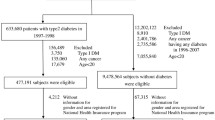
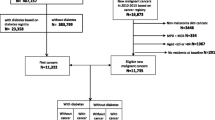
Abstract
Background
Although the association between type 2 diabetes and cancer has been reported, few epidemiological studies have been conducted in Japanese patients whose leading cause of death is cancer. We prospectively studied the incidence of site-specific cancer, risk factors for developing cancer, cancer death, and survival in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes.
Methods
We followed 4923 participants (mean age, 65 years) with type 2 diabetes attending an outpatient diabetes clinic for a median of 5.3 years (follow-up rate, 99.0%).
Results
During the follow-up period, cancer occurred in 450 participants (incidence rate, 22.3/1000 person-years in men and 12.2/1000 person-years in women). In men, prostate cancer was the most common cancer (4.3/1000 person-years), colorectal cancer was the second (3.6/1000 person-years), and gastric cancer was the third (3.3/1000 person-years). In women, colorectal cancer was the most common cancer (2.6/1000 person-years), gastric cancer was the second (2.0/1000 person-years), and breast cancer was the third (1.4/1000 person-years). Smoking, male sex, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, family history of cancer, and reduced intake of isoflavone daidzein were significant risk factors for developing cancer using multivariable Cox proportional hazards models. The leading cancer death was lung cancer in men and pancreatic cancer in women. The survival was the best for prostate cancer and the worst for pancreatic cancer (2-year cancer-specific survival 95.4%, 30.0%, respectively).
Conclusions
Since the leading cause of death in patients with type 2 diabetes is cancer in Japan, clinicians should be aware of epidemiological data regarding cancer besides diabetic complications.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Inoue M, Iwasaki M, Otani T, Sasazuki S, Noda M, Tsugane S. Diabetes mellitus and the risk of cancer: results from a large-scale population-based cohort study in Japan. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1871–7.
Kasuga M, Ueki K, Tajima N, Noda M, Ohashi K, Noto H, Goto A, Ogawa W, Sakai R, Tsugane S, Hamajima N, Nakagama H, Tajima K, Miyazono K, Imai K. Report of the JDS/JCA joint committee on diabetes and cancer. Diabetol Intern. 2013;4:81–96.
Shikata K, Ninomiya T, Kiyohara Y. Diabetes mellitus and cancer risk: review of the epidemiological evidence. Cancer Sci. 2013;104:9–14.
Goto A, Noto H, Noda M, Ueki K, Kasuga M, Tajima N, Ohashi K, Sakai R, Tsugane S, Hamajima N, Tajima K, Imai K, Nakagama H. Report of the Japan Diabetes Society (JDS)/Japanese Cancer Association (JCA) Joint Committee on Diabetes and Cancer, Second Report. Diabetol Intern. 2016;7:12–5.
Saito E, Charvat H, Goto A, Matsuda T, Noda M, Sasazuki S, Inoue M. Burden of cancer associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Japan, 2010–2030. Cancer Sci. 2016;107:521–7.
Pearson-Stuttard J, Zhou B, Kontis V, Bentham J, Gunter MJ, Ezzati M. Worldwide burden of cancer attributable to diabetes and high body-mass index: a comparative risk assessment. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018;6:95–104.
Noto H, Goto A, Tsujimoto T, Osame K, Noda M. Latest insights into the risk of cancer in diabetes. J Diabetes Investig. 2013;4:225–32.
Nakamura J, Kamiya H, Haneda M, Inagaki N, Tanizawa Y, Araki E, Ueki K, Nakayama T. Causes of death in Japanese patients with diabetes based on the results of a survey of 45,708 cases during 2001–2010: report of committee on causes of death in diabetes mellitus. Diabetol Intern. 2017;8:117–36.
Sasazuki S, Charvat H, Hara A, Wakai K, Nagata C, Nakamura K, Tsuji I, Sugawara Y, Tamakoshi A, Matsuo K, Oze I, Mizoue T, Tanaka K, Inoue M, Tsugane S. Diabetes mellitus and cancer risk: pooled analysis of eight cohort studies in Japan. Cancer Sci. 2013;104:1499–507.
Dabrowski M, Szymanska-Garbacz E, Miszczyszyn Z, Derezinski T, Czupryniak L. Risk factors for cancer development in type 2 diabetes: a retrospective case-control study. BMC Cancer. 2016;16:785.
Ohnishi H, Saitoh S, Akasaka H, Furukawa T, Mori M, Miura T. Combination of type 2 diabetes and smoking increases total cancer mortality in Japanese men using competing risk analysis: the Tanno-Sobetsu study. Diabetol Intern. 2016;7:167–72.
Ohkuma T, Fujii H, Iwase M, Kikuchi Y, Ogata S, Idewaki Y, Ide H, Doi Y, Hirakawa Y, Nakamura U, Kitazono T. Impact of sleep duration on obesity and the glycemic level in patients with type 2 diabetes: the Fukuoka Diabetes Registry. Diabetes Care. 2013;36:611–7.
Ainsworth BE, Haskell WL, Whitt MC, Irwin ML, Swartz AM, Strath SJ, O’Brien WL, Bassett DR Jr, Schmitz KH, Emplaincourt PO, Jacobs DR Jr, Leon AS. Compendium of physical activities: an update of activity codes and MET intensities. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2000;32:S498–504.
Kobayashi SHS, Murakami K, Sasaki S, Okubo H, Hirota N, Notsu A, Fukui M, Date C. Both comprehensive and brief self-administered diet history questionnaires satisfactorily rank nutrient intakes in Japanese adults. J Epidemiol. 2012;22:151–9.
Hori M, Matsuda T, Shibata A, Katanoda K, Sobue T, Nishimoto H. Cancer incidence and incidence rates in Japan in 2009: a study of 32 population-based cancer registries for the Monitoring of Cancer Incidence in Japan (MCIJ) project. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2015;45:884–91.
http://globocan.iarc.fr/old/FactSheets/cancers/prostate-new.asp. Accessed 17 June 2018.
Center MM, Jemal A, Lortet-Tieulent J, Ward E, Ferlay J, Brawley O, Bray F. International variation in prostate cancer incidence and mortality rates. Eur Urol. 2012;61:1079–92.
Xu H, Jiang HW, Ding GX, Zhang H, Zhang LM, Mao SH, Ding Q. Diabetes mellitus and prostate cancer risk of different grade or stage: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2013;99:241–9.
Long XJ, Lin S, Sun YN, Zheng ZF. Diabetes mellitus and prostate cancer risk in Asian countries: a meta-analysis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012;13:4097–100.
Inoue M, Sawada N, Matsuda T, Iwasaki M, Sasazuki S, Shimazu T, Shibuya K, Tsugane S. Attributable causes of cancer in Japan in 2005—systematic assessment to estimate current burden of cancer attributable to known preventable risk factors in Japan. Ann Oncol. 2012;23:1362–9.
Inoue M, Tsuji I, Wakai K, Nagata C, Mizoue T, Tanaka K, Tsugane S. Evaluation based on systematic review of epidemiological evidence among Japanese populations: tobacco smoking and total cancer risk. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2005;35:404–11.
Iso H, Ikeda A, Inoue M, Sato S, Tsugane S. Serum cholesterol levels in relation to the incidence of cancer: the JPHC study cohorts. Int J Cancer. 2009;125:2679–86.
Nago N, Ishikawa S, Goto T, Kayaba K. Low cholesterol is associated with mortality from stroke, heart disease, and cancer: the Jichi Medical School Cohort Study. J Epidemiol. 2011;21:67–74.
Kuzu OF, Noory MA, Robertson GP. The role of cholesterol in cancer. Cancer Res. 2016;76:2063–70.
Inoue M, Tsugane S. Impact of alcohol drinking on total cancer risk: data from a large-scale population-based cohort study in Japan. Br J Cancer. 2005;92:182–7.
Inoue M, Yamamoto S, Kurahashi N, Iwasaki M, Sasazuki S, Tsugane S. Daily total physical activity level and total cancer risk in men and women: results from a large-scale population-based cohort study in Japan. Am J Epidemiol. 2008;168:391–403.
Inoue M, Sobue T, Tsugane S. Impact of body mass index on the risk of total cancer incidence and mortality among middle-aged Japanese: data from a large-scale population-based cohort study—the JPHC study. Cancer Causes Control. 2004;15:671–80.
Kuriyama S, Tsubono Y, Hozawa A, Shimazu T, Suzuki Y, Koizumi Y, Suzuki Y, Ohmori K, Nishino Y, Tsuji I. Obesity and risk of cancer in Japan. Int J Cancer. 2005;113:148–57.
Zhang FF, Haslam DE, Terry MB, Knight JA, Andrulis IL, Daly MB, Buys SS, John EM. Dietary isoflavone intake and all-cause mortality in breast cancer survivors: the Breast Cancer Family Registry. Cancer. 2017;123:2070–79.
Applegate CC, Rowles JL, Ranard KM, Jeon S, Erdman JW. Soy consumption and the risk of prostate cancer: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients. 2018;10:40.
Yu Y, Jing X, Li H, Zhao X, Wang D. Soy isoflavone consumption and colorectal cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2016;6:25939.
Wada K, Tsuji M, Tamura T, Konishi K, Kawachi T, Hori A, Tanabashi S, Matsushita S, Tokimitsu N, Nagata C. Soy isoflavone intake and stomach cancer risk in Japan: from the Takayama study. Int J Cancer. 2015;137:885–92.
Tsugane S, Sasazuki S, Kobayashi M, Sasaki S. Salt and salted food intake and subsequent risk of gastric cancer among middle-aged Japanese men and women. Br J Cancer. 2004;90:128–34.
Cancer Statistics in Japan 2017 Tokyo: Foundation for Promotion of Cancer Research (FPCR). 2018.
https://kapweb.chiba-cancer-registry.org. Accessed 17 June 2018.
Lee J, Giovannucci E, Jeon JY. Diabetes and mortality in patients with prostate cancer: a meta-analysis. SpringerPlus. 2016;5:1548.
Li J, Liu J, Gao C, Liu F, Zhao H. Increased mortality for colorectal cancer patients with preexisting diabetes mellitus: an updated meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 2017;8:62478–88.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Drs. Yutaka Kiyohara, Yasufumi Doi, Toshiharu Ninomiya, Shigenobu Kanba, Dongchon Kang, Shuzo Kumagai, Shinako Kaizu, Yoichiro Hirakawa, Chisa Matsumoto, Chie Kitaoka (Kyushu University), Nobutaka Tsutsu, Nobuhiro Sasaki (Fukuoka Red Cross Hospital), Kiyohide Nunoi, Yuichi Sato, Yuji Uchizono, Ayumi Yamauchi, Kaori Itoh, Chie Kono (St. Mary’s Hospital), Sakae Nohara, Hirofumi Imoto, Kazushi Amano, (Steel Memorial Yawata Hospital), Daisuke Gotoh, Toshitaka Himeno, Masae Toyonaga (Kyushu Central Hospital), Noriyasu Shinohara, Ayako Tsutsumi (Fukuoka Higashi Medical Center), Masahiro Nakano, Mina Matsuo, Shoko Morimoto, Tomoko Hyodo (Hakujyuji Hospital), Masae Minami (Clinic Minami Masae), Miya Wada (Wada Miya Naika Clinic), Yoshifumi Yokomizo (Yokomizo Naika Clinic), Masanori Kikuchi, Yohei Kikuchi (Kikuchi Naika Clinic), Riku Nomiyama (Suzuki Naika Clinic), Shin Nakamura (Nakamura Naika Clinic), Kenji Tashiro (Oshima Eye Hospital), Mototaka Yoshinari (Yoshinari Naika Clinic), Kojiro Ichikawa (Fukutsu Naika Clinic), Teruo Omae (Hisayama Research Institute For Lifestyle Diseases), Hiroaki Ooboshi, and Shigeru Tanaka (Fukuoka Dental College). The authors also thank clinical research coordinators Chiho Ohba (Hisayama Research Institute For Lifestyle Diseases) and Kayoko Sekioka, Yoko Nishioka (Kyushu University), and those in the administration office, Tomoko Matake (Hisayama Research Institute For Lifestyle Diseases) and Junko Ishimatsu (Kyushu University). In addition, we thank H. Nikki March, PhD, from Edanz Group (www.edanzediting.com/ac) for editing a draft of this manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported, in part, by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science KAKENHI (Grant numbers 23249037 and 23659353 to M.I., and 16K00861 to H.F.) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest associated with this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Iwase, M., Fujii, H., Idewaki, Y. et al. Prospective study of cancer in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: the Fukuoka Diabetes Registry. Diabetol Int 10, 260–267 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-019-00390-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-019-00390-0