Abstract
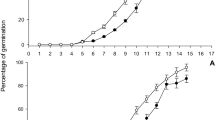
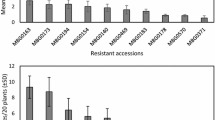
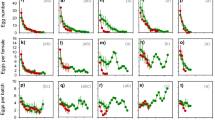
The planthoppers Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) and Sogatella furcifera (Horváth) co-occur on rice Oryza sativa L., throughout much of Asia. Nilaparvata lugens is regarded as the more destructive rice pest. Interactions between these two species on individual rice plants can be positive (interspecific facilitation) or negative (interspecific competition). However, the outcome of their interactions on resistant rice varieties has received little attention despite the potential consequences for adaptation to resistance. In this study, we examine interactions between nymphs of these two species on resistant (IR62 and ADR52) and susceptible (IR22) rice varieties. IR62 was resistant to N. lugens at all plant ages, but only older plants were resistant to S. furcifera. ADR52 was resistant to S. furcifera, and gained moderate resistance to N. lugens as the plants aged. Nilaparvata lugens facilitated weight gain in S. furcifera even on the resistant IR62 variety. However, facilitation by N. lugens was reduced on older ADR52 plants when resistance against S. furcifera was strongest. Sogatella furcifera reduced weight gain in N. lugens on susceptible varieties, but failed to out-compete N. lugens where plants expressed S. furcifera-resistance. Our preliminary results indicate that competition from S. furcifera could slow adaptation by N. lugens to resistant rice varieties. Facilitation by N. lugens of S. furcifera on resistant rice, which is expected to increase adaptation rates in the latter species, likely depends on the relative strengths of resistance against both planthoppers.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bottrell DG, Schoenly KG (2012) Resurrecting the ghost of green revolutions past: the brown planthopper as a recurring threat to high-yielding rice production in tropical Asia. J Asia-Pac Entomol 15:122–140
Cao T-T, Backus EA, Lou Y-G, Cheng J-A (2013a) Feeding-induced interactions between Nilaparvata lugens and Laodelphax striatellus (Hemiptera: Delphacidae): effects on feeding behavior and honeydew excretion. Environ Entomol 42:987–997
Cao T-T, Lü J, Lou Y-G, Cheng J-A (2013b) Feeding-induced interactions between two rice planthoppers Nilaparvata lugens and Sogatella furcifera (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) effects on feeding and honeydew excretion. Environ Entomol 42:1281–1291
Cheng J, Zhao W, Lou Y, Zhu Z (2001) Intra- and inter-specific effects of the brown planthopper and white backed planthopper on their population performance. J Asia-Pac Entomol 4:85–92
Crisol E, Almazan MLP, Jones PW, Horgan FG (2013) Planthopper–rice interactions: unequal stresses on pure-line and hybrid rice under similar experimental conditions. Entomol Exp Appl 147:18–32
Denno RF, Kaplan I (2007) Plant-mediated interactions in herbivorous insects: mechanisms, symmetry, and challenging the paradigms of competition past. In: Ohgushi T, Craig TP, Price PW (eds) Ecological communities: plant mediation in indirect interaction webs. Cambridge University Press, London, pp 19–50
Denno RF, Mcclure MS, Ott JR (1995) Interspecific interactions in phytophagous insects: competition reexamined and resurrected. Annu Rev Entomol 40:297–331
Fujita D, Kohli A, Horgan FG (2013) Rice resistance to planthoppers and leafhoppers. Crit Rev Plant Sci 32:162–191
Gomi K, Satoh M, Ozawa R, Shinonaga Y, Sanada S, Sasaki K, Matsumura M, Ohashi Y, Kanno H, Akimitsu K, Takabayashi J (2010) Role of hydroperoxide lyase in white-backed planthopper (Sogatella furcifera Horváth)-induced resistance to bacterial blight in rice, Oryza sativa L. Plant J 61:46–57
GRiSP (Global Rice Science Partnership) (2013) Rice almanac, 4th edn. International Rice Research Institute, Los Baños, p 283
Hernandez JE, Khush GS (1981) Genetics of resistance to white backed planthopper in some rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties. Oryza 18:44–50
Horgan FG (2012) Diversity and defense: plant-herbivore interactions at multiple scales and trophic level. In: Gurr GM, Wratten SD, Snyder WE, Read DMY (eds) Biodiversity and insect pests: key issues for sustainable management. Wiley-Blackwell, Oxford, pp 241–258
Horgan FG, Crisol E (2013) Hybrid rice and insect herbivores in Asia. Entomol Exp Appl 148:1–19
Horgan FG, Ramal AF, Bentur JS, Kumar R, Bhanu KV, Sarao PS, Iswanto EH, Chien HV, Phyu MH, Bernal CC, Almazan MLP, Alam MZ, Lu Z, Huang SH (2015) Virulence of brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens) populations from South and South East Asia against resistant rice varieties. Crop Prot 78:222–231
Jairin J, Phengrat K, Teangdeerith S, Vanavichit A, Toojinda T (2007) Mapping of a broad-spectrum brown planthopper resistance gene, Bph3, on rice chromosome 6. Mol Breed 19:35–44
Kartohardjono A, Heinrichs EA (1984) Populations of the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) (Homoptera: Delphacidae), and its predators on rice varieties with different levels of resistance. Environ Entomol 13:359–365
Kenmore PE, Cariño FO, Perez CA, Dyck VA, Gutierrez AP (1984) Population regulation of the rice brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) within rice fields in the Philippines. J Plant Prot 1:19–37
Khush GS, Virk PS (2005) IR varieties and their impact. International Rice Research Institute, Los Baños, p 163
Matsumura M, Suzuki Y (2003) Direct and feeding-induced interactions between two rice planthoppers, Sogatella furcifera and Nilaparvata lugens: effects on dispersal capacity and performance. Ecol Entomol 28:174–182
Messina FJ, Sorenson SM (2001) Effectiveness of lacewing larvae in reducing Russian wheat aphid populations on susceptible and resistant wheat. Biol Control 21:19–26
Moran NA, Whitham TG (1990) Interspecific competition between root-feeding and leaf-galling aphids mediated by host-plant resistance. Ecology 71:1050–1058
Myint KKM, Yasui H, Takagi M, Matsumura M (2009) Virulence of long-term laboratory populations of the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål), and whitebacked planthopper, Sogatella furcifera (Horváth) (Homoptera: Delphacidae), on rice differential varieties. Appl Entomol Zool 44:149–153
Myint KKM, Fujita D, Matsumura M, Sonoda T, Yoshimura A, Yasui H (2012) Mapping and pyramiding of two major genes for resistance to the brown planthopper [Nilaparvata lugens (Stål)] in the rice cultivar ADR52. Theor Appl Genet 124:495–504
Ojala K, Julkunen-Tiitto R, Lindstrom L, Mappes J (2005) Diet affects the immune defence and life-history traits of an arctiid moth Parasemia plantaginis. Evol Ecol Res 7:1153–1170
Peñalver Cruz A (2014) Interactions between crop management and rice resistance to the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål.): fertilizer levels, insecticides, biocontrol and the integrity of resistance. Ph.D. thesis, Lancaster University, pp 13–36
Peñalver Cruz A, Arida A, Heong KL, Horgan FG (2011) Aspects of brown planthopper adaptation to resistant rice varieties with the Bph3 gene. Entomol Exp Appl 141:245–257
Rubia-Sanchez EG, Heong KL (1989) Vertical distribution of two hopper species on rice plants. Int Rice Res Notes 14:6
Rubia-Sanchez EG, Suzuki Y, Arimura K, Miyamoto K, Matsumura M, Watanabe T (2003) Comparing Nilaparvata lugens (Stâl) and Sogatella furcifera (Horvath) (Homoptera: Delphacidae) feeding effects on rice plant growth processes at the vegetative stage. Crop Prot 22:967–974
Satoh M, Gomi K, Matsumura M, Takabayashi J, Sasaki K, Ohashi Y, Kanno H (2009) White backed planthopper-induced disease resistance in rice. In: Heong KL, Hardy B (eds) Planthoppers: new threats to the sustainability of intensive rice production systems in Asia. International Rice Research Institute, Los Baños, pp 327–339
Sidhu GS, Khush GS (1978) Genetic analysis of brown planthopper resistance in 20 varieties of rice Oryza sativa L. Theor Appl Genet 53:199–203
Srinivasan TS, Almazan MLP, Fujita D, Ramal AF, Yasui H, Subbarayalu MK, Horgan FG (2015) Current utility of the BPH25 and BPH26 genes and possibilities for further resistance against plant- and leafhoppers from the donor cultivar ADR52. Appl Entomol Zool (in press)
Widawsky D, Rozelle S, Jin S, Huang J (1998) Pesticide productivity, host-plant resistance and productivity in China. Agri Econ 19:203–217
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Arizza Arida, Ellen Genil, Alberto Naredo, Reyuel Quintana, and Vincent Vertudes for help and advice during the experiments. We thank three anonymous reviewers for helpful comments on the manuscript. Funding for this research was provided by the Global Rice Science Partnership (GRiSP); TSS was funded through a Global Rice Science Scholarship (GRiSS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srinivasan, T.S., Almazan, M.L.P., Bernal, C.C. et al. Interactions between nymphs of Nilaparvata lugens and Sogatella furcifera (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) on resistant and susceptible rice varieties. Appl Entomol Zool 51, 81–90 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-015-0373-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-015-0373-4