Abstract
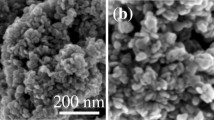
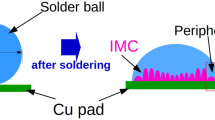
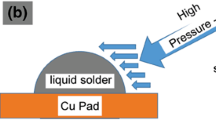
Solder ball of initial diameter 1.4 mm, was reflow soldered with Cu substrate at 523.15 K using flux doped with Cu@Ag core–shell nanoparticles (NPs) in the proportion 0–2 wt%. The solders were then air cooled to room temperature. The use of NPs, by reducing the base height (H) of the solder and enhanced the diameter (W) of the solder, caused an overall increase in the spread ratio of the solder. The altered magnitudes of heat and mass transfer in these geometrically different but constant volume specimens were analyzed using finite element method. The occurrence of differential concentration gradient, radial thermal gradient and velocity magnitudes, in solders with differing geometry were numerically elaborated. The \(\hbox {Cu}_{6}\hbox {Sn}_{5}\)intermetallic compound (IMC) formed at the Cu/Sn interface, was obtained to be the thickest for the specimen using undoped flux, whereas it was found to be smallest for the sample processed with flux containing 0.5% NPs. From the growth kinetics study, it has been inferred that IMC thickness is linearly proportional to the geometrical parameter H and \(\hbox {W}^b\), with b < 1.
Graphical Abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annuar, S., Mahmoodian, R., Hamdi, M., Tu, K.-N.: Intermetallic compounds in 3D integrated circuits technology: a brief review. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 18(1), 1–11 (2017)
Tu, K.N., Liu, Y., Li, M.: Effect of Joule heating and current crowding on electromigration in mobile technology. Appl. Phys. Rev. 4(1), 011101 (2017)
Chang, C.C., Lin, Y.W., Wang, Y.W., Kao, C.R.: The effects of solder volume and cu concentration on the consumption rate of Cu pad during reflow soldering. J. Alloys Compd. 492(1), 99–104 (2010)
Islam, M.N., Sharif, A., Chan, Y.C.: Effect of volume in interfacial reaction between eutectic Sn–3.5Ag–0.5Cu solder and Cu metallization in microelectronic packaging. J. Electron. Mater. 34(2), 143–149 (2005)
Liu, L., Huang, M.: Effect of solder volume on interfacial reactions between Sn3.5Ag0.75Cu solder balls and Cu pad. In: International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology and High Density Packaging, pp. 299–304 (2010)
Shen, J., Chan, Y.C.: Effect of metal/ceramic nanoparticle-doped fluxes on the wettability between Sn–Ag–Cu solder and a Cu layer. J. Alloys Compd. 477(1–2), 909–914 (2009)
Shang, S., Kunwar, A., Wang, Y., Yao, J., Ma, H., Wang, Y.: Synthesis of Cu@Ag core–shell nanoparticles for characterization of thermal stability and electric resistivity. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. Submitted (2018)
Shang, S., Kunwar, A., Wu, Y., Ma, H.: Effects of Cu nanoparticles doped flux on the microstructure of IMCs between Sn solder and Cu substrate. In: International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology, pp. 1577–1581. IEEE (2017)
Ribes, A., Caremoli, C.: Salome platform component model for numerical simulation. In: 31st Annual International Computer Software and Applications Conference, (COMPSAC 2007), (Compsac), vol. 2, pp. 553–564 (2007)
Rizvi, M.J., Lu, H., Bailey, C.: Modeling the diffusion of solid copper into liquid solder alloys. Thin Solid Films 517(5), 1686–1689 (2009)
Kunwar, A., Ma, H., Ma, H., Sun, J., Zhao, N., Huang, M.: On the increase of intermetallic compound’s thickness at the cold side in liquid Sn and SnAg solders under thermal gradient. Mater. Lett. 172, 211–215 (2016)
Kunwar, A., Guo, B., Shang, S., Raback, P., Wang, Y., Chen, J., Ma, H., Song, X., Zhao, N.: Roles of interfacial heat transfer and relative solder height on segregated growth behavior of intermetallic compounds in Sn/Cu joints during furnace cooling. Intermetallics 93, 186–196 (2018)
Malinen, M., Raback, P.: Elmer finite element solver for multiphysics and multiscale problems. Multiscale Model. Methods Appl. Mater. Sci. 19, 101–113 (2013)
Ayachit, U., Bauer, A., Chaudhary, A., DeMarle, D., Geveci, B., Jourdain, S., Lutz, K., Marion, P., Maynard, R., Shetty, N., Yuan, Y.: The ParaView Guide. Kitware Inc., ParaView, New York (2008)
Cheung, N., Santos, N.S., Quaresma, J.M.V., Dulikravich, G.S., Garcia, A.: Interfacial heat transfer coefficients and solidification of an aluminum alloy in a rotary continuous caster. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 52(1–2), 451–459 (2009)
Gancarz, T., Moser, Z., Gasior, W., Pstrus, J., Henein, H.: A comparison of surface tension, viscosity, and density of sn and snag alloys using different measurement techniques. Int. J. Thermophys. 32(6), 1210–1233 (2011)
Meydaneri, F., Gunduz, M., Ozdemir, M., Saatci, B.: Determination of thermal conductivities of solid and liquid phases for rich-Sn compositions of Sn–Mg alloy. Met. Mater. Int. 18(1), 77–85 (2012)
Gancarz, T., Gasior, W., Henein, H.: Physicochemical properties of Sb, Sn, Zn, and Sb–Sn system. Int. J. Thermophys. 34(2), 250–266 (2013)
Ma, H., Kunwar, A., Guo, B., Sun, J., Jiang, C., Wang, Y., Song, X., Zhao, N., Ma, H.: Effect of cooling condition and Ag on the growth of intermetallic compounds in Sn-based solder joints. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 122(12), 1–10 (2016)
Kunwar, A., Givernaud, J., Ma, H., Meng, Z., Shang, S., Wang, Y., Ma, H.: Modelling the melting of Sn0.7Cu solder using the enthalpy method. In: International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology, Wuhan, China, pp. 166–169 (2016)
Bo, S., Lu, X.G., Ohtani, H.: The implementation of an algorithm to calculate thermodynamic equilibria for multi-component systems with non-ideal phases in a free software. Comput. Mater. Sci. 101, 127–137 (2015)
Bo, S., Kattner, U.R., Palumbo, M., Fries, S.G.: Opencalphad—a free thermodynamic software. Integr. Mater. Manuf. Innov. 4(1), 1 (2015)
Tay, S.L., Haseeb, A.S.M.A., Johan, M.R., Munroe, P.R., Quadir, M.Z.: Influence of Ni nanoparticle on the morphology and growth of interfacial intermetallic compounds between Sn–3.8Ag–0.7Cu lead-free solder and copper substrate. Intermetallics 33, 8–15 (2013)
Chan, Y.H., Arafat, M.M., Haseeb, A.S.M.A.: Effects of reflow on the interfacial characteristics between Zn nanoparticles containing Sn–3.8Ag–0.7Cu solder and copper substrate. Solder. Surf. Mt. Technol. 25(2), 91–98 (2013)
Li, Y., Chan, Y.C.: Effect of silver (Ag) nanoparticle size on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Sn58BiAg composite solders. J. Alloys Compd. 645, 566–576 (2015)
Arenas, M.F., Acoff, V.L.: Contact angle measurements of Sn–Ag and Sn–Cu lead-free solders on copper substrates. J. Electron. Mater. 33(12), 1452–1458 (2004)
Bhanushali, S., Ghosh, P., Ganesh, A., Cheng, W.: 1D copper nanostructures: progress, challenges and opportunities. Small 11(11), 1232–1252 (2015)
Saiz, E., Tomsia, A.P., Rauch, N., Scheu, C., Ruehle, M., Benhassine, M., Seveno, D., De Coninck, J., Lopez-Esteban, S.: Nonreactive spreading at high temperature: molten metals and oxides on molybdenum. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 76(4), 1–15 (2007)
Aarts, D.G.A.L., Lekkerkerker, H.N.W., Guo, H., Wegdam, G.H., Bonn, D.: Hydrodynamics of droplet coalescence. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95(16), 1–4 (2005)
Bhardwaj, R., Longtin, J.P., Attinger, D.: A numerical investigation on the influence of liquid properties and interfacial heat transfer during microdroplet deposition onto a glass substrate. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 50(15–16), 2912–2923 (2007)
Tran, A.T.T., Hyland, M.M., Shinoda, K., Sampath, S.: Influence of substrate surface conditions on the deposition and spreading of molten droplets. Thin Solid Films 519(8), 2445–2456 (2011)
Tran, A.T.T., Hyland, M.M., Shinoda, K., Sampath, S.: Inhibition of molten droplet deposition by substrate surface hydroxides. Surf. Coat. Technol. 206(6), 1283–1292 (2011)
Silva, B.L., Cheung, N., Garcia, A., Spinelli, J.E.: Evaluation of solder/substrate thermal conductance and wetting angle of Sn–0.7 wt%Cu-(0–0.1 wt%Ni) solder alloys. Mater. Lett. 142, 163–167 (2015)
Zhang, Z.H., Cao, H.J., Yang, H.F., Li, M.Y., Yu, Y.X.: Hexagonal-rod growth mechanism and kinetics of the primary Cu6Sn5 phase in liquid Sn-based solder. J. Electron. Mater. 45(11), 5985–5995 (2016)
Haseeb, A.S.M.A., Leong, Y.M., Arafat, M.M.: In-situ alloying of Sn–3.5Ag solder during reflow through Zn nanoparticle addition and its effects on interfacial intermetallic layers. Intermetallics 54, 86–94 (2014)
Meng, F., Morin, S.A., Forticaux, A., Jin, S.: Screw dislocation driven growth of nanomaterials. Acc. Chem. Res. 46(7), 1616–1626 (2013)
Gusak, A.M., Tu, K.N.: Kinetic theory of flux-driven ripening. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 66(11), 1–14 (2002)
Li, J.F., Mannan, S.H., Clode, M.P., Whalley, D.C., Hutt, D.A.: Interfacial reactions between molten Sn–Bi–X solders and Cu substrates for liquid solder interconnects. Acta Mater. 54(11), 2907–2922 (2006)
Dybkov, V.I.: Growth Kinetics of Chemical Compound Layers. Cambridge International Science Publishing, Cambridge (1998)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos: 51871040 and 51571049), “Research Fund for International Young Scientists” of National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number: 51750110504) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant Number: 2017M611215).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shang, S., Kunwar, A., Wang, Y. et al. Geometrical Effects of Cu@Ag Core–Shell Nanoparticles Treated Flux on the Growth Behaviour of Intermetallics in Sn/Cu Solder Joints. Electron. Mater. Lett. 15, 253–265 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-018-00116-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-018-00116-5