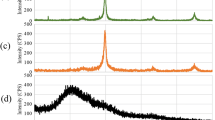
Abstract
13X zeolite was synthesized for removal of tetracycline from aqueous solution. To improve the removal efficiency, FAU zeolite was exposed to ion exchange process with \(\hbox {Cu}^{+2}\). The experiments were designed by the Design-Expert 7.0.0 software. The effect of experimental parameters including initial tetracycline (TC) concentration (50, 156.5, 525, 893.5, 1000 ppm) \(\hbox {Cu}^{+2}\) dosages (0, 0.3, 1.3, 2.2, 3 g/g) solution pH (2, 3, 6.5, 10, 11) and contact time (20, 34.6, 85, 135.4 min) was evaluated on TC removal efficiency. For minimizing the number of experiments for a complete evaluation, response surface methodology and central composite design were applied by means of Design-Expert 7.0.0 software. Results revealed that FAU zeolite adsorbent was effective in removal of tetracycline, where the removal efficiency was 85%. In fact, by increasing initial TC concentration from 156.5 to 890 mg/L, the removal efficiency was increased, while further increase in initial TC concentration over 890 mg/L did not cause a significant enhancement in its removal efficiency. Amount of exchanged Cu to 1.75 g/g had a positive effect on the removal efficiency but in over 1.75 g/g dosages, the removal efficiency showed a decreasing trend. The Design-Expert 7.0.0 software reported that the optimal operating conditions are TC concentration—810.5 ppm, \(\hbox {Cu}^{+2}\) dosages—0.6 g/g, solution pH—5.3, and contact time—113.6 min. The adsorption isotherms were fitted by Sips and Freundlich and Redlich–Peterson models. Finally, the adsorption kinetics were also studied by pseudo-second-order equation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chea, V.; Paolucci-Jeanjean, D.; Belleville, M.P.; Sanchez, J.: Optimization and characterization of an enzymatic membrane for the degradation of phenolic compounds. Catal. Today 193, 49–56 (2012)
Alsager, O.A.; Alnajrani, M.N.; Abuelizz, H.A.; Aldaghmani, I.A.: Removal of antibiotics from water and waste milk by ozonation: kinetics, byproducts, and antimicrobial activity. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 158, 114–122 (2018)
Feng, L.; Casas, M.E.; Ottosen, L.D.M.; Møller, H.B.; Bester, K.: Removal of antibiotics during the anaerobic digestion of pig manure. Sci. Tot. Environ. 603–604, 219–225 (2017)
Ali, Imran; Aboul-Enein, Hassan Y.: Instrumental Methods in Metal Ions Speciation: Chromatography, Capillary Electrophoresis and Electrochemistry. Taylor & Francis Ltd., New York (2006)
Ali, Imran; Aboul-Enein, Hassan Y.; Gupta, Vinod K.; Chromatography, Nano; Electrophoresis, Capillary: Pharmaceutical and Environmental Analyses. Wiley, Hoboken (2009)
Basheer, Al Arsh: Chemical chiral pollution: impact on the society and science and need of the regulations in the 21st century. Chirality 30, 402–406 (2018)
Gupta, V.K.; Ali, I.; Dekker, M.: Encyclopedia of Surface and Colloid Science, pp. 136–166. Marcel Dekker, New York (2002)
Baquero, F.; Martínez, J.-L.; Cantón, R.: Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance in water environments. Curr. Opin. Biotech. 19, 260–265 (2008)
Liu, F.; Ying, G.-G.; Tao, R.; Zhao, J.-L.; Yang, J.-F.; Zhao, L.-F.: Effects of six selected antibiotics on plant growth and soil microbial and enzymatic activities. Environ. Pollut. 157, 1636–1642 (2009)
Wei-ming, L.; Yan-yu, B.; Qi-xing, Z.: Degradation pathways and main degradation products of tetracycline antibiotics: research progress. Ying. Shengtai Xu. 23, 2300–2308 (2012)
Radjenović, J.; Petrović, M.; Ventura, F.; Barceló, D.: Rejection of pharmaceuticals in nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membrane drinking water treatment. Water Res. 42, 3601–3610 (2008)
Ali, Imran; Gupta, V.K.: Advances in water treatment by adsorption technology. Nat. Protocol 1, 2661–2667 (2006)
Ali, Imran; Hassan, Y.; Aboul-Enein, : Speciation of arsenic and chromium metal ions by reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography. Chemosphere 48, 275–278 (2002)
Ali, Imran; Gupta, Vinod K.; Khan, Tabrez A.; Asim, Mohd: removal of arsenate from aqueous solution by electro-coagulation method using Al-Fe electrodes. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 7, 1898–1907 (2012)
Meher, Alok Kumar; Das, Sera; Rayalu, Sadhana; Bansival, Amit: Enhanced arsenic removal from drinking water by iron-enriched aluminosilicate adsorbent prepared from fly ash. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 21, 3218–3229 (2014)
Ali, Imran; Khan, Tabrez A.; Asim, Mohd: Removal of arsenate from groundwater by electrocoagulation method. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 19, 1668–1676 (2012)
Ali, Imran; AL-Othman, Zeid A.; Alwarthan, Abdulrahman: Molecular uptake of congo red dye from water on iron composite nano particles. J. Mol. Liq. 224, 171–176 (2016)
Ali, Imran; AL-Othman, Zeid A.; Sanagi, Mohd Marsin: Green synthesis of iron nano-impregnated adsorbent for fast removal of fluoride from water. J. Mol. Liq. 211, 457–465 (2015)
Alharbi, Omar M.L.; Basheer, Al Arsh; Khattab, Rafat A.; Ali, Imran: Health and environmental effects of persistent organic pollutants. J. Mol. Liq. 263, 442–453 (2018)
Ali, Imran; Alharbi, Omar M.L.; Alothman, Zeid A.; Badjah, Ahmad Yacine; Basheer, Al Arsh: Artificial neural network modelling of amido black dye sorption on iron composite nano material: kinetics and thermodynamics studies. J. Mol. Liq. 250, 1–8 (2018)
Burakova, Elena A.; Dyachkova, Tatyana P.; Rukhov, Artem V.; Tugolukov, Evgeny N.; Galunin, Evgeny V.; Tkachev, Alexey G.; ArshBasheer, Al; Ali, Imran: Novel and economic method of carbon nanotubes synthesis on a nickel magnesium oxide catalyst using microwave radiation. J. Mol. Liq. 253, 340–346 (2018)
Deblonde, T.; Cossu-Leguille, C.; Hartemann, P.: Emerging pollutants in wastewater: a review of the literature. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 214, 442–448 (2011)
Heberer, T.: Occurrence, fate, and removal of pharmaceutical residues in the aquatic environment: a review of recent research data. Toxicol. Lett. 131, 5–17 (2002)
Kümmerer, K.: Antibiotics in the aquatic environment—a review—Part I. Chemosphere 75, 417–434 (2009)
Ali, Imran: New generation adsorbents for water treatment. Chem. Revs. (ACS) 112, 5073–5091 (2012)
Ali, Imran; khan, Tabrez A.; Asim, Mohd: Removal of arsenic from water by electrocoagulation and electrodialysis techniques. Sepn. Purfn. Rev. 40, 25–42 (2011)
Ali, Imran; Althman, zeid A.; Alwarthan, Abdulrahman: Supra molecular mechanism of the removal of 17-\(\beta \)-estradiol endocrine disturbing pollutant from water on functionalized iron nano particles. J. Mol. Liq. 441, 123–129 (2017)
Ali, Imran; Althman, zeid A.; Alwarthan, Abdulrahman: Uptake of propranolol on ionic liquid iron nanocomposite adsorbent: Kinetic, thermodynamics and mechanism of adsorption. J. Mol. Liq. 236, 205–213 (2017)
Ali, Imran; Althman, zeid A.; Alwarthan, Abdulrahman: Molecular uptake of congo red dye from water on iron composite nano particles. J. Mol. Liq. 224, 171–176 (2016)
Dehghani, Mohammad Hadi; Sanaei, Daryoush; Ali, Imran; Bhatnagar, Amit: Removal of chromium(VI) from aqueous solution using treated waste newspaper as a low-cost adsorbent: kinetic modeling and isotherm studies. J. Mol. Liq. 215, 671–679 (2016)
Ali, Imran; Kumar, Chakresh: Advances in arsenic speciation techniques. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 84, 947–964 (2004)
Fayaz, Mufida; Bhat, Musadiq H.; Kumar, Amit; Jain, Ashok K.: Comparative studies on different solvents used for the extraction of phytochemicals from the plant parts of Arnebia benthamii. (Wall Ex. G. Don) Johnston. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 3, 220–224 (2017)
Ali, Imran; Althman, zeid A.; Alwarthan, Abdulrahman: Sorption, kinetics and thermodynamics studies of atrazine herbicide removal from water using iron nano-composite material. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Toxicol. 13, 733–742 (2016)
Ali, Imran; Althman, Zeid A.; Alwarthan, Abdulrahman: Removal of secbumeton herbicide from water on composite nanoadsorbent. Desal. Water Treat. 57, 10409–10421 (2016)
Ali, Imran; Althman, zeid A.; Alharbi, Omar M.L.: Uptake of pantoprazole drug residue from water using novel synthesized composite iron nano adsorbent. J. Mol. Liq. 218, 465–472 (2016)
Ali, Imran; Althman, zeid A.; Alwarthan, Abdulrahman: Green synthesis of functionalized iron nano particles and molecular liquid phase adsorption of ametryn from water. J. Mol. Liq. 221, 1168–1174 (2016)
Ali, Imran; Althman, zeid A.; Alwarthan, Abdulrahman: Synthesis of composite iron nano adsorbent and removal of ibuprofen drug residue from water. J. Mol. Liq. 219, 858–864 (2016)
Ali, Imran; Asim, Mohd; Khan, T.A.: Arsenite removal from water by electro-coagulation on zinc-zinc and copper–copper electrodes. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 10, 377–384 (2013)
Lv, J.-M.; Ma, Y.-L.; Chang, X.; Fan, S.-B.: Removal and removing mechanism of tetracycline residue from aqueous solution by using Cu-13X. Chem. Eng. J. 273, 247–253 (2015)
Ma, Y.; Yan, C.; Alshameri, A.; Qiu, X.; Zhou, C.; li, D.: Synthesis and characterization of 13X zeolite from low-grade natural kaolin. Adv. Powder Technol. 25, 495–499 (2014)
Scherzer, J.: Octane-enhancing, zeolitic FCC catalysts: scientific and technical aspects. Catal. Rev. 31, 215–354 (1989)
Zhang, Z.Y.; Shi, T.B.; Jia, C.Z.; Ji, W.J.; Chen, Y.; He, M.Y.: Adsorptive removal of aromatic organosulfur compounds over the modified Na–Y zeolites. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 82, 1–10 (2008)
Fakhri, A.; Adami, S.: Adsorption and thermodynamic study of Cephalosporins antibiotics from aqueous solution onto MgO nanoparticles. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 45, 1001–1006 (2014)
Chaouati, N.; Soualah, A.; Chater, M.: Adsorption of phenol from aqueous solution onto zeolites Y modified by silylation. Comp. Ren. Chim. 16, 222–228 (2013)
Liang, Z.; Zhaob, Z.; Sun, T.; Shi, W.; Cui, F.: Adsorption of quinolone antibiotics in spherical mesoporous silica: effects of the retained template and its alkyl chain length. J. Hazard. Mater. 305, 8–14 (2016)
Barzamini, R.; Falamaki, C.; Mahmoudi, R.: Adsorption of ethyl, iso-propyl, n-butyl and iso-butyl mercaptans on AgX zeolite: equilibrium and kinetic study. Fuel 130, 46–53 (2014)
Fukahori, S.; Fujiwara, T.; Ito, R.; Funamizu, N.: pH-dependent adsorption of sulfa drugs on high silica zeolite: modeling and kinetic study. Desalin 275, 237–242 (2011)
Ötker, H.M.; Akmehmet-Balcıoğlu, I.: Adsorption and degradation of enrofloxacin, a veterinary antibiotic on natural zeolite. J. Hazard. Mater. 122, 251–258 (2005)
Braschi, I.; Blasioli, S.; Gigli, L.; Gessa, C.E.; Alberto, A.; Martucci, A.: Removal of sulfonamide antibiotics from water: evidence of adsorption into an organophilic zeolite Y by its structural modifications. J. Hazard Mater. 178(1–3), 218–225 (2010)
Wang, Y.-J.; Jia, D.-A.; Sun, R.-J.; Zhu, H.-W.; Zhou, D.-M.: Adsorption and cosorption of tetracycline and copper(II) on montmorillonite as affected by solution pH. Environ. Sci. Technol. 42, 3254–3259 (2008)
Samarghandi, M.R.; Al-Musawi, T.J.; Mohseni-Bandpi, A.; Zarrabi, M.: Adsorption of cephalexin from aqueous solution using natural zeolite and zeolite coated with manganese oxide nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 211, 431–441 (2015)
Zhou, Y.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Gan, N.; Li, Q.; Cuan, J.: Detection and removal of antibiotic tetracycline in water with a highly stable luminescent MOF. Sens. Actu. B: Chem. 262, 137–143 (2018)
Alidadi, H.; Dolatabadi, M.; Davoudi, M.; Barjasteh-Askari, F.; Jamali-Behnam, F.; Hosseinzadeh, A.: Enhanced removal of tetracycline using modified sawdust: optimization, isotherm, kinetics, and regeneration studies. Proc. Saf. Environ. Prot. 117, 51–60 (2018)
Treacy, M.M.J.; Higgins, J.B.; Commission, I.Z.A.S.: Collection of Simulated XRD Powder Patterns for Zeolites. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2007)
Kwak, J.-S.: Application of Taguchi and response surface methodologies for geometric error in surface grinding process. Int. J. Mach. Tool Manuf. 45, 327–334 (2005)
Bradley, N.: The response surface methodology. Indiana University South Bend 71, 4–68 (2007)
Montgomery, D.C.: Design and Analysis of Experiments. Wiley, New York (2008)
Schmidt, S.R.; Launsby, R.G.: Understanding Industrial Designed Experiments. Air Academy Press, Colorado Springs (1989)
Gorji, S.; Bahram, M.: Experimental design for the study and optimization of the effect of different surfactants on the spectrophotometric determination of sulfide based on phenothiazine dye production. Anal. Methods 2, 948–953 (2010)
Po-Hsiang, C.; Li, Z.; Jiang, W.-T.; Jean, J.-S.: Adsorption and intercalation of tetracycline by swelling clay minerals Appl. Clay Sci. 46, 27–36 (2009)
Huang, H.; Zou, Y.L.; Li, Y.N.: Experimental and modeling studies of sorption of tetracycline onto zeolite in the presence of copper(II). Adv. Mater. Res. 512–515, 2355–2360 (2012)
Wang, Y.-J.; Jia, D.-A.; Sun, R.-J.; Zhu, H.-W.; Zhou, D.-M.: Adsorption and cosorption of tetracycline and copper(II) on montmorillonite as affected by solution pH Environ. Sci. Technol. 42(9), 3254–3259 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahimi, A., Bayati, B. & Khamforoush, M. Synthesis and Application of Cu-X zeolite for Removal of Antibiotic from Aqueous Solution: Process Optimization Using Response Surface Methodology. Arab J Sci Eng 44, 5381–5397 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3644-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3644-x