Abstract
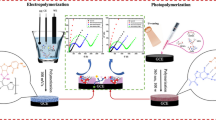
Combining high recognition selectivity with excellent electrochemiluminescent (ECL) performance, the imprinted poly(luminol-p-aminothiophenol) was prepared by the electrochemical copolymerization of luminol and p-aminothiophenol onto the gold electrode surface in the presence of triazophos. The recognition selectivity and ECL of the imprinted poly(luminol-p-aminothiophenol) were studied using triazophos as analyte. It was found that the imprinted poly(luminol-p-aminothiophenol) presented better ECL emission to triazophos than that of the polyluminol. On this basis, a reagentless ECL sensor based on the imprinted poly(luminol-p-aminothiophenol) as recognition elements is established for the detection of ultra-trace triazophos residues in the environmental water samples under near neutral condition. The resulting reagentless ECL sensor shows wide linear ranges from \(1.0 \times 10^{-10}\) to \(1.0 \times 10^{-6}\) M with lower detection limit of \(5.8 \times 10^{-11}\) M for triazophos.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Gui, W.J.; Wang, S.T.; Guo, Y.R.; Zhu, G.N.: Development of a one-step strip for the detection of triazophos residues in environmental samples. Anal. Biochem. 377, 202–208 (2008)
Du, D.; Huang, X.; Cai, J.; Zhang, A.D.: Amperometric detection of triazophos pesticide using acetylcholinesterase biosensor based on multiwall carbon nanotube–chitosan matrix. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 127, 531–535 (2007)
Xiong, J.; Hu, B.: Comparison of hollow fiber liquid phase microextraction and dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for the determination of organosulfur pesticides in environmental and beverage samples by gas chromatography with flame photometric detection. J. Chromatogr. A. 1193, 7–18 (2008)
Galán-Cano, F.; Lucena, R.; Cárdenas, S.; Valcárcel, M.: Dispersive micro-solid phase extraction with ionic liquid-modified silica for the determination of organophosphate pesticides in water by ultra performance liquid chromatography. Microchem. J. 106, 311–317 (2013)
Romero-González, R.; Garrido, F.A.; Martínez, V.J.L.: Multiresidue method for fast determination of pesticides in fruit juices by ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled to Tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 76, 211–225 (2008)
Du, P.F.; Jin, M.J.; Chen, G.; Zhang, C.; Cui, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, P.; Jiang, Z.; Cao, X.; She, Y.; Jin, F.; Wang, J.: Competitive colorimetric triazophos immunoassay employing magnetic microspheres and multi-labeled gold nanoparticles along with enzymatic signal enhancement. Microchim. Acta 184, 3705–3712 (2017)
Guo, Y.R.; Liu, S.Y.; Gui, W.J.; Zhu, G.N.: Gold immunochromatographic assay for simultaneous detection of carbofuran and triazophos in water samples. Anal. Biochem. 389, 32–39 (2009)
Zhang, C.; Du, P.F.; Jiang, Z.J.; Jin, M.J.; Chen, G.; Cao, X.L.; Cui, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.D.; Li, R.X.; Abd El-Aty, A.M.; Wang, J.: A simple and sensitive competitive bio-barcode immunoassay for triazophos based on multi-modified gold nanoparticles and fluorescent signal amplification. Anal. Chim. Acta 999, 123–131 (2018)
Ju, K.J.; Feng, J.X.; Feng, J.J.; Zhang, Q.L.; Xu, T.Q.; Wei, J.; Wang, A.J.: Biosensor for pesticide triazophos based on its inhibition of acetylcholinesterase and using a glassy carbon electrode modified with coral-like gold nanostructures supported on reduced graphene oxide. Microchim. Acta 182, 2427–2434 (2015)
Du, D.; Cai, J.; Song, D.D.; Zhang, A.D.: Rapid determination of triazophos using acetylcholinesterase biosensor based on sol–gel interface assembling multiwall carbon nanotubes. J. Appl. Electrochem. 37, 893–898 (2007)
Haupt, K.; Mosbach, K.: Molecularly imprinted polymers and their use in biomimetic sensors. Chem. Rev. 100, 495–2504 (2000)
Wulff, G.: Enzyme-like catalysis by molecularly imprinted polymers. Chem. Rev. 102, 1–27 (2002)
Guan, G.J.; Liu, B.H.; Wang, W.Y.; Zhang, Z.P.: Imprinting of molecular recognition sites on nanostructures and its applications in chemosensors. Sensors 8, 8291–8320 (2008)
Lu, C.; Zhou, W.; Han, B.; Yang, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.: Surface-imprinted core–shell nanoparticles for sorbent assays. Anal. Chem. 79, 5457–5461 (2007)
Gao, D.M.; Zhang, Z.P.; Wu, M.H.; Xie, C.G.; Guan, G.J.; Wang, D.P.: A surface functional monomer-directing strategy for highly dense imprinting of TNT at surface of silica nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 7859–7866 (2007)
Titirici, M.M.; Sellergren, B.: Thin Molecularly imprinted polymer films via reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer polymerization. Chem. Mater. 18, 1773–1779 (2006)
Liu, H.B.; Qiao, L.; Gan, N.; Lin, S.H.; Cao, Y.T.; Hu, F.T.; Wang, J.Y.; Chen, Y.J.: Electro-deposited poly-luminol molecularly imprinted polymer coating on carboxyl graphene for stir bar sorptive extraction of estrogens in milk. J. Chromatogr. B. 1027, 50–56 (2016)
Nabid, M.R.; Taheri, S.S.; Sedghi, R.; Rezaei, S.J.T.: Synthesis and characterization of chemiluminescent conducting polyluminol via biocatalysis. Macromol. Res. 19, 280–285 (2011)
Riskin, M.; Tel-Vered, R.; Bourenko, T.; Granot, E.; Willner, I.: Imprinting of molecular recognition sites through eletropolymerization of functionalized Au nanoparticles: development of an electrochemical TNT sensor based on \(\pi \)-donor–acceptor interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 9726–9733 (2008)
Li, H.F.; Xie, C.G.; Li, S.Q.; Xu, K.: Electropolymerized molecular imprinting on gold nanoparticle-carbon nanotube modified electrode for electrochemical detection of triazophos. Colloids Surf. B. 89, 175–181 (2012)
Li, H.F.; Xie, T.; Ye, L.L.; Wang, Y.W.; Xie, C.G.: Core-shell magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles for the extraction of triazophos residues from vegetables. Microchim. Acta 184, 1011–1019 (2017)
Richter, M.M.: Electrochemiluminescence (ECL). Chem. Rev. 104, 3003–3036 (2004)
Nobeshima, T.; Morimoto, T.; Nakamura, K.; Kobayashi, N.: Advantage of an AC-driven electrochemiluminescent cell containing a \(\text{ Ru(bpy) }_{3}^{2+}\) complex for quick response and high efficiency. J. Mater. Chem. 20, 10630–10633 (2010)
Wang, X.F.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, J.J.; Chen, H.Y.: Signal-on electrochemiluminescence biosensors based on CdS-carbon nanotube nanocomposite for the sensitive detection of choline and acetylcholine. Adv. Funct. Mater. 19, 1444–1450 (2009)
Rong, J.F.; Chi, Y.W.; Zhang, Y.J.; Chen, L.C.; Chen, G.N.: Enhanced electrochemiluminescence of luminol-\(\text{ O }_{2}\) system at gold-hydrophobic ionic liquid water interface. Electrochem. Commun. 12, 270–273 (2010)
Chu, H.H.; Guo, W.Y.; Di, J.W.; Wu, Y.; Tu, Y.F.: Study on sensitization from reactive oxygen species for electrochemiluminescence of luminol in neutral medium. Electroanalysis 21, 1630–1635 (2009)
Li, H.F.; Xie, C.G.; Fu, X.C.: Electrochemiluminescence sensor for sulfonylurea herbicide with molecular imprinting core–shell nanoparticles/chitosan composite film modified glassy carbon electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 181, 858–866 (2013)
Li, H.F.; Xie, T.; Shi, D.D.; Jin, J.; Xie, C.G.: Enhanced electrochemiluminescence of luminol at the gold nanoparticle/carbon nanotube/electropolymerised molecular imprinting composite membrane interface for selective recognition of triazophos. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 96, 1300–1311 (2016)
Sassolas, A.; Blum, L.J.; Leca-Bouvier, B.D.: Electrogeneration of polyluminol and chemiluminescence for new disposable reagentless optical sensors. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 390, 865–871 (2008)
Zhang, G.F.; Chen, H.Y.: Studies of polyluminol modified electrode and its application in electrochemiluminescence analysis with flow system. Anal. Chim. Acta 419, 25–31 (2000)
Sassolas, A.; Blum, L.J.; Leca-Bouvier, B.D.: Polymeric luminol on pre-treated screen-printed electrodes for the design of performant reagentless (bio) sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 139, 214–221 (2009)
Li, G.X.; Lian, J.L.; Zheng, X.W.; Cao, J.: Electrogenerated chemiluminescence biosensor for glucose based on poly(luminol-aniline) nanowires composite modified electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 26, 643–648 (2010)
Ferreira, V.; Cascalheira, A.C.; Abrantes, L.M.: Electrochemical copolymerisation of luminol with aniline: a new route for the preparation of self-doped polyanilines. Electrochim. Acta 53, 3803–3811 (2008)
Xie, C.G.; Li, H.F.; Li, S.Q.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Z.P.: Surface molecular self-assembly for organophosphate pesticide imprinting in electropolymerized poly(p-aminothiophenol) membranes on a gold nanoparticle modified glassy carbon electrode. Anal. Chem. 82, 241–249 (2010)
Leca-Bouvier, B.D.; Sassolas, A.; Blum, L.J.: Polyluminol/hydrogel composites as new electrochemiluminescent-active sensing layers. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 406, 5657–5667 (2014)
Cui, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.F.: Multichannel electrochemiluminescence of luminol in neutral and alkaline aqueous solutions on a gold nanoparticle self-assembled electrode. Anal. Chem. 76, 4002–4010 (2004)
Li, G.X.; Zheng, X.W.; Song, L.: Electrochemiluminescence characterization of poly(luminol-benzidine) composite films and their analytical application. Electroanalysis 21, 845–852 (2009)
Bhamore, J.R.; Ganguly, P.; Kailasa, S.K.: Molecular assembly of 3-mercaptopropinonic acid and guanidine acetic acid on silver nanoparticles for selective colorimetric detection of triazophos in water and food samples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 233, 485–495 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Wang, Y., Zha, H. et al. Reagentless Electrochemiluminescence Sensor for Triazophos Based on Molecular Imprinting Electropolymerized Poly(Luminol-p-Aminothiophenol) Composite-Modified Gold Electrode. Arab J Sci Eng 44, 145–152 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3289-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3289-9