Abstract
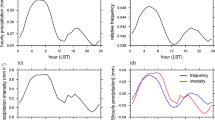
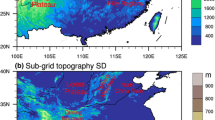
Based on the high-density hourly rain-gauge data from 265 stations over the Qilian Mountains in Northwest China, climatic mean diurnal variations of summer rainfall over different topographies of this area are investigated. Influences of the gauge elevations on the diurnal variation of rainfall are also revealed. Distinct regional features of diurnal variations in rainfall are observed over the Qilian Mountains. Rainfall over the Qinghai Lake areas shows a single nocturnal peak. A dominant, late-afternoon peak of rainfall occurs over the mountain tops. Over the northeastern and southeastern slopes, a dominant diurnal peak appears in the late afternoon, and an evident second peak is found in the early morning, respectively. The strengths of the early-morning peaks in the rainfall frequency are closely related to the rainfall events with different durations over the two slopes. The early-morning peak is dominant across plains with low elevations. From the mountain tops to the plains, the diurnal peaks of rainfall gradually vary from the dominant late-afternoon peak to the dominant early-morning peak with the enhanced early-morning peak in concurrent with the decreasing gauge elevation over the northeastern and southeastern slopes. Further examination indicates that the rainfall at higher elevations over the northeastern and southeastern slopes occurs more readily in the afternoon, compared to the lower elevations. This phenomenon corresponds to the result that the proportion of the rainfall frequency occurring during the early-morning period decreases with increasing elevations over the two slopes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barros, A. P., and T. J. Lang, 2003: Monitoring the monsoon in the Himalayas: Observations in central Nepal, June 2001. Mon. Wea. Rev., 131: 1408–1427, doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(2003) 131<1408:MTMITH>2.0.CO;2.
Basist, A., G. D. Bell, and V. Meentemeyer, 1994: Statistical relationships between topography and precipitation patterns. J. Climate, 7: 1305–1315, doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(1994)007< 1305:SRBTAP>2.0.CO;2.
Bonacina, L. C. W., R. M. Poulter, S. E. Ashmore, et al., 1945: Orographic rainfall and its place in the hydrology of the globe. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 71: 41–55, doi: 10.1002/qj.49707130705.
Burbank, D. W., A. E. Blythe, J. Putkonen, et al., 2003: Decoupling of erosion and precipitation in the Himalayas. Nature, 426: 652–655, doi: 10.1038/nature02187.
Chen, H. M., W. H. Yuan, J. Li, et al., 2012: A possible cause for different diurnal variations of warm season rainfall as shown in station observations and TRMM 3B42 data over the southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 29: 193–200, doi: 10.1007/s00376-011-0218-1.
Ding, X. R., 2003: Water increasing effect of mountains and its value of water resources. J. Mountain Res., 21: 681–685, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2003.06.007. (in Chinese)
Fujinami H., S. Nomura, and T. Yasunari, 2005: Characteristics of diurnal variations in convection and precipitation over the southern Tibetan Plateau during summer. SOLA, 1: 49–52, doi: 10.2151/sola.2005-014.
Gou, X., F. Chen, M. Yang, et al., 2005: Climatic response of thick leaf spruce (Piceacrassifolia) tree-ring width at different elevations over Qilian Mountains, northwestern China. J. Arid Environ., 61: 513–524, doi: 10.1016/j.jaridenv.2004.09.011.
Jia, W. X., Y. S. Zhang, and Z. X. Li, 2014: Spatial and temporal change of rainfall extremes in Qilian Mountains and Hexi Corridor in recent 50 years. Scientia Geogra. Sinica, 34: 1002–1009, doi: 10.11821/xb201205006. (in Chinese)
Li, J., T. R. Chen, and N. N. Li, 2017: Diurnal variation of summer precipitation across the central Tianshan Mountains. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol., 56: 1537–1550, doi: 10.1175/JAMC-D-16-0265.1.
Li, X., Q. Zhang, and C. Y. Xu, 2014: Assessing the performance of satellite-based precipitation products and its dependence on topography over Poyang Lake basin. Theor. Appl. Climatol., 115: 713–729, doi: 10.1007/s00704-013-0917-x.
Li, Y. Y., Q. Zhang, X. Xu, et al., 2010: Relationship between precipitation and terrain over the Qilian Mountains and their ambient areas. J. Glaciol. Geocryol., 32: 52–61. (in Chinese)
Liang, H., J. M. Liu, and Y. Chen, 2010: Characteristics and cause of diurnal variation of precipitable water vapor derived from ground-based GPS in Qilian Mountains in summer. Plateau Meteor., 29: 726–736. (in Chinese)
Liu, X. M., M. J. Zhang, S. J. Wang, et al., 2016: Diurnal variation of summer precipitation and its influencing factors over the Qilian Mountains during 2008–2014. Acta Geogra. Sinica, 71: 754–767, doi: 10.11821/dlxb201605005. (in Chinese)
Prudhomme, C., and D. W. Reed, 1999: Mapping extreme rainfall in a mountainous region using geostatistical techniques: A case study in Scotland. Int. J. Climatol., 19: 1337–1356, doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0088(199910)19:12<1337:AID-JOC421> 3.0.CO;2-G.
Qian, J. H., A. W. Robertson, and V. Moron, 2010: Interactions among ENSO, the monsoon, and diurnal cycle in rainfall variability over Java, Indonesia. J. Atmos. Sci., 67: 3509–3524, doi: 10.1175/2010JAS3348.1.
Singh, P., and K. Nakamura, 2009: Diurnal variation in summer precipitation over the central Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 114, D20107, doi: 10.1029/2009JD011788.
Weisse, A. K., and P. Bois, 2001: Topographic effects on statistical characteristics of heavy rainfall and mapping in the French Alps. J. Appl. Meteor., 40: 720–740, doi: 10.1175/15 20-0450(2001)040<0720:TEOSCO>2.0.CO;2.
Yin, X. Z., Q. Zhang, Q. Y. Xu, et al., 2009: Characteristics of climate change in Qilian Mountains region in recent 50 years. Plateau Meteor., 28: 85–90. (in Chinese)
Yu, R. C., and J. Li, 2016: Regional characteristics of diurnal peak phases of precipitation over contiguous China. Acta Meteor. Sinica, 74: 18–30, doi: 10.11676/qxxb2016.011. (in Chinese)
Yu, R. C., Y. P. Xu, T. J. Zhou, et al., 2007: Relation between rainfall duration and diurnal variation in the warm season precipitation over central eastern China. Geophys. Res. Lett., 34, L13703, doi: 10.1029/2007GL030315.
Zhang, J., and D. L. Li, 2004: Analysis on distribution characteristics of rainfall over the Qilian Mountain and Heihe Valley. Plateau Meteor., 23: 81–88, doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0534. 2004.01.012. (in Chinese)
Zhang, L., Q. Zhang, J. Y. Feng, et al., 2014: A study of atmospheric water cycle over the Qilian Mountains (I): Variation of annual water vapor transport. J. Glaciol. Geocryol., 36: 1079–1091, doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0240.2014.0130. (in Chinese)
Zhou, T. J., R. C. Yu, H. M. Chen, et al., 2008: Summer precipitation frequency, intensity, and diurnal cycle over China: A comparison of satellite data with raingauge observations. J. Climate, 21: 3997–4010, doi: 10.1175/2008JCLI2028.1.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the Editor and the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and valuable suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41675075, 91637210, and 41375004).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Li, J., Chen, H. et al. Diurnal Variations of Summer Precipitation over the Qilian Mountains in Northwest China. J Meteorol Res 33, 18–30 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-019-8103-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-019-8103-4