotecan or etoposide synergistically enhanced the induction of apoptosis in both HeLa and SiHa cells. This enhanced apoptosis induction was found to be mediated through increased ROS production and induction of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. We also found that the combination treatment resulted in inhibition of the PI3K/AKT and NF-κB pro-survival pathways and in activation of the ERK pathway, which is associated with intrinsic apoptosis.
Conclusions
From our data we conclude that combinations of panobinostat and the topoisomerase inhibitors topotecan or etoposide provoke strong cell death responses in cervical cancer-derived cells via induction of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway. Since this drug combination may potentially be effective in the treatment of cervical cancer, further preclinical investigations are warranted.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Sun, Z. Sheng, C. Ma, K. Tang, R. Zhu, Z. Wu, R. Shen, J. Feng, D. Wu, D. Huang, D. Huang, J. Fei, Q. Liu, Z. Cao, Combining genomic and network characteristics for extended capability in predicting synergistic drugs for cancer. Nat Commun 6, 8481 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9481
S. Grant, Is the focus moving toward a combination of targeted drugs? Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 21, 629–637 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beha.2008.08.003
M. Bots, R.W. Johnstone, Rational combinations using HDAC inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res 15, 3970–3977 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2786
J. Gray, C.L. Cubitt, S. Zhang, A. Chiappori, Combination of HDAC and topoisomerase inhibitors in small cell lung cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 13, 614–622 (2012). https://doi.org/10.4161/cbt.19848
A. Ferraro, Altered primary chromatin structures and their implications in cancer development. Cell Oncol 39, 195–210 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-016-0276-6
L. Nolan, P.W. Johnson, A. Ganesan, G. Packham, S.J. Crabb, Will histone deacetylase inhibitors require combination with other agents to fulfil their therapeutic potential? Br J Cancer 99, 689–694 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6604557
M.S. Kim, M. Blake, J.H. Baek, G. Kohlhagen, Y. Pommier, F. Carrier, Inhibition of histone deacetylase increases cytotoxicity to anticancer drugs targeting DNA. Cancer Res 63, 7291–7300 (2003)
K. Ozaki, F. Kishikawa, M. Tanaka, T. Sakamoto, S. Tanimura, M. Kohno, Histone deacetylase inhibitors enhance the chemosensitivity of tumor cells with cross-resistance to a wide range of DNA-damaging drug. Cancer Sci 99, 376–384 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1349-7006.2007.00669.x
L. Wasim, M. Chopra, Panobinostat induces apoptosis via production of reactive oxygen species and synergizes with topoisomerase inhibitors in cervical cancer cells. Biomed Pharmacother 84, 1393–1405 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.10.057
R.S. Hotchkiss, A. Strasser, J.E. McDunn, P.E. Swanson, Cell Death. N Engl J Med 361, 1570–1583 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra0901217
J.F. Kerr, C.M. Winterford, B.V. Harmon, Apoptosis. Its significance in cancer and cancer therapy. Cancer 73, 2013–2026 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0142(19940415)73:8<2013::AID-CNCR2820730802>3.0.CO;2-J
K.T. Thurn, S. Thomas, A. Moore, P.N. Munster, Rational therapeutic combinations with histone deacetylase inhibitors for the treatment of cancer. Future Oncol 7, 263–283 (2011). https://doi.org/10.2217/fon.11.2
O. Martinez-Iglesias, L. Ruiz-Llorente, R. Sanchez-Martinez, L. Garcia, A. Zambrano, A. Aranda, Histone deacetylase inhibitors: Mechanism of action and therapeutic use in cancer. Clin Transl Oncol 10, 395–398 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-008-0221-x
D.R. Budman, A. Calabro, L. Rosen, M. Lesser, Identification of unique synergistic drug combinations associated with downexpression of survivin in a preclinical breast cancer model system. Anti-Cancer Drugs 23, 272–279 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1097/CAD.0b013e32834ebda4
Y. Cai, X. Yan, G. Zhang, W. Zhao, S. Jiao, The predictive value of ERCC1 and p53 for the effect of panobinostat and cisplatin combination treatment in NSCLC. Oncotarget 6, 18997–19005 (2015). https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.3620
S. Venkannagari, W. Fiskus, K. Peth, P. Atadja, M. Hidalgo, A. Maitra, K.N. Bhalla, Superior efficacy of co-treatment with dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 and pan-histone deacetylase inhibitor against human pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget 3, 1416–1427 (2012). https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.724
G. Wang, H. Edwards, J.T. Caldwell, S.A. Buck, W.Y. Qing, J.W. Taub, Y. Ge, Z. Wang, Panobinostat synergistically enhances the cytotoxic effects of cisplatin, doxorubicin or etoposide on high-risk neuroblastoma cells. PLoS One 8, e76662 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0076662
F. Bruzzese, M. Rocco, S. Castelli, E. Di Gennaro, A. Desideri, A. Budillon, Synergistic antitumor effect between vorinostat and topotecan in small cell lung cancer cells is mediated by generation of reactive oxygen species and DNA damage-induced apoptosis. Mol Cancer Ther 8, 3075–3087 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-0254
D. Chen, J. Cao, L. Tian, F. Liu, X. Sheng, Induction of apoptosis by casticin in cervical cancer cells through reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrial signaling pathways. Oncol Rep 26, 1287–1294 (2011). https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2011.1367
L. Gao, M. Gao, G. Yang, Y. Tao, Y. Kong, R. Yang, X. Meng, G. Ai, R. Wei, H. Wu, X. Wu, J. Shi, Synergistic activity of carfilzomib and Panobinostat in multiple myeloma cells via modulation of ROS generation and ERK1/2. Biomed Res Int 2015, 459052 (2015)
O. Sordet, Q.A. Khan, I. Plo, P. Pourquier, Y. Urasaki, A. Yoshida, S. Antony, G. Kohlhagen, E. Solary, M. Saparbaev, J. Laval, Y. Pommier, Apoptotic topoisomerase I-DNA complexes induced by staurosporine-mediated oxygen radicals. J Biol Chem 279, 50499–50504 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M410277200
M.D. Brand, C. Affourtit, T.C. Esteves, K. Green, A.J. Lambert, S. Miwa, J.L. Pakay, N. Parker, Mitochondrial superoxide: Production, biological effects, and activation of uncoupling proteins. Free Radic Biol Med 37(6), 755–767 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.05.034
M. Ott, V. Gogvadze, S. Orrenius, B. Zhivotovsky, Mitochondria, oxidative stress and cell death. Apoptosis 12, 913–922 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-007-0756-2
J.K. Brunelle, A. Letai, Control of mitochondrial apoptosis by the Bcl-2 family. J Cell Sci 122, 437–441 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.031682
B. Leibowitz, J. Yu, Mitochondrial signaling in cell death via the Bcl-2 family. Cancer Biol Ther 9, 417–422 (2010). https://doi.org/10.4161/cbt.9.6.11392
V.J. Bouchard, M. Rouleau, G.G. Poirier, PARP-1, a determinant of cell survival in response to DNA damage. Exp Hematol 31, 446–454 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-472X(03)00083-3
D.A. Altomare, J.R. Testa, Perturbations of the AKT signaling pathway in human cancer. Oncogene 24, 7455–7464 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209085
G. Song, G. Ouyang, S. Bao, The activation of Akt/PKB signaling pathway and cell survival. J Cell Mol Med 9, 59–71 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2005.tb00337.x
K. Vazquez-Santillan, J. Melendez-Zajgla, L. Jimenez-Hernandez, G. Martinez-Ruiz, V. Maldonado, NF-kappaB signaling in cancer stem cells: A promising therapeutic target? Cell Oncol 38, 327–339 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-015-0236-6
F. Chang, J.T. Lee, P.M. Navolanic, L.S. Steelman, J.G. Shelton, W.L. Blalock, R.A. Franklin, J.A. McCubrey, Involvement of PI3K/Akt pathway in cell cycle progression, apoptosis, and neoplastic transformation: A target for cancer chemotherapy. Leukemia 17, 590–603 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402824
M. Barkett, T.D. Gilmore, Control of apoptosis by Rel/NF-kappaB transcription factors. Oncogene 18, 6910–6924 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203238
C. Bubici, S. Papa, C.G. Pham, F. Zazzeroni, G. Franzoso, The NF-kappaB-mediated control of ROS and JNK signaling. Histol Histopathol 21, 69–80 (2006). https://doi.org/10.14670/HH-21.69
C. Yu, B.B. Friday, J.P. Lai, A. McCollum, P. Atadja, L.R. Roberts, A.A. Adjei, Abrogation of MAPK and Akt signaling by AEE788 synergistically potentiates histone deacetylase inhibitor-induced apoptosis through reactive oxygen species generation. Clin Cancer Res 13, 1140–1148 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1751
S. Cagnol, J.C. Chambard, ERK and cell death: Mechanisms of ERK-induced cell death--apoptosis, autophagy and senescence. FEBS J 277, 2–21 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07366.x
Z. Lu, S. Xu, ERK1/2 MAP kinases in cell survival and apoptosis. IUBMB Life 58, 621–631 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1080/15216540600957438
J.A. McCubrey, L.S. Steelman, W.H. Chappell, S.L. Abrams, E.W. Wong, F. Chang, B. Lehmann, D.M. Terrian, M. Milella, A. Tafuri, F. Stivala, M. Libra, J. Basecke, C. Evangelisti, A.M. Martelli, R.A. Franklin, Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell growth, malignant transformation and drug resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta 1773, 1263–1284 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.10.001
M.J. Chuang, S.T. Wu, S.H. Tang, X.M. Lai, H.C. Lai, K.H. Hsu, K.H. Sun, G.H. Sun, S.Y. Chang, D.S. Yu, P.W. Hsiao, S.M. Huang, T.L. Cha, The HDAC inhibitor LBH589 induces ERK-dependent prometaphase arrest in prostate cancer via HDAC6 inactivation and down-regulation. PLoS One 8, e73401 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0073401
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the University of Delhi, India, for providing funds in the form of a DUR&D grant and a UGC-SAP grant and UGC, New Delhi, India, for providing a fellowship to LW. We also wish to thank Mr. Prateek Arora for helping in FCM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 2.54 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wasim, L., Chopra, M. Synergistic anticancer effect of panobinostat and topoisomerase inhibitors through ROS generation and intrinsic apoptotic pathway induction in cervical cancer cells. Cell Oncol. 41, 201–212 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-017-0366-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-017-0366-0