Abstract
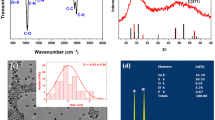
The nanocomposite film of conducting poly(m-aminophenol) with copper nanoparticles (PmAP/Cu) prepared by a single-step process has been demonstrated as the sensor material for selective detection of methanol vapor. Different techniques like Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) were used to evaluate the interfacial interactions between PmAP and Cu nanoparticles within their conducting nanocomposites. The induced doping interaction through fluctuating electrostatic charge transfer between free –OH groups of the PmAP and Cu nanoparticles was confirmed from the spectral characterizations. About 3 wt% of Cu nanoparticles having average size of around 30–50 nm confirmed by the SEM and TEM analysis, was optimized inside the PmAP matrix in terms of better dispersion as well as achieving the highest conductivity (1.05 × 10−6 S/cm). The sensing performances, viz., % response, response time, recovery time, selectivity and reproducibility of the nanocomposites were studied towards methanol vapor at different concentrations. The mechanism of selective methanol vapor sensing by PmAP/Cu nanocomposite film has been explained on the basis of selective dipole interaction characterized by zeta potential measurement.
Graphical Abstract














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jososwiz, M., Jantana, J.: Chemical Sensor Technology, p. 153. Elsevier, Amsterdam (1988)
Adhikari, B., Kar, P.: Chemical Sensors, vol. 3, p. 1. Momentum Press LLC, NJ (2010)
Kar, P., Choudhury, A., Verma, S.K.: Fundamentals of Conjugated Polymer Blends, Copolymers and Composites, p. 621. Wiley-Scrivener, NJ (2015)
Bartlett, P.N., Ling-chung, S.K.: Conducting polymer gas sensors. II. Response of polypyrrole to methanol vapour. Sensor. Actuator. 19, 141 (1989)
Blackwood, D., Jososwiz, M.: Work function and spectroscopic studies of interactions between conducting polymers and organic vapors. J. Phys. Chem-US. 95, 493 (1991)
Inzelt, G.: Applications of Conducting Polymers, p. 225. Springer, Berlin (2008)
Debarnot, D.N., Epaillard, F.P.: Polyaniline as a newsensitive layer for gas sensors. Anal. Chim. Acta 475, 1 (2003)
Negi, Y.S., Adhyapak, P.V.: Development in polyaniline conducting polymers. Polym. Rev. 42, 35 (2002)
Syed, A.A., Dinesan, M.K.: Review: polyaniline: a novel polymeric material. Talanta 38, 815 (1991)
Gardner, J.W., Bartlett, P.N.: A brief history of electronic noses. Sensor. Actuat. B-Chem. 18–19, 211 (1994)
Gardner, J.W., Bartlett, P.N.: Electronic Noses, p. 78. Oxford University Press, London (1999)
Andrews, L.S., Clary, J.J., Terrill, J.B., Bolte, H.F.: Subchronic inhalation toxicity of methanol. J. Toxicol. Env. Health 20, 117 (1987)
Athawale, A.A., Kulkarni, M.V.: Polyaniline and its substituted derivatives as sensor for aliphatic alcohols. Sensor. Actuat. B-Chem. 67, 173 (2000)
Athawale, A.A., Bhagwat, S.V., Katre, P.P.: Nanocomposite of Pd–polyaniline as a selective methanol sensor. Sensor. Actuat. B-Chem. 114, 263 (2006)
Jiang, L., Jun, H.K., Hoh, Y.S., Lim, J.O., Lee, D.D., Huh, J.S.: Sensing characteristics of polypyrrole–poly(vinyl alcohol) methanol sensors prepared by in situ vapor state polymerization. Sensor. Actuat. B-Chem. 105, 132 (2005)
de Melo, C.P., Neto, B.B., de Lima, E.G., de Lira, L.F.B., de Souza, J.E.G.: Use of conducting polyoyrrole blends as gas sensors. Sensor. Actuat. B-Chem. 109, 348 (2005)
Kar, P., Pradhan, N.C., Adhikari, B.: Application of sulfuric acid doped poly (m-aminophenol) as aliphatic alcohol vapor sensor material. Sensor. Actuat. B-Chem. 140, 525 (2009)
Verma, S.K., Kar, P., Yang, D.J., Choudhury, A.: Poly (m-aminophenol)/functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotube nanocomposite based alcohol sensors. Sensor. Actuat. B-Chem. 219, 199 (2015)
Kar, P., Pradhan, N.C., Adhikari, B.: A novel route for the synthesis of processable conducting poly (m-aminophenol). Mater. Chem. Phys. 111, 59 (2008)
Kar, P., Pradhan, N.C., Adhikari, B.: Doping of processable conducting poly(m-aminophenol) with silver nanoparticles. Polym. Advan. Technol. 22, 1060 (2011)
Kar, P., Pradhan, N.C., Adhikari, B.: Ammonia sensing by hydrochloric acid doped poly (m-aminophenol)–silver nanocomposite. J. Mater. Sci. 46, 2905 (2011)
Lee, J., Choi, J., Hong, J., Jung, D., Shim, S.E.: Conductive silicone/acetylene black composite film as a chemical vapor sensor. Synthetic. Met. 160, 1030 (2010)
Schroder, D.K.: Semiconductor Material and Device Characterization, p. 2. Wiley, New York (1990)
Riddick, J., Bunger, A.: Techniques of Chemistry, vol. 2, p. 904. Wiley, New York (1986)
Firth, A.V., Haggata, S.W., Khanna, P.K., Williams, S.J., Allen, J.W., Magennis, S.W., Samuel, I.D.W., Cole-Hamilton, J.: Production and luminescent properties of CdSe and CdS nanoparticle–polymer composites. J. Lumin. 109, 163 (2004)
Pearce, T.C., Schiffman, S.S., Nagle, H.T., Grander, J.W. (eds.): Handbook of Machine Olfaction, p. 1. Wiley, Weinheim (2003)
Niasari, M.S., Fereshteh, Z., Davar, F.: Synthesis of oleylamine capped copper nanocrystals via thermal reduction of a new precursor. Polyhedron 28, 126 (2009)
Kar, P.: Doping in Conjugated Polymers, p. 1. Wiley-Scrivener, NJ (2013)
Choudhury, A., Kar, P., Mukherjee, M., Adhikari, B.: Polyaniline/silver nanocomposite based acetone vapour sensor. Sens. Lett. 7, 592 (2009)
Kar, P., Mishra, A.: The role of polyvinyl alcohol in one-step chemical synthesis of water based copper nanofluid. Nanosci. Nanotech. Let. 5, 935 (2013)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by the BIT, Mesra Ranchi for this work inform of Institute Master’s Project. The authors also thankful to IIT, Bombey, India for sample analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhuyan, M., Samanta, S. & Kar, P. Selective Sensing of Methanol by Poly(m-aminophenol)/Copper Nanocomposite. Electron. Mater. Lett. 14, 161–172 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-018-0010-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-018-0010-9