Abstract
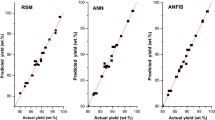
Non-edible feedstock is attaining importance due to authentic concerns behind the utilization of food crops for fuel production. Aegle marmelos seed is one such feedstock with high oil content portraying a better entrant among other non-edible feedstock. In this study, optimization of oil extraction, and biodiesel production from Aegle marmelos seeds had been reported. Oil extraction performed with n-hexane was optimized by response surface methodology (RSM) and artificial neural network (ANN). The influence of five parameters on oil extraction, namely particle size, acid concentration, solvent-to-seed ratio, extraction time and temperature were investigated. A comparison of performance evaluation between RSM and ANN was executed. The lower value of coefficient of determination (\(R^{2} = 0.998\)), root mean square error (\({ RMSE} = 0.2784\)), standard error of prediction (\({ SEP} = 0.7068\)) and absolute average deviation (\({ AAD} = 0.3425\)) for ANN compared to those of \(R^{2}\) (0.9769), RMSE (0.5349), SEP (1.3326) and AAD (1.1072) for RSM showed the prediction competence of the ANN was much better than RSM. Among the process parameters studied, solvent-to-seed ratio was the most influential variable on oil yield. The maximum oil yield of 45.99 wt% was obtained at optimum conditions, with an acid value of 18.92 mg KOH \(\hbox {g}^{-1}\). Hence, a dual-stage acid-base transesterification was employed to produce biodiesel. It was followed by \(^{1}\)H NMR spectroscopy study and fuel properties analysis. The highest conversion of 98% was ascertained using \(^{1}\)H NMR spectroscopy, and the biodiesel fuel properties were found to comply with ASTM standards.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atabani, A.E.; Badruddin, I.A.; Masjuki, H.H.; Chong, W.T.; Lee, K.T.: Pangium edule Reinw: a promising non-edible oil feedstock for biodiesel production. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 40, 583–594 (2014)
Sharma, P.C.; Bhatia, V.; Bansal, N.; Sharma, A.: A review on bael tree. Indian J. Nat. Prod. Resour. 6, 171–178 (2007)
Meziane, S.; Kadi, H.; Daoud, K.; Hannane, F.: Application of experimental design method to the oil extraction from olive cake. J. Food Process. Preserv. 33, 176–185 (2008)
Meziane, S.: Optimization of oil extraction from olive pomace using response surface methodology. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 19, 315–322 (2013)
Betiku, E.; Adepoju, T.F.; Omole, A.K.; Aluko, S.E.: Statistical approach to the optimization of oil extraction from beniseed ( Sesamum indicum) oilseeds. J. Food Sci. Eng. 2, 351–357 (2012)
Betiku, E.; Adepoju, T.F.: Sorrel (Hibiscus sabdariffa) seed oil extraction optimization and quality characterization. Am. Chem. Sci. J. 3, 449–458 (2013)
Bagheri, H.; Abdul Manap, M.Y.B.; Solati, Z.: Response surface methodology applied to supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of Piper nigrum L. essential oil. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 57, 149–155 (2014)
Liu, Z.; Mei, L.; Wang, Q.; Shao, Y.; Tao, Y.: Optimization of subcritical fluid extraction of seed oil from Nitraria tangutorum using response surface methodology. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 56, 168–174 (2014)
Chuah, L.F.; Bokhari, A.; Yusup, S.; Klemeš, J.J.; Abdullah, B.; Akbar, M.M.: Optimisation and kinetic studies of acid esterification of high free fatty acid rubber seed oil. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 41, 2515–2526 (2016)
Basri, M.; Rahman, R.N.Z.R.A.; Ebrahimpour, A.; Salleh, A.B.; Gunawan, E.R.; Rahman, M.B.A.: Comparison of estimation capabilities of response surface methodology (RSM) with artificial neural network (ANN) in lipase-catalyzed synthesis of palm-based wax ester. BMC Biotechnol. 7, 53 (2007)
Rajendra, M.; Jena, P.C.; Raheman, H.: Prediction of optimized pretreatment process parameters for biodiesel production using ANN and GA. Fuel 88, 868–875 (2009)
Betiku, E.; Taiwo, A.E.: Modeling and optimization of bioethanol production from breadfruit starch hydrolyzate vis-a-vis response surface methodology and artificial neural network. Renew. Energy 74, 87–94 (2015)
Betiku, E.; Omilakin, O.R.; Ajala, S.O.; Okeleye, A.A.; Taiwo, A.E.; Solomon, B.O.: Mathematical modeling and process parameters optimization studies by artificial neural network and response surface methodology: a case of non-edible neem ( Azadirachta indica) seed oil biodiesel synthesis. Energy. 72, 266–273 (2014)
Betiku, E.; Ajala, S.O.: Modeling and optimization of Thevetia peruviana (yellow oleander) oil biodiesel synthesis via Musa paradisiacal (plantain) peels as heterogeneous base catalyst: a case of artificial neural network vs response surface methodology. Ind. Crops Prod. 53, 314–322 (2014)
Mason, R.L.; Richard, F.; Gunst, R.F.; Hess, J.L.: Statistical Design and Analysis of Experiments with Applications to Engineering and Science. Wiley, Hoboken (2003)
Marchitan, N.; Cojocaru, C.; Mereuta, A.; Duca, G.; Cretescu, I.; Gonta, M.: Modeling and optimization of tartaric acid reactive extraction from aqueous solutions: a comparison between response surface methodology and artificial neural network. Sep. Purif. Technol. 75, 273–285 (2010)
Akintunde, A.M.; Ajala, S.O.; Betiku, E.: Optimization of Bauhinia monandra seed oil extraction via artificial neural network and response surface methodology: a potential biofuel candidate. Ind. Crop. Prod. 67, 387–394 (2015)
Sarve, A.N.; Varma, M.N.; Sonawane, S.S.: Response surface optimization and artificial neural network modeling of biodiesel production from crude mahua (Madhuca indica) oil under supercritical ethanol conditions using CO2 as co-solvent. RSC Adv. 5, 69702–69713 (2015)
Bas, D.; Boyaci, I.H.: Modeling and optimization II: comparison of estimation capabilities of response surface methodology with artificial neural networks in a biochemical reaction. J. Food Eng. 78, 846–854 (2007)
Sarve, A.; Sonawane, S.S.; Varma, M.N.: Ultrasound assisted biodiesel production from sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) oil using barium hydroxide as a heterogeneous catalyst: Comparative assessment of prediction abilities between response surface methodology (RSM) and artificial neural network (ANN). Ultrason. Sonochem. 26, 218–228 (2015)
Garson, G.D.: Interpreting neural network connection weights. Artif. Intell. Expert 6, 47–51 (2009)
Fadhil, A.B.; Ahmed, K.M.; Dheyab, M.M.: Silybum marianum L. seed oil: a novel feedstock for biodiesel production. Arab. J. Chem. 10, S683–S690 (2012)
Van Gerpen, J.: Biodiesel processing and production. Fuel Process. Technol. 86, 1097–1107 (2005)
Chongkhong, S.; Tongurai, C.; Chetpattananondh, P.; Bunyakan, C.: Biodiesel production by esterification of palm fatty acid distillate. Biomass Bioenergy 31, 563–568 (2007)
Sampath, K.P.; Umadevi, M.; Bhowmik, D.; Singh, D.M.; Dutta, A.S.: Recent trends in medicinal uses and health benefits of Indian traditional herbs Aegle marmelos. Pharma Innov. 1, 57–65 (2012)
Bharti, R.K.; Srivastava, S.; Thakur, I.S.: Extraction of extracellular lipids from chemoautotrophic bacteria Serratia sp. ISTD04 for production of biodiesel. Bioresour. Technol. 165, 201–204 (2014)
Kakati, J.; Gogoi, T.K.; Pakshirajan, K.: Production of biodiesel from Amari (Amoora Wallichii King) tree seeds using optimum process parameters and its characterization. Energy Convers. Manag. 135, 281–290 (2017)
Shambhu, V.B.; Bhattacharya, T.K.; Chaudhary, S.K.; Das, S.: Compatibility of Jatropha oil bio-diesel and petro diesel as an engine fuel based on their characteristic fuel properties. Agric. Mech. Asia Africa Lat. Am. 43(2), 43–49 (2012)
Sivakumar, P.; Sindhanaiselvan, S.; Gandhi, N.N.; Devi, S.S.; Renganathan, S.: Optimization and kinetic studies on biodiesel production from underutilized Ceiba Pentandra oil. Fuel 103, 693–698 (2013)
Mani, S.; Jaya, S.; Vadivambal, R.: Optimization of solvent extraction of Moringa (Moringa Oleifera) Seed Kernel Oil Using response surface methodology. Food Bioprod. Process. 85, 328–335 (2007)
Rhazi, N.; Hannache, H.; Oumam, M.; Sesbou, A.; Charrier, B.; Pizzi, A.; Charrier-El Bouhtoury, F.: Green extraction process of tannins obtained from Moroccan Acacia mollissima barks by microwave: modeling and optimization of the process using the response surface methodology RSM. Arab. J. Chem. 12, 3745–3758 (2015)
Acikel, U.; Ersan, M.; Sag Acikel, Y.: Optimization of critical medium components using response surface methodology for lipase production by Rhizopus delemar. Food Bioprod. Process. 88, 31–39 (2010)
Taghavifar, H.; Mardani, A.: Application of artificial neural networks for the prediction of traction performance parameters. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 13, 35–43 (2014)
Hamed, M.M.; Khalafallah, M.G.; Hassanien, E.A.: Prediction of wastewater treatment plant performance using artificial neural networks. Environ. Model. Softw. 19, 919–928 (2004)
Holubar, P.; Zani, L.; Hager, M.; Fröschl, W.; Radak, Z.; Braun, R.: Advanced controlling of anaerobic digestion by means of hierarchical neural networks. Water Res. 36, 2582–2588 (2002)
Eryilmaz, T.; Yesilyurt, M.K.; Taner, A.; Celik, S.A.: Prediction of kinematic viscosities of biodiesels derived from edible and non-edible vegetable oils by using artificial neural networks. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 40, 3745–3758 (2015)
Gasim, H.A.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Hasnain Isa, M.; Alemu, L.T.: Optimization of anaerobic treatment of petroleum refinery wastewater using artificial neural networks. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 6, 2077–2082 (2013)
Vani, S.; Sukumaran, R.K.; Savithri, S.: Prediction of sugar yields during hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass using artificial neural network modeling. Bioresour. Technol. 188, 128–135 (2015)
Sharma, A.; Kumari, S.; Wongputtisin, P.; Nout, M.J.R.; Sarkar, P.K.: Optimization of soybean processing into kinema, a Bacillus-fermented alkaline food, with respect to a minimum level of antinutrients. J. Appl. Microbiol. 119, 162–176 (2015)
Salehi, I.; Shirani, M.; Semnani, A.; Hassani, M.; Habibollahi, S.: Comparative study between response surface methodology and artificial neural network for adsorption of crystal violet on magnetic activated carbon. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 41, 2611–2621 (2016)
Prakash Maran, J.; Sivakumar, V.; Thirugnanasambandham, K.; Sridhar, R.: Artificial neural network and response surface methodology modeling in mass transfer parameters predictions during osmotic dehydration of Carica papaya L. Alex. Eng. J. 52, 507–516 (2013)
Bokhari, A.; Yusup, S.; Ahmad, M.M.: Optimization of the parameters that affects the solvent extraction of crude rubber seed oil using response surface methodology (RSM). Recent Adv. Eng. 28–33 (2012)
Knothe, G.: Analyzing biodiesel: standards and other methods. Jaocs 83, 823–33 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Selvan, S.S., Pandian, P.S., Subathira, A. et al. Comparison of Response Surface Methodology (RSM) and Artificial Neural Network (ANN) in Optimization of Aegle marmelos Oil Extraction for Biodiesel Production. Arab J Sci Eng 43, 6119–6131 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3272-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3272-5