Abstract
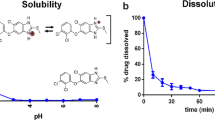
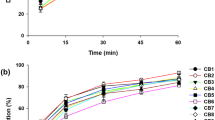
The aim of the present investigation was to enhance the solubility, dissolution, and oral bioavailability of praziquantel (PZQ), a poorly water-soluble BCS II drug (Biopharmaceutical Classification System), using a solid dispersion (SD) technique involving hydrophilic copolymers. The SD formulations were prepared by a solvent evaporation method with PZQ and PEG 4000 (polyethylene glycol 4000), PEG 6000, or P 188 polymers at various weight ratios or a combination of PEG 4000/P 188. The optimized SD formulation, which had the highest solubility in distilled water, was further characterized by its surface morphology, crystallinity, and dissolution in 0.1 M HCl with 0.2% w/v of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS). X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) revealed the amorphous form of PZQ in the SDs. Moreover, at an oral dosage of 5 mg/kg PZQ, the SDs had higher Cmax values and areas under the curve (AUCs) compared to those of commercial PZQ tablets. Preparation of PZQ-loaded SDs using PEG 4000/P 188 is a promising strategy to improve the oral bioavailability of PZQ.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chaud MV, Lima AC, MMDC V, Paganelli MO, Paula FC, Pedreiro LN, et al. Development and evaluation of praziquantel solid dispersions in sodium starch glycolate. Trop J Pharm Res. 2013;12(2):163–8. https://doi.org/10.4314/tjpr.v12i2.5.
Dinora GE, Julio R, Nelly C, Lilian YM, Cook HJ. In vitro characterization of some biopharmaceutical properties of praziquantel. Int J Pharm. 2005;295(1–2):93–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2004.01.033.
Passerini N, Albertini B, Perissutti B, Rodriguez L. Evaluation of melt granulation and ultrasonic spray congealing as techniques to enhance the dissolution of praziquantel. Int J Pharm. 2006;318(1–2):92–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2006.03.028.
Cheng L, Lei L, Guo SR. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of praziquantel loaded implants based on PEG/PCL blends. Int J Pharm. 2010;387(1–2):129–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2009.12.010.
Parrot-Lopez H, Perret F, Bertino-Ghera B. Les cyclodextrines amphiphiles et leurs applications. Élaboration de nanoparticules de cyclodextrines amphiphiles pour des applications biomédicales. Ann Pharm Fr. 2010;68(1):12–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharma.2009.12.002.
Xu XM, Khan MA, Burgess DJ. A two-stage reverse dialysis in vitro dissolution testing method for passive targeted liposomes. Int J Pharm. 2012;426(1–2):211–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2012.01.030.
Rodrigues SG, Chaves ID, de Melo NFS, de Jesus MB, Fraceto LF, Fernandes SA, et al. Computational analysis and physico-chemical characterization of an inclusion compound between praziquantel and methyl-beta-cyclodextrin for use as an alternative in the treatment of schistosomiasis. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem. 2011;70(1–2):19–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-010-9852-y.
Cheng L, Guo SR, Wu WP. Characterization and in vitro release of praziquantel from poly(epsilon-caprolactone) implants. Int J Pharm. 2009;377(1–2):112–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2009.05.007.
Mourao SC, Costa PI, Salgado HRN, Gremiao MPD. Improvement of antischistosomal activity of praziquantel by incorporation into phosphatidylcholine-containing liposomes. Int J Pharm. 2005;295(1–2):157–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2005.02.009.
Gurunath S, Kumar SP, Basavaraj NK, Patil PA. Amorphous solid dispersion method for improving oral bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs. J Pharm Res. 2013;6(4):476–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jopr.2013.04.008.
Giri TK, Kumar K, Alexander A, Ajazuddin BH, Tripathi DK. A novel and alternative approach to controlled release drug delivery system based on solid dispersion technique. Bull Facul Pharmacy Cairo Univ. 2012;50(2):147–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bfopcu.2012.07.002.
Shi N-Q, Lei Y-S, Song L-M, Yao J, Zhang X-B, Wang X-L. Impact of amorphous and semicrystalline polymers on the dissolution and crystallization inhibition of pioglitazone solid dispersions. Powder Technol. 2013;247:211–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2013.06.039.
Frizon F, Eloy JD, Donaduzzi CM, Mitsui ML, Marchetti JM. Dissolution rate enhancement of loratadine in polyvinylpyrrolidone K-30 solid dispersions by solvent methods. Powder Technol. 2013;235:532–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2012.10.019.
Frizon F, Eloy JDO, Donaduzzi CM, Mitsui ML, Marchetti JM. Dissolution rate enhancement of loratadine in polyvinylpyrrolidone K-30 solid dispersions by solvent methods. Powder Technol. 2013;235:532–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2012.10.019.
M E-B, G F, M F. Improvement of solubility and dissolution rate of indomethacin by solid dispersions in Gelucire 50/13 and PEG4000. Saudi pharmaceutical journal : SPJ : the official publication of the Saudi Pharmaceutical Society. 2009;17(3):217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2009.08.006.
Castro SG, Bruni SS, Lanusse CE, Allemandi DA, Palma SD. Improved albendazole dissolution rate in Pluronic 188 solid dispersions. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2010;11(4):1518–25. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-010-9517-6.
Moneghini M, Kikic I, Voinovich D, Perissutti B, Filipović-Grcić J. Processing of carbamazepine-PEG 4000 solid dispersions with supercritical carbon dioxide: preparation, characterisation, and in vitro dissolution. Int J Pharm. 2001;222(1):129–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-5173(01)00711-6.
Herrmann S, Winter G, Mohl S, Siepmann F, Siepmann J. Mechanisms controlling protein release from lipidic implants: effects of PEG addition. J Control Release. 2007;118(2):161–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2006.11.001.
Verheyen S, Blaton N, Kinget R, Mooter GVD. Mechanism of increased dissolution of diazepam and temazepam from polyethylene glycol 6000 solid dispersions. Int J Pharm. 2002;249(1–2):45–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-5173(02)00532-X.
Zhai H, Li S, Andrews G, Jones D, Bell S, Walker G. Nucleation and growth in fluidised hot melt granulation. Powder Technol. 2009;189(2):230–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2008.04.021.
Vilhelmsen T, Eliasen H, Schaefer T. Effect of a melt agglomeration process on agglomerates containing solid dispersions. Int J Pharm. 2005;303(1–2):132–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2005.07.012.
Guo MR, Fu Q, Wu CN, Guo ZB, Li M, Sun J, et al. Rod shaped nanocrystals exhibit superior in vitro dissolution and in vivo bioavailability over spherical like nanocrystals: a case study of lovastatin. Colloids Surf B-Biointerfaces. 2015;128:410–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2015.02.039.
Lowe S, Sher E, Wishart G, Jackson K, Yuen E, Brittain C, et al. An assessment of the central disposition of intranasally administered insulin lispro in the cerebrospinal fluid of healthy volunteers and beagle dogs. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2017;7(1):11–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-016-0325-8.
Li ZB, Zhang WJ, Gao Y, Xiang RW, Liu Y, Hu MM, et al. Development of self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system for oral bioavailability enhancement of valsartan in beagle dogs. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2017;7(1):100–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-016-0342-7.
Bolourchian N, Mahboobian MM, Dadashzadeh S. The effect of PEG molecular weights on dissolution behavior of simvastatin in solid dispersions. Iran J Pharm Res. 2013;12:9–18.
Oelmeier SA, Dismer F, Hubbuch J. Molecular dynamics simulations on aqueous two-phase systems—single PEG-molecules in solution. BMC Biophys. 2012;5(1):14. https://doi.org/10.1186/2046-1682-5-14.
Dhore PW, Dave VS, Saoji SD, Gupta D, Raut NA. Influence of carrier (polymer) type and drug-carrier ratio in the development of amorphous dispersions for solubility and permeability enhancement of ritonavir. 2017.
Leonardi D, Barrera MG, Lamas MC, Salomon CJ. Development of prednisone: polyethylene glycol 6000 fast-release tablets from solid dispersions: solid-state characterization, dissolution behavior, and formulation parameters. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2007;8(4):221–8. https://doi.org/10.1208/pt0804108.
Essa EA, Balata GF. Preparation and characterization of domperidone solid dispersions. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2012;25(4):783–91.
Castro SG, Bruni SFS, Urbizu LP, Confalonieri A, Ceballos L, Lanusse CE, et al. Enhanced dissolution and systemic availability of albendazole formulated as solid dispersions. Pharm Dev Technol. 2013;18(2):434–42. https://doi.org/10.3109/10837450.2012.693509.
Leuner C, Dressman J. Improving drug solubility for oral delivery using solid dispersions. European Journal of Pharmaceutics & Biopharmaceutics Official Journal of Arbeitsgemeinschaft Fur Pharmazeutische Verfahrenstechnik E V. 2000;50(1):47–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0939-6411(00)00076-X.
Taylor LS, Zografi G. Spectroscopic characterization of interactions between PVP and indomethacin in amorphous molecular dispersions. Pharm Res. 1997;14(12):1691.
Tang XC, Pikal MJ, Taylor LS. A spectroscopic investigation of hydrogen bond patterns in crystalline and amorphous phases in dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers. Pharm Res 2002;19(4):477, 483, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015147729564.
Sethia S, Squillante E. Solid dispersion of carbamazepine in PVPK30 by conventional solvent evaporation and supercritical methods. Int J Pharm. 2004;272(1–2):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2003.11.025.
Fernández M, Margarit MV, Rodríguez IC, Cerezo A. Dissolution kinetics of piroxicam in solid dispersions with polyethylene glycol 4000. Int J Pharm. 1993;98(1–3):29–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-5173(93)90037-G.
Margarit MV, Rodríguez IC, Cerezo A. Physical characteristics and dissolution kinetics of solid dispersions of ketoprofen and polyethylene glycol 6000. Int J Pharm. 1994;108(2):101–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-5173(94)90320-4.
Funding
This research was supported by the Key Laboratory of Animal Disease Control and Prevention ordinary (120105) operated by Northeast Agricultural University and also supported by the Supporting Program for Sci & Tech Research of China (2015BAD11B03-07) and by the earmarked fund for China Agriculture Research System (CARS-35).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was performed according to the Guiding Principles in the Use of Animals in Toxicology, as amended in 2008 by the Society of Toxicology.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Wang, T., Ding, W. et al. Dissolution and oral bioavailability enhancement of praziquantel by solid dispersions. Drug Deliv. and Transl. Res. 8, 580–590 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-018-0487-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-018-0487-7