Abstract
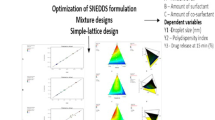
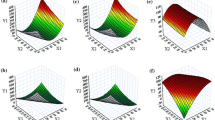
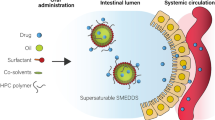
The work describes systematic development of nanomicellar cationic supersaturable self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (CS-SNEDDS) for augmenting oral biopharmaceutical performance of raloxifene hydrochloride. Plain SNEDDS formulation containing Capryol 90, Cremophor RH 40, and Transcutol HP was optimized using D-optimal mixture design. SNEDDS were characterized for emulsification time, globule size, in vitro drug release, and ex vivo permeation. The CS-SNEDDS formulation was prepared from the optimized SNEDDS by adding oleylamine as the cationic charge inducer and HPMC as the polymeric precipitation inhibitor. Evaluation of CS-SNEDDS was carried out through in vitro cell line studies on Caco-2 and MCF-7 cells, in situ perfusion, and in vivo pharmacokinetic studies, which indicated significant improvement in biopharmaceutical attributes of the drug from CS-SNEDDS over plain drug.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singh B, Garg B, Chaturvedi SC, Arora S, Mandsaurwale R, Kapil R, et al. Formulation development of gastroretentive tablets of lamivudine using the floating-bioadhesive potential of optimized polymer blends. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2012;64:654–69.
Gupta H, Bhandari D, Sharma A. Recent trends in oral drug delivery: a review. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2009;3:162–73.
Thanki K, Gangwal RP, Sangamwar AT, Jain S. Oral delivery of anticancer drugs: challenges and opportunities. J Control Release. 2013;170:15–40.
Mazzaferro S, Bouchemal K, Ponchel G. Oral delivery of anticancer drugs I: general considerations. Drug Discov Today. 2012;18:25–34.
Stuurman FE, Nuijen B, Beijnen JH, Schellens JHM. Oral anticancer drugs: mechanisms of low bioavailability and strategies for improvement. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2013;52:399–414.
Lee WL, Chao HT, Cheng MH, Wang PH. Rationale for using raloxifene to prevent both osteoporosis and breast cancer in postmenopausal women. Maturitas. 2008;60:92–107.
Snyder KR, Sparano N, Malinowski JM. Raloxifene hydrochloride. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2000;57:1669–75. quiz 1676-8
Heringa M. Review on raloxifene: profile of a selective estrogen receptor modulator. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2003;41:331–45.
Chen Y, Jia X, Chen J, Wang J, Hu M. The pharmacokinetics of raloxifene and its interaction with apigenin in rat. Molecules. 2010;15:8478–87.
Tran TH, Poudel BK, Marasini N, Chi SC, Choi HG, Yong CS, et al. Preparation and evaluation of raloxifene-loaded solid dispersion nanoparticle by spray-drying technique without an organic solvent. Int J Pharm. 2013;443:50–7.
Tran TH, Poudel BK, Marasini N, Woo JS, Choi HG, Yong CS, et al. Development of raloxifene-solid dispersion with improved oral bioavailability via spray-drying technique. Arch Pharm Res. 2013;36:86–93.
Wempe MF, Wacher VJ, Ruble KM, Ramsey MG, Edgar KJ, Buchanan NL, et al. Pharmacokinetics of raloxifene in male Wistar-Hannover rats: influence of complexation with hydroxybutenyl-beta-cyclodextrin. Int J Pharm. 2008;346:25–37.
Jha RK, Tiwari S, Mishra B. Bioadhesive microspheres for bioavailability enhancement of raloxifene hydrochloride: formulation and pharmacokinetic evaluation. AAPS Pharm SciTech. 2011;12:650–7.
Jagadish B, Yelchuri R, K B, et al. Enhanced dissolution and bioavailability of raloxifene hydrochloride by co-grinding with different superdisintegrants. Chem Pharm Bull. 2010;58:293–300.
Fontana MC, Beckenkamp A, Buffon A, Beck RC. Controlled release of raloxifene by nanoencapsulation: effect on in vitro antiproliferative activity of human breast cancer cells. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014;9:2979–91.
Kushwaha AK, Vuddanda PR, Karunanidhi P, et al. Development and evaluation of solid lipid nanoparticles of raloxifene hydrochloride for enhanced bioavailability. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:584549.
Tran TH, Ramasamy T, Cho HJ, Kim YII, Poudel BK, Choi HG, et al. Formulation and optimization of raloxifene-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles to enhance oral bioavailability. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2014;14:4820–31.
Singh B, Bandopadhyay S, Kapil R, Singh R, Katare O. Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS): formulation development, characterization, and applications. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 2009;26:427–521.
Porter CJ, Trevaskis NL, Charman WN. Lipids and lipid-based formulations: optimizing the oral delivery of lipophilic drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2007;6:231–48.
Kohli K, Chopra S, Dhar D, Arora S, Khar RK. Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems: an approach to enhance oral bioavailability. Drug Discov Today. 2010;15:958–65.
Singh B, Beg S, Khurana RK, Sandhu PS, Kaur R, Katare OP. Recent advances in self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS). Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 2014;31:121–85.
Gao P, Morozowich W. Development of supersaturatable self-emulsifying drug delivery system formulations for improving the oral absorption of poorly soluble drugs. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2006;3:97–110.
Mathews CDC, Sugano K. Supersaturable formulations. Drug Deliv Systems. 2010;25:371–4.
Brouwers J, Brewster ME, Augustijns P. Supersaturating drug delivery systems: the answer to solubility-limited oral bioavailability? J Pharm Sci. 2009;98:2549–72.
Elsheikh MA, Elnaggar YS, Gohar EY, Abdallah OY. Nanoemulsion liquid preconcentrates for raloxifene hydrochloride: optimization and in vivo appraisal. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:3787–802.
Singh B, Singh R, Bandyopadhyay S, Kapil R, Garg B. Optimized nanoemulsifying systems with enhanced bioavailability of carvedilol. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2013;101:465–74.
Beg S, Jena SS, Patra Ch N, et al. Development of solid self-nanoemulsifying granules (SSNEGs) of ondansetron hydrochloride with enhanced bioavailability potential. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2013;101:414–23.
Singh B, Kaur T, Singh S. Correction of raw dissolution data for loss of drug during sampling. Ind J Pharm Sci. 1997;59:196–9.
Gao P, Rush BD, Pfund WP, Huang T, Bauer JM, Morozowich W, et al. Development of a supersaturable SEDDS (S-SEDDS) formulation of paclitaxel with improved oral bioavailability. J Pharm Sci. 2003;92:2386–98.
Klein S. The use of biorelevant dissolution media to forecast the in vivo performance of a drug. AAPS J. 2010;12:397–406.
Jain AK, Thanki K, Jain S. Solidified self-nanoemulsifying formulation for oral delivery of combinatorial therapeutic regimen: part I. Formulation development, statistical optimization, and in vitro characterization. Pharm Res. 2013;31:923–45.
Beg S, Sharma G, Thanki K, Jain S, Katare OP, Singh B. Positively charged self-nanoemulsifying oily formulations of olmesartan medoxomil: systematic development, in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo evaluation. Int J Pharm. 2015;493:466–82.
Singh B, Khurana L, Bandyopadhyay S, Kapil R, Katare OOP. Development of optimized self-nano-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SNEDDS) of carvedilol with enhanced bioavailability potential. Drug Deliv. 2011;18:599–612.
Yang ZY, Zhang ZF, He XB, et al. Validation of a novel HPLC method for the determination of raloxifene and its pharmacokinetics in rat plasma. Chromatographia. 2006;65:197.
Chen ZQ, Liu Y, Zhao JH, Wang L, Feng NP. Improved oral bioavailability of poorly water-soluble indirubin by a supersaturatable self-microemulsifying drug delivery system. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:1115–25.
Beg S, Sandhu PS, Batra RS, et al. QbD-based systematic development of novel optimized solid self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (SNEDDS) of lovastatin with enhanced biopharmaceutical performance. Drug deliv 2014; 1–20.
Tripathi CB, Beg S, Kaur R, Shukla G, Bandopadhyay S, Singh B. Systematic development of optimized SNEDDS of artemether with improved biopharmaceutical and antimalarial potential. Drug Deliv. 2016;23:3209–23.
Gao P, Akrami A, Alvarez F, Hu J, Li L, Ma C, et al. Characterization and optimization of AMG 517 supersaturatable self-emulsifying drug delivery system (S-SEDDS) for improved oral absorption. J Pharm Sci. 2009;98:516–28.
Xu S, Dai WG. Drug precipitation inhibitors in supersaturable formulations. Int J Pharm. 2013;453:36–43.
Singh G, Pai RS. In vitro and in vivo performance of supersaturable self-nanoemulsifying system of trans-resveratrol. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2016;44:510–6.
Gao P, Guyton ME, Huang T, Bauer JM, Stefanski KJ, Lu Q. Enhanced oral bioavailability of a poorly water soluble drug PNU-91325 by supersaturatable formulations. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2004;30:221–9.
Khanfar M, Sheikh Salem M, Hawari R. Formulation factors affecting the release of ezetimibe from different liquisolid compacts. Pharm Dev Technol 2012
Gulsun T, Gursoy RN, Oner L. Design and characterization of nanocrystal formulations containing ezetimibe. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2011;59:41–5.
Chen Y, Chen C, Zheng J, Chen Z, Shi Q, Liu H. Development of a solid supersaturatable self-emulsifying drug delivery system of docetaxel with improved dissolution and bioavailability. Biol Pharm Bull. 2011;34:278–86.
Thomas N, Holm R, Garmer M, et al. Supersaturated self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (super-SNEDDS) enhance the bioavailability of the poorly water-soluble drug simvastatin in dogs. AAPS J. 2012;15:219–27.
Warren DB, Benameur H, Porter CJ, et al. Using polymeric precipitation inhibitors to improve the absorption of poorly water-soluble drugs: a mechanistic basis for utility. J Drug Target. 2010;18:704–31.
Raghavan SL, Trividic A, Davis AF, Hadgraft J. Effect of cellulose polymers on supersaturation and in vitro membrane transport of hydrocortisone acetate. Int J Pharm. 2000;193:231–7.
Thomas N, Holm R, Mullertz A, et al. In vitro and in vivo performance of novel supersaturated self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (super-SNEDDS). J Control Release. 2012;160:25–32.
Marques RC, Cole E, Kruep D, et al. Liquid-filled gelatin capsules. USP Pharmacopeial. Forum. 2009;35:1029–41.
Madan J, Chawla G, Arora V, Malik R, Bansal AK. Unbiased membrane permeability parameters for gabapentin using boundary layer approach. AAPS J. 2005;7:E224–30.
Oh DM, Curl RL, Amidon GL. Estimating the fraction dose absorbed from suspensions of poorly soluble compounds in humans: a mathematical model. Pharm Res. 1993;10:264–70.
Takekuma Y, Takenaka T, Kiyokawa M, Yamazaki K, Okamoto H, Kitabatake A, et al. Evaluation of effects of polymorphism for metabolic enzymes on pharmacokinetics of carvedilol by population pharmacokinetic analysis. Biol Pharm Bull. 2007;30:537–42.
Polli JE, Rekhi GS, Augsburger LL, Shah VP. Methods to compare dissolution profiles and a rationale for wide dissolution specifications for metoprolol tartrate tablets. J Pharm Sci. 1997;86:690–700.
Rao MRP, Aghav S, Sukre G, et al. Determination of required HLB of Capryol 90. J Dispers Sci Technol. 2012;35:161–7.
Rao Z, Si L, Guan Y, Pan H, Qiu J, Li G. Inhibitive effect of cremophor RH40 or tween 80-based self-microemulsiflying drug delivery system on cytochrome P450 3A enzymes in murine hepatocytes. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol. 2010;30:562–8.
Bandyopadhyay S, Katare OP, Singh B. Development of optimized supersaturable self-nanoemulsifying systems of ezetimibe: effect of polymers and efflux transporters. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2014;11:479–92.
Sharma G, Beg S, Thanki K, Katare OP, Jain S, Kohli K, et al. Systematic development of novel cationic self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems of candesartan cilexetil with enhanced biopharmaceutical performance. RSC Adv. 2015;5:71500–13.
Farahmandjou M. Effect of oleic acid and oleylamine surfactants on the size of FePt nanoparticles. J Supercond Novel Magn. 2012;25:2075–9.
Mourdikoudis S, Liz-Marz án LM. Oleylamine in nanoparticle synthesis. Chem Mater. 2013;25:1465–76.
Chokprasombata K, Sirisathitkula C, Hardinga P, et al. Monodisperse magnetic nanoparticles: effects of surfactants on the reaction between iron acetylacetonate and platinum acetylacetonate. Revista Mexicana de Fısica. 2013;59:224–8.
Harris RA, Shumbula PM, van der Walt H. Analysis of the interaction of surfactants oleic acid and oleylamine with iron oxide nanoparticles through molecular mechanics modeling. Langmuir. 2015;31:3934–43.
Mourdikoudis S, Liz-Marzán LM. Oleylamine in nanoparticle synthesis. Chem Mater. 2013;25:1465–76.
Nan Z, Lijun G, Tao W, Dongqin Q. Evaluation of carbamazepine (CBZ) supersaturatable self-microemulsifying (S-SMEDDS) formulation in-vitro and in-vivo. Iran J Pharm Res. 2012;11:257–64.
Song WH, Yeom DW, Lee DH, et al. In situ intestinal permeability and in vivo oral bioavailability of celecoxib in supersaturating self-emulsifying drug delivery system. Arch Pharm Res. 2013;37:626–35.
Brewster ME, Vandecruys R, Verreck G, Peeters J. Supersaturating drug delivery systems: effect of hydrophilic cyclodextrins and other excipients on the formation and stabilization of supersaturated drug solutions. Pharmazie. 2008;63:217–20.
Feeney OM, Crum MF, McEvoy CL, et al. 50 years of oral lipid-based formulations: provenance, progress and future perspectives. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016;101:167–94.
Chen Y, Li G, Wu X, Chen Z, Hang J, Qin B, et al. Self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (SMEDDS) of vinpocetine: formulation development and in vivo assessment. Biol Pharm Bull. 2008;31:118–25.
Sun M, Zhai X, Xue K, Hu L, Yang X, Li G, et al. Intestinal absorption and intestinal lymphatic transport of sirolimus from self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems assessed using the single-pass intestinal perfusion (SPIP) technique and a chylomicron flow blocking approach: linear correlation with oral bioavailabilities in rats. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2011;43:132–40.
Beg S, Swain S, Singh HP, Patra CN, Rao MEB. Development, optimization, and characterization of solid self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems of valsartan using porous carriers. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2012;13:1416–27.
Garg B, Katare OP, Beg S, Lohan S, Singh B. Systematic development of solid self-nanoemulsifying oily formulations (S-SNEOFs) for enhancing the oral bioavailability and intestinal lymphatic uptake of lopinavir. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2016;141:611–22.
Sandhu PS, Beg S, Mehta F, Singh B, Trivedi P. Novel dietary lipid-based self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems of paclitaxel with p-gp inhibitor: implications on cytotoxicity and biopharmaceutical performance. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2015;12:1809–22.
Bandyopadhyay S, Beg S, Katare OP, Sharma G, Singh B. QbD-oriented development of self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (SNEDDS) of valsartan with improved biopharmaceutical performance. Curr Drug Deliv. 2015;12:544–63.
Acknowledgements
The authors deeply acknowledge the support provided by M/s Zydus Cadila (Ahmedabad, India), M/s Gattefosse (Saint Priest, France), M/s BASF (Mumbai, India), M/s Colorcon Asia Pvt. Ltd. (Verna, India), M/s ACG Capsules (Mumbai, India), and M/s Stat-Ease (Minneapolis, USA) in conducting the present research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 70 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jain, A., Kaur, R., Beg, S. et al. Novel cationic supersaturable nanomicellar systems of raloxifene hydrochloride with enhanced biopharmaceutical attributes. Drug Deliv. and Transl. Res. 8, 670–692 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-018-0514-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-018-0514-8