Abstract
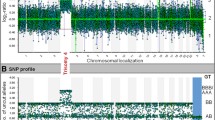
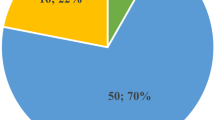
It is estimated that 10–15 % of all clinically recognised pregnancies results in a miscarriage, most of which occur during the first trimester. Large-scale chromosomal abnormalities have been found in up to 50 % of first-trimester spontaneous abortions and, for several decades, standard cytogenetic analysis has been used for their identification. Recent studies have proven that array comparative genomic hybridisation (array-CGH) is a useful tool for the detection of genome imbalances in miscarriages, showing a higher resolution, a significantly higher detection rate and overcoming problems of culture failures, maternal contamination and poor chromosome morphology. In this study, we investigated the possibility that submicroscopic chromosomal changes, not detectable by conventional cytogenetic analysis, exist in euploid miscarriages and could be causative for the spontaneous abortion. We analysed with array-CGH technology 40 foetal tissue samples derived by first-trimester miscarriages with a normal karyotype. A whole-genome microarray with a 100-Kb resolution was used for the analysis. Forty-five copy number variants (CNVs), ranging in size between 120 Kb and 4.3 Mb, were identified in 31 samples (24 gains and 21 losses). Ten samples (10/31, 32 %) have more than one CNV. Thirty-one CNVs (68 %) were defined as common CNVs and 14 were classified as unique. Six genes and five microRNAs contained within these CNVs will be discussed. This study shows that array-CGH is useful for detecting submicroscopic CNVs and identifying candidate genes which could account for euploid miscarriages.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams RH, Porras A, Alonso G, Jones M, Vintersten K, Panelli S, Valladares A, Perez L, Klein R, Nebreda AR (2000) Essential role of p38alpha MAP kinase in placental but not embryonic cardiovascular development. Mol Cell 6:109–116
Bell KA, Van Deerlin PG, Haddad BR, Feinberg RF (1999) Cytogenetic diagnosis of “normal 46,XX” karyotypes in spontaneous abortions frequently may be misleading. Fertil Steril 71:334–341
Benkhalifa M, Kasakyan S, Clement P, Baldi M, Tachdjian G, Demirol A, Gurgan T, Fiorentino F, Mohammed M, Qumsiyeh MB (2005) Array comparative genomic hybridization profiling of first-trimester spontaneous abortions that fail to grow in vitro. Prenat Diagn 25:894–900
Cross JC, Baczyk D, Dobric N, Hemberger M, Hughes M, Simmons DG, Yamamoto H, Kingdom JC (2003) Genes, development and evolution of the placenta. Placenta 24:123–130
Dodd IB, Micheelsen MA, Sneppen K, Thon G (2007) Theoretical analysis of epigenetic cell memory by nucleosome modification. Cell 129:813–822
Dória S, Carvalho F, Ramalho C, Lima V, Francisco T, Machado AP, Brandão O, Sousa M, Matias A, Barros A (2009) An efficient protocol for the detection of chromosomal abnormalities in spontaneous miscarriages or foetal deaths. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 147:144–150
Fox AH, Lamond AI (2010) Paraspeckles. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2:1–14
Freiberg RA, Hammond EM, Dorie MJ, Welford SM, Giaccia AJ (2006) DNA damage during reoxygenation elicits a Chk2-dependent checkpoint response. Mol Cell Biol 26:1598–1609
Gasa R, Mrejen C, Leachman N, Otten M, Barnes M, Wang J, Chakrabarti S, Mirmira R, German M (2004) Proendocrine genes coordinate the pancreatic islet differentiation program in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101:13245–13250
Gheorghe CP, Goyal R, Mittal A, Longo LD (2010) Gene expression in the placenta: maternal stress and epigenetic responses. Int J Dev Biol 54:507–523
Goddijn M, Leschot NJ (2000) Genetic aspects of miscarriage. Baillieres Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol 14:855–865
Hassold T, Chen N, Funkhouser J, Jooss T, Manuel B, Matsuura J, Matsuyama A, Wilson C, Yamane JA, Jacobs PA (1980) A cytogenetic study of 1000 spontaneous abortions. Ann Hum Genet 44:151–178
Hemberger M (2007) Epigenetic landscape required for placental development. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:2422–2436
Henrichsen CN, Chaignat E, Reymond A (2009) Copy number variants, diseases and gene expression. Hum Mol Genet 18:R1–R8
Jacobs PA, Hassold TJ (1995) The origin of numerical chromosome abnormalities. Adv Genet 33:101–133
Kamei T, Jones SR, Chapman BM, McGonigle KL, Dai G, Soares MJ (2002) The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway modulates the endocrine differentiation of trophoblast cells. Mol Endocrinol 16:1469–1481
Klose RJ, Kallin EM, Zhang Y (2006) JmjC-domain-containing proteins and histone demethylation. Nat Rev Genet 7:715–727
Lomax B, Tang S, Separovic E, Phillips D, Hillard E, Thomson T, Kalousek DK (2000) Comparative genomic hybridization in combination with flow cytometry improves results of cytogenetic analysis of spontaneous abortions. Am J Hum Genet 66:1516–1521
Lujambio A, Ropero S, Ballestar E, Fraga MF, Cerrato C, Setién F, Casado S, Suarez-Gauthier A, Sanchez-Cespedes M, Git A, Spiteri I, Das PP, Caldas C, Miska E, Esteller M (2007) Genetic unmasking of an epigenetically silenced microRNA in human cancer cells. Cancer Res 67:1424–1429
Menasha J, Levy B, Hirschhorn K, Kardon NB (2005) Incidence and spectrum of chromosome abnormalities in spontaneous abortions: new insights from a 12-year study. Genet Med 7:251–263
Menten B, Swerts K, Delle Chiaie B, Janssens S, Buysse K, Philippé J, Speleman F (2009) Array comparative genomic hybridization and flow cytometry analysis of spontaneous abortions and mors in utero samples. BMC Med Genet 10:89–93
Perry GH, Ben-Dor A, Tsalenko A, Sampas N, Rodriguez-Revenga L, Tran CW, Scheffer A, Steinfeld I, Tsang P, Yamada NA, Park HS, Kim JI, Seo JS, Yakhini Z, Laderman S, Bruhn L, Lee C (2008) The fine-scale and complex architecture of human copy-number variation. Am J Hum Genet 82:685–695
Philipp T, Philipp K, Reiner A, Beer F, Kalousek DK (2003) Embryoscopic and cytogenetic analysis of 233 missed abortions: factors involved in the pathogenesis of developmental defects of early failed pregnancies. Hum Reprod 18:1724–1732
Rajcan-Separovic E, Diego-Alvarez D, Robinson WP, Tyson C, Qiao Y, Harvard C, Fawcett C, Kalousek D, Philipp T, Somerville MJ, Stephenson MD (2010a) Identification of copy number variants in miscarriages from couples with idiopathic recurrent pregnancy loss. Hum Reprod 25:2913–2922
Rajcan-Separovic E, Qiao Y, Tyson C, Harvard C, Fawcett C, Kalousek D, Stephenson M, Philipp T (2010b) Genomic changes detected by array CGH in human embryos with developmental defects. Mol Hum Reprod 16:125–134
Robberecht C, Schuddinck V, Fryns JP, Vermeesch JR (2009) Diagnosis of miscarriages by molecular karyotyping: benefits and pitfalls. Genet Med 11:646–654
Saito Y, Liang G, Egger G, Friedman JM, Chuang JC, Coetzee GA, Jones PA (2006) Specific activation of microRNA-127 with downregulation of the proto-oncogene BCL6 by chromatin-modifying drugs in human cancer cells. Cancer Cell 9:435–443
Schaeffer AJ, Chung J, Heretis K, Wong A, Ledbetter DH, Lese Martin C (2004) Comparative genomic hybridization-array analysis enhances the detection of aneuploidies and submicroscopic imbalances in spontaneous miscarriages. Am J Hum Genet 74:1168–1174
Shimokawa O, Harada N, Miyake N, Satoh K, Mizuguchi T, Niikawa N, Matsumoto N (2006) Array comparative genomic hybridization analysis in first-trimester spontaneous abortions with ‘normal’ karyotypes. Am J Med Genet A 140:1931–1935
Zhang YX, Zhang YP, Gu Y, Guan FJ, Li SL, Xie JS, Shen Y, Wu BL, Ju W, Jenkins EC, Brown WT, Zhong N (2009) Genetic analysis of first-trimester miscarriages with a combination of cytogenetic karyotyping, microsatellite genotyping and arrayCGH. Clin Genet 75:133–140
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Galliera Genetic Bank of Galliera Hospital—Network of Telethon Genetic Biobanks (project GTB07001) for the conservation of samples.
Funding
This work was funded by the Scientific Committee of E.O. Ospedali Galliera, Genova, Italy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Viaggi, C.D., Cavani, S., Malacarne, M. et al. First-trimester euploid miscarriages analysed by array-CGH. J Appl Genetics 54, 353–359 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-013-0157-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-013-0157-x