Abstract
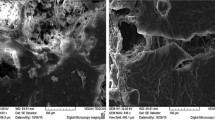
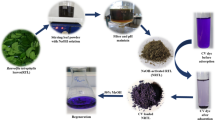
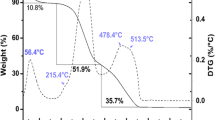
The present study investigates the use of cheap, readily available natural adsorbent, Artocarpus odoratissimus leaves (TL), for the removal of toxic rhodamine B (RhB) dye from simulated wastewater. TL showed resilience when tested in a wide range of pH and was able to maintain its adsorption capacity with the highest removal of RhB at pH 3. Investigation of the effect of ionic strength was carried out using four different salts, namely \(\hbox {KNO}_{3}\), NaCl, \(\hbox {NaNO}_{3}\) and KCl. Of these, only \(\hbox {KNO}_{3}\) influenced the removal of RhB dye, while the other three salts did not show any significant effect. Maximum adsorption capacity, \(q_{\max }\), of 104.96 mg/g was based on the Langmuir isotherm being the best fit model with highest \(R^{2}\) value close to unity and lowest error values. Adsorption mechanism followed the pseudo second-order kinetics with rate constant \(k_{2}\) of 1.274 and 0.616 g/mmol min using 100 and 500 mg/L dye, respectively. Regeneration studies confirmed TL can be regenerated and reused thereby adding value to TL as a potential adsorbent in remediation of dye wastewater. SEM and FTIR were used to characterize the adsorption of RhB onto TL.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pirbazari, A.E.; Saberikhah, E.; Badrouh, M.; Emami, M.S.: Alkali treated Foumanat tea waste as an efficient adsorbent for methylene blue adsorption from aqueous solution. Water Resour. Ind. 6, 64–80 (2014)
Nawaz, M.S.; Ahsan, M.: Comparison of physico-chemical, advanced oxidation and biological techniques for the textile wastewater treatment. Alex. Eng. J. 53(3), 717–722 (2014)
Fosso-Kankeu, E.; Webster, A.; Ntwampe, I.O.; Waanders, F.B.: Coagulation/flocculation potential of polyaluminium chloride and bentonite clay tested in the removal of methyl red and crystal violet. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 42(4), 1389–1397 (2017)
Verma, A.; Sangwan, P.; Dixit, D.: Sonophotocatalytic degradation studies of alizarin reactive red dye. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 39(11), 7477–7482 (2014)
Vaiano, V.; Matarangolo, M.; Sacco, O.; Sannino, D.: Photocatalytic treatment of aqueous solutions at high dye concentration using praseodymium-doped ZnO catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 209, 621–630 (2017)
Castro, F.D.; Bassin, J.P.; Dezotti, M.: Treatment of a simulated textile wastewater containing the Reactive Orange 16 azo dye by a combination of ozonation and moving-bed biofilm reactor: evaluating the performance, toxicity, and oxidation by-products. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. 24(7), 6307–6316 (2017)
Li, X.; Jin, X.; Zhao, N.; Angelidaki, I.; Zhang, Y.: Novel bio-electro-Fenton technology for azo dye wastewater treatment using microbial reverse-electrodialysis electrolysis cell. Bioresour. Technol. 228, 322–329 (2017)
Clematis, D.; Cerisola, G.; Panizza, M.: Electrochemical oxidation of a synthetic dye using a BDD anode with a solid polymer electrolyte. Electrochem. Commun. 75, 21–24 (2017)
Maleki, A.; Daraei, H.; Hosseini, E.A.; Azizi, S.; Faez, E.; Gharibi, F.: Azo dye DB71 degradation using ultrasonic-assisted Fenton process: modeling and process optimization. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 40(2), 295–301 (2015)
Bandari, F.; Safa, F.; Shariati, S.: Application of response surface method for optimization of adsorptive removal of eriochrome black T using magnetic multi-wall carbon nanotube nanocomposite. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 40(12), 3363–3372 (2015)
Senthilkumar, S.; Prabhu, H.J.; Perumalsamy, M.: Response surface optimization for biodegradation of textile azo dyes using isolated bacterial strain Pseudomonas sp. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 38(9), 2279–2291 (2013)
Deniz, F.; Karaman, S.; Saygideger, S.D.: Biosorption of a model basic dye onto Pinus brutia Ten.: evaluating of equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic data. Desalination 270(1), 199–205 (2011)
Heydartaemeh, M.R.; Ardejani, F.D.; Badii, K.; Shabani, K.S.; Mousavi, S.E.: FeCl\(_{2}\)/FeCl\(_{3}\)/perlite nanoparticles as a novel magnetic material for adsorption of green malachite dye. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 39(5), 3383–3392 (2014)
Liu, Z.; Zhong, X.; Wang, Y.; Ding, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, G.; Liao, S.: An efficient adsorption of manganese oxides/activated carbon composite for lead (II) ions from aqueous solution. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2514-2
Lim, L.B.L.; Priyantha, N.; Cheng, H.H.; Mohamad Zaidi, N.A.H.: Perkia speciosa (Petai) pod as potential low-cost adsorbent for the removal of toxic crystal violet dye. Sci. Bruneiana 15, 99–106 (2016)
Mohammed, R.R.: Removal of heavy metals from waste water using black teawaste. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 37(6), 1505–1520 (2012)
Dahri, M.K.; Kooh, M.R.R.; Lim, L.B.L.: Application of Casuarina equisetifolia needle for the removal of methylene blue and malachite green dyes from aqueous solution. Alex. Eng. J. 54(4), 1253–1263 (2015)
Chieng, H.I.; Lim, L.B.L.; Priyantha, N.; Tennakoon, D.T.B.: Sorption characteristics of peat of Brunei Darussalam III: equilibrium and kinetics studies on adsorption of crystal violet (CV). Int. J. Earth Sci. Eng. 6, 791–801 (2013)
Reddy, N.A.; Lakshmipathy, R.; Sarada, N.C.: Application of Citrullus lanatus rind as biosorbent for removal of trivalent chromium from aqueous solution. Alex. Eng. J. 53(4), 969–975 (2014)
Lim, L.B.L.; Priyantha, N.; Chan, C.M.; Matassan, D.; Chieng, H.I.; Kooh, M.R.R.: Adsorption behavior of methyl violet 2B using duckweed: equilibrium and kinetics studies. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 39(9), 6757–6765 (2014)
Postai, D.L.; Rodrigues, C.A.: Adsorption of cationic dyes ssing waste from fruits of Eugenia umbelliflora berg (Myrtaceae). Arab. J. Sci. Eng. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2819-1
Kooh, M.R.R.; Dahri, M.K.; Lim, L.B.L.; Lim, L.H.: Batch adsorption studies on the removal of acid blue 25 from aqueous solution using Azolla pinnata and soya bean waste. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 41(7), 2453–2464 (2016)
Khalid, A.; Zubair, M.: A comparative study on the adsorption of Eriochrome Black T dye from aqueous solution on graphene and acid-modified graphene. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2543-x
Mittal, A.: Adsorption kinetics of removal of a toxic dye, Malachite Green, from wastewater by using hen feathers. J. Hazard. Mater. 133(1), 196–202 (2006)
Tahir, U.; Yasmin, A.; Khan, U.H.: Phytoremediation: potential flora for synthetic dyestuff metabolism. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 28(2), 119–130 (2016)
Uddin, M.; Rukanuzzaman, M.; Khan, M.; Rahman, M.; Islam, M.: Jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus) leaf powder: an effective adsorbent for removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions. Ind. J. Chem. Technol. 16(2), 142–149 (2009)
Nazari, M.; Forouzandeh, M.A.; Divarathne, C.M.; Sidiroglou, F.; Martinez, M.R.; Konstas, K.; Muir, B.W.; Hill, A.J.; Duke, M.C.; Hill, M.R.: UiO-66 MOF end-face-coated optical fiber in aqueous contaminant detection. Opt. Lett. 41(8), 1696–1699 (2016)
Laili, A.N.; Ananingsih, I.; Wiyasa, I.W.A.; Indrawan, I.W.A.; Barlianto, W.; Yueniwati, Y.: Protective effect of combined vitamin C and E against ovarian and endometrial toxicity in rats that receiving oral rhodamine B. Biomark. Genom. Med. 7(4), 154–158 (2015)
De Gisi, S.; Lofrano, G.; Grassi, M.; Notarnicola, M.: Characteristics and adsorption capacities of low-cost sorbents for wastewater treatment: a review. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 9, 10–40 (2016)
Dahri, M.K.; Chieng, H.I.; Lim, L.B.L.; Priyantha, N.; Mei, C.C.: Cempedak durian (Artocarpus sp.) peel as a biosorbent for the removal of toxic methyl violet 2B from aqueous solution. Korean Chem. Eng. Res. 53(5), 576–583 (2015)
Lim, L.B.L.; Priyantha, N.; Chieng, H.I.; Dahri, M.K.: Artocarpus camansi Blanco (Breadnut) core as low-cost adsorbent for the removal of methylene blue: equilibrium, thermodynamics, and kinetics studies. Desalin. Water Treat. 57(12), 5673–5685 (2016)
Priyantha, N.; Lim, L.B.L.; Tennakoon, D.T.B.; Mohd Mansor, N.H.; Dahri, M.K.; Chieng, H.I.: Breadfruit (Artocarpus altilis) waste for bioremediation of Cu (II) and Cd (II) ions from aqueous medium. Ceylon J. Sci. Phys. Sci. 17, 19–29 (2013)
Lim, L.B.L.; Priyantha, N.; Tennakoon, D.T.B.; Dahri, M.K.: Biosorption of cadmium (II) and copper (II) ions from aqueous solution by core of Artocarpus odoratissimus. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 19(8), 3250–3256 (2012)
Dahri, M.K.; Lim, L.B.L.; Priyantha, N.; Chan, C.M.: Removal of Acid blue 25 using Cempedak Durian peel from aqueous medium: isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics studies. Int. Food Res. J. 23(3), 1154–1163 (2016)
Lim, L.B.L.; Priyantha, N.; Hei Ing, C.; Dahri, M.K.; Tennakoon, D.T.B.; Zehra, T.; Suklueng, M.: Artocarpus odoratissimus skin as a potential low-cost biosorbent for the removal of methylene blue and methyl violet 2B. Desalin. Water Treat. 53(4), 964–975 (2015)
Lim, L.B.L.; Priyantha, N.; Lai, M.H.F.; Salleha, R.M.; Zehra, T.: Utilization of Artocarpus hybrid (Nanchem) skin for the removal of Pb (II): equilibrium, thermodynamics, kinetics and regeneration studies. Int. Food Res. J. 22(3), 1043–1052 (2015)
Tang, Y.P.; Linda, B.L.L.; Franz, L.W.: Proximate analysis of Artocarpus odoratissimus (Tarap) in Brunei Darussalam. Int. Food Res. J. 20(1), 409–415 (2013)
Lim, L.B.L.; Chieng, H.I.; Wimmer, F.L.: The nutrient composition of Artocarpus champeden and its hybrid (Nanchem) in Negara Brunei Darussalam. ASEAN J. Sci. Technol. Dev. 28, 122–138 (2011)
Hameed, B.H.: Removal of cationic dye from aqueous solution using jackfruit peel as non-conventional low-cost adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 162(1), 344–350 (2009)
Lim, L.B.L.; Priyantha, N.; Mohamad Zaidi, N.A.H.: A superb modified new adsorbent, Artocarpus odoratissimus leaves, for removal of cationic methyl violet 2B dye. Environ. Earth Sci. 75(16), 1179 (2016)
Lim, L.B.L.; Priyantha, N.; Cheng, H.H.; Mohamad Zaidi, N.A.H.: Adsorption characteristics of Artocarpus odoratissimus leaf toward removal of toxic crystal violet dye: isotherm, thermodynamics and regeneration studies. J. Environ. Biotechnol. Res. 4(1), 32–40 (2016)
Chieng, H.I.; Lim, L.B.L.; Priyantha, N.: Sorption characteristics of peat from Brunei Darussalam for the removal of rhodamine B dye from aqueous solution: adsorption isotherms, thermodynamics, kinetics and regeneration studies. Desalin. Water Treat. 55(3), 664–677 (2015)
Gad, H.M.H.; El-Sayed, A.A.: Activated carbon from agricultural by-products for the removal of Rhodamine-B from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 168(2), 1070–1081 (2009)
Deshpande, A.V.; Kumar, U.: Effect of method of preparation on photophysical properties of Rh-B impregnated sol-gel hosts. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 306(2), 149–159 (2002)
Arivoli, S.; Henkuzhali, M.: Kinetic, mechanistic, thermodynamic and equilibrium studies on the adsorption of Rhodamine B by acid activated low cost carbon. J. Chem. 5(2), 187–200 (2008)
Wang, Z.; Shen, D.; Shen, F.; Wu, C.; Gu, S.: Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics studies on biosorption of Rhodamine B from aqueous solution by earthworm manure derived biochar. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 120, 104–114 (2017)
Kooh, M.R.R.; Lim, L.B.L.; Lim, L.H.; Dahri, M.K.: Separation of toxic rhodamine B from aqueous solution using an efficient low-cost material, Azolla pinnata, by adsorption method. Environ. Monit. Assess. 188(2), 108 (2016)
Kooh, M.R.R.; Dahri, M.K.; Lim, L.B.L.: The removal of rhodamine B dye from aqueous solution using Casuarina equisetifolia needles as adsorbent. Cogent Environ. Sci. 2(1), 1140553 (2016)
Walia, T.P.S.; Kansal, I.: Removal of Rhodamine-B by adsorption on walnut shell charcoal. J. Surf. Sci. Technol. 24(3–4), 179–193 (2008)
Hu, Y.; Guo, T.; Ye, X.; Li, Q.; Guo, M.; Liu, H.; Wu, Z.: Dye adsorption by resins: effect of ionic strength on hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions. Chem. Eng. J. 228, 392–397 (2013)
Langmuir, I.: The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Part I. Solids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 38(11), 2221–2295 (1916)
Freundlich, H.M.F.: Over the adsorption in solution. J. Phys. Chem. 57(385471), 1100–1107 (1906)
Temkin, M.I.; Pyzhev, V.: Kinetics of ammonia synthesis on promoted iron catalysts. Acta Physiochim. URSS 12(3), 217–222 (1940)
Redlich, O.J.P.; Peterson, D.L.: A useful adsorption isotherm. J. Phys. Chem. 63(6), 1024–1024 (1959)
Sips, R.: On the structure of a catalyst surface. J. Chem. Phys. 16(5), 490–495 (1948)
Sharma, S.; Imran, A.: Adsorption of Rhodamine B dye from aqueous solution onto acid activated mango (Mangifera indica) leaf powder: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 3(10), 286–297 (2011)
Prasad, A.L.; Santhi, T.: Adsorption of hazardous cationic dyes from aqueous solution onto Acacia nilotica leaves as an eco friendly adsorbent. Sustain. Environ. Res. 22(2), 113–122 (2012)
Hossain, M.A.; Alam, M.S.: Adsorption kinetics of Rhodamine-B on used black tea leaves. Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 9(1), 2 (2012)
Kooh, M.R.R.; Dahri, M.K.; Lim, L.B.L.: Jackfruit seed as a sustainable adsorbent for the removal of Rhodamine B dye. J. Environ. Biotechnol. Res. 4(1), 7–16 (2016)
Khan, T.A.; Dahiya, S.; Ali, I.: Use of kaolinite as adsorbent: equilibrium, dynamics and thermodynamic studies on the adsorption of Rhodamine B from aqueous solution. Appl. Clay Sci. 69, 58–66 (2012)
El Haddad, M.; Mamouni, R.; Saffaj, N.: Adsorptive removal of basic dye rhodamine B from aqueous media onto animal bone meal as new low cost adsorbent. Glob. J. Hum. Soc. Sci. Res. 12(10-B) (2012)
Shah, J.; Jan, M.R.; Haq, A.; Khan, Y.: Removal of Rhodamine B from aqueous solutions and wastewater by walnut shells: kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics studies. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 7(4), 428–436 (2013)
Liu, K.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Gou, X.; Duan, Y.: Adsorption and removal of rhodamine B from aqueous solution by tannic acid functionalized graphene. Coll. Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 477, 35–41 (2015)
Qi, Z.-P.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, Z.-R.; Kong, Q.; Chen, Q.-F.; Zhao, C.-S.; Liu, Y.-Z.; Miao, M.-S.; Wang, C.: Rhodamine B removal from aqueous solutions using loofah sponge and activated carbon prepared from loofah sponge. Desalin. Water Treat. 57(60), 29421–29433 (2016)
Mohammed, M.I.; Baytak, S.: Synthesis of bentonite-carbon nanotube nanocomposite and its adsorption of Rhodamine dye from water. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 41(12), 4775–4785 (2016)
Postai, D.L.; Demarchi, C.A.; Zanatta, F.; Melo, D.C.C.; Rodrigues, C.A.: Adsorption of rhodamine B and methylene blue dyes using waste of seeds of Aleurites Moluccana, a low cost adsorbent. Alex. Eng. J. 55(2), 1713–1723 (2016)
Selvam, P.P.; Preethi, S.; Basakaralingam, P.; Thinakaran, N.; Sivasamy, A.; Sivanesan, S.: Removal of rhodamine B from aqueous solution by adsorption onto sodium montmorillonite. J. Hazard. Mater. 155(1), 39–44 (2008)
Kumar, V.; Kaith, B.S.; Jindal, R.: Synthesis of hybrid ion exchanger for rhodamine B dye removal: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 55(39), 10492–10499 (2016)
Postai, D.L.; Rodrigues, C.A.: Adsorption of cationic dyes using waste from fruits of Eugenia umbelliflora Berg (Myrtaceae). Arab. J. Sci. Eng. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2819-1
Lagergren, S.: Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption geloster stoffe. Kungliga Sven. Vetenskapsakademiens Handl. 24, 1–39 (1898)
Ho, Y.-S.; McKay, G.: Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 34(5), 451–465 (1999)
Febrianto, J.; Kosasih, A.N.; Sunarso, J.; Ju, Y.-H.; Indraswati, N.; Ismadji, S.: Equilibrium and kinetic studies in adsorption of heavy metals using biosorbent: a summary of recent studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 162(2), 616–645 (2009)
Attallah, O.A.; Al-Ghobashy, M.A.; Nebsen, M.; Salem, M.Y.: Removal of cationic and anionic dyes from aqueous solution with magnetite/pectin and magnetite/silica/pectin hybrid nanocomposites: kinetic, isotherm and mechanism analysis. RSC Adv. 6(14), 11461–11480 (2016)
Plazinski, W.; Rudzinski, W.; Plazinska, A.: Theoretical models of sorption kinetics including a surface reaction mechanism: a review. Adv. Coll. Interface Sci. 152(1), 2–13 (2009)
Saha, P.; Chowdhury, S.: Insight Into adsorption thermodynamics. In: Tadashi, M. (ed.) Thermodynamics. InTech. https://doi.org/10.5772/13474 (2011)
Hayeeye, F.; Sattar, M.; Chinpa, W.; Sirichote, O.: Kinetics and thermodynamics of Rhodamine B adsorption by gelatin/activated carbon composite beads. Coll. Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 513, 259–266 (2017)
Akar, E.; Altinişik, A.; Seki, Y.: Using of activated carbon produced from spent tea leaves for the removal of malachite green from aqueous solution. Ecol. Eng. 52, 19–27 (2013)
Altınışık, A.; Gür, E.; Seki, Y.: A natural sorbent, Luffa cylindrica for the removal of a model basic dye. J. Hazard. Mater. 179(1), 658–664 (2010)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Government of Negara Brunei Darussalam and the Universiti Brunei Darussalam for the PhD scholarship support for Nur Afiqah Hazirah Mohamad Zaidi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohamad Zaidi, N.A.H., Lim, L.B.L., Priyantha, N. et al. Artocarpus odoratissimus Leaves as an Eco-friendly Adsorbent for the Removal of Toxic Rhodamine B Dye in Aqueous Solution: Equilibrium Isotherm, Kinetics, Thermodynamics and Regeneration Studies. Arab J Sci Eng 43, 6011–6020 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3228-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3228-9