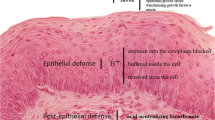
Abstract
The pathophysiology of gastroesophageal reflux disease is complex and linked to an intricate valve mechanism at the level of the esophagogastric junction that must counteract a trans-diaphragmatic pressure gradient, which is constantly forcing gastric contents upwards. Surgical antireflux therapy is usually aimed towards reinforcement of this valve mechanism. The valve mechanism is made up by the intra-abdominal length of the esophagus; the diaphragmatic sphincter, the angle of His, and the lower esophageal sphincter: all these elements must be restored with an antireflux procedure. Hiatal approximation and fundoplication determine excellent outcomes in patients in whom the abnormal reflux is mostly due to the valve mechanism. In patients with altered intra-abdominal pressure due to obesity, a bariatric procedure such as a Roux-en-Y gastric bypass is probably more appropriate. For patients with an altered intra-thoracic pressure such as in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, a fundoplication has been shown to be beneficial in resolving symptoms and avoiding progression of the diseases.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Menezes MA, Herbella FAM (2017) Pathophysiology of gastroesophageal reflux disease. World J Surg 41(7):1666–1671
Harding SM, Allen JE, Blumin JH, Warner EA, Pellegrini CA, Chan WW (2013) Respiratory manifestations of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1300:43–52. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.12231
Herbella FA, Andolfi C, Vigneswaran Y, Patti MG, Pinna BR (2016) Importance of esophageal manometry and pH monitoring for the evaluation of otorhinolaryngologic (ENT) manifestations of GERD. A multicenter study. J Gastrointest Surg 20(10):1673–1678. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-016-3212-1
Schlottmann F, Herbella FA, Allaix ME, Rebecchi F, Patti MG (2017) Surgical treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. World J Surg 41(7):1685–1690. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-017-3955-1
Makris KI, Lee T, Mittal SK (2009) Roux-en-Y reconstruction for failed fundoplication. J Gastrointest Surg 13(12):2226–2232
Nadaleto BF, Herbella FA, Patti MG (2016) Gastroesophageal reflux disease in the obese: pathophysiology and treatment. Surgery 159(2):475–486
Neto SC, Herbella FA, Silva LC, Patti MG (2014) Ratio between proximal/distal gastroesophageal reflux does not discriminate abnormal proximal reflux. World J Surg 38(4):890–896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-013-2341-x
Johnson LF, Demeester TR (1974) Twenty-four-hour pH monitoring of the distal esophagus. A quantitative measure of gastroesophageal reflux. Am J Gastroenterol 62(4):325–332
Jamieson JR, Stein HJ, DeMeester TR, Bonavina L, Schwizer W, Hinder RA, Albertucci M (1992) Ambulatory 24-h esophageal pH monitoring: normal values, optimal thresholds, specificity, sensitivity, and reproducibility. Am J Gastroenterol 87(9):1102–1111
Herbella FA, Patti MG (2010) Gastroesophageal reflux disease: from pathophysiology to treatment. World J Gastroenterol 16(30):3745–3749
Benati CD, Herbella FA, Patti MG (2014) Manometric parameters in patients with suspected gastroesophageal reflux disease and normal pH monitoring. GED Gastroenterol Endosc Dig 33(2):52–57
Del Grande LM, Herbella FA, Bigatao AM, Abrao H, Jardim JR, Patti MG (2016) Pathophysiology of gastroesophageal reflux in patients with chronic pulmonary obstructive disease is linked to an increased transdiaphragmatic pressure gradient and not to a defective esophagogastric barrier. J Gastrointest Surg 20(1):104–110
Roman S, Holloway R, Keller J, Herbella F, Zerbib F, Xiao Y, Bernard L, Bredenoord AJ, des Varannes SB, Chen M, Fox M, Kahrilas PJ, Mittal RK, Penagini R, Savarino E, Sifrim D, Wu J, Decullier E, Pandolfino JE, Mion F (2017) Validation of criteria for the definition of transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxations using high-resolution manometry. Neurogastroenterol Motil 29(2):e12920. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.12920 (Epub 2016 Jul 31)
Miller L, Vegesna A, Kalra A, Besetty R, Dai Q, Korimilli A, Brasseur JG (2007) New observations on the gastroesophageal antireflux barrier. Gastroenterol Clin N Am 36(3):601–617
Pandolfino JE, Kim H, Ghosh SK, Clarke JO, Zhang Q, Kahrilas PJ (2007) High-resolution manometry of the EGJ: an analysis of crural diaphragm function in GERD. Am J Gastroenterol 102(5):1056–1063 (Epub 2007 Feb 23)
DeMeester TR, Wernly JA, Bryant GH, Little AG, Skinner DB (1979) Clinical and in vitro analysis of determinants of gastroesophageal competence. A study of the principles of antireflux surgery. Am J Surg 137(1):39–46
Franzén T, Tibbling L (2014) Is the severity of gastroesophageal reflux dependent on hiatus hernia size? World J Gastroenterol 20(6):1582–1584. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i6.1582
Kahrilas PJ, Shi G, Manka M, Joehl RJ (2000) Increased frequency of transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxation induced by gastric distention in reflux patients with hiatal hernia. Gastroenterology 118(4):688–695
Menezes MA, Herbella FA, Patti MG (2016) Laparoscopic antireflux surgery in patients with connective tissue diseases. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 26(4):296–298
Su A, Gandhy R, Barlow C, Triadafilopoulos G (2017) Clinical and manometric characteristics of patients with Parkinson’s disease and esophageal symptoms. Dis Esophagus 30(4):1–6
Diener U, Patti MG, Molena D, Fisichella PM, Way LW (2001) Esophageal dysmotility and gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Gastrointest Surg 5(3):260–265
Herbella FA, Tedesco P, Nipomnick I, Fisichella PM, Patti MG (2007) Effect of partial and total laparoscopic fundoplication on esophageal body motility. Surg Endosc 21(2):285–288
Herbella FA, Sweet MP, Tedesco P, Nipomnick I, Patti MG (2007) Gastroesophageal reflux disease and obesity. Pathophysiology and implications for treatment. J Gastrointest Surg 11(3):286–290
Gourcerol G, Benanni Y, Boueyre E, Leroi AM, Ducrotte P (2013) Influence of gastric emptying on gastro-esophageal reflux: a combined pH-impedance study. Neurogastroenterol Motil 25(10):800. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.12181
Pregun I, Bakucz T, Banai J, Molnár L, Pavlik G, Altorjay I, Orosz P, Csernay L, Tulassay Z, Herszényi L (2009) Gastroesophageal reflux disease: work-related disease? Dig Dis 27(1):38–44. https://doi.org/10.1159/000210102 (Epub 2009 May 8)
Stylopoulos N, Rattner DW (2005) The history of hiatal hernia surgery: from Bowditch to laparoscopy. Ann Surg 241(1):185–193
Allison PR (1973) Hiatus hernia: (a 20-year retrospective survey). Ann Surg 178(3):273–276
Herbella FA (2017) Secrets for successful laparoscopic antireflux surgery. Ann Laparosc Endosc Surg 2:46
Watson DI, Jamieson GG, Devitt PG, Matthew G, Britten-Jones RE, Game PA, Williams RS (1995) Changing strategies in the performance of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication as a result of experience with 230 operations. Surg Endosc 9(9):961–966
Herbella FA, Patti MG, Del Grande JC (2011) Hiatal mesh repair—current status. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 21(2):61–66
Richter J, Kumar A, Lipka S, Miladinovic B, Velanovich V (2018) Efficacy of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication vs transoral incisionless fundoplication or proton pump inhibitors in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2017.12.021 (Epub ahead of print)
Herbella FA, Oliveira DR, Del Grande JC (2004) Eponyms in esophageal surgery. Dis Esophagus 17(1):1–9
Nissen R (1956) Gastropexy as the lone procedure in the surgical repair of hiatus hernia. Am J Surg 92(3):389–392
Herbella FA, Del Grande J (2001) Human cadavers as an experimental model for esophageal surgery. Dis Esophagus 14(3–4):218–222
Aye RW, Rehse D, Blitz M, Kraemer SJ, Hill LD (2011) The Hill antireflux repair at 5 institutions over 25 years. Am J Surg 201(5):599–604
Varshney S, Kelly JJ, Branagan G, Somers SS, Kelly JM (2002) Angelchik prosthesis revisited. World J Surg 26(1):129–133 (Epub 2001 Nov 26)
Asti E, Bonitta G, Lovece A, Lazzari V, Bonavina L (2016) Longitudinal comparison of quality of life in patients undergoing laparoscopic Toupet fundoplication versus magnetic sphincter augmentation: observational cohort study with propensity score analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 95(30):e4366. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000004366
Salvador R, Costantini M, Capovilla G, Polese L, Merigliano S (2017) Esophageal penetration of the magnetic sphincter augmentation device: history repeats itself. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 27(8):834–838. https://doi.org/10.1089/lap.2017.0182 (Epub 2017 Jun 6)
Bonavina L, Attwood S (2016) Laparoscopic alternatives to fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux: the role of magnetic augmentation and electrical stimulation of the lower esophageal sphincter. Dis Esophagus 29(8):996–1001. https://doi.org/10.1111/dote.12425 (Epub 2015 Dec 17)
Weijenborg PW, Savarino E, Kessing BF, Roman S, Costantini M, Oors JM, Smout AJ, Bredenoord AJ (2015) Normal values of esophageal motility after antireflux surgery; a study using high-resolution manometry. Neurogastroenterol Motil 27(7):929–935. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.12554
Xu JY, Xie XP, Song GQ, Hou XH (2007) Healing of severe reflux esophagitis with PPI does not improve esophageal dysmotility. Dis Esophagus 20(4):346–352
Gerritsen A, Furnée EJ, Gooszen HG, Wondergem M, Hazebroek EJ (2013) Evaluation of gastrectomy in patients with delayed gastric emptying after antireflux surgery or large hiatal hernia repair. World J Surg 37(5):1065–1071. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-013-1953-5
Williams VA, Watson TJ, Gellersen O, Feuerlein S, Molena D, Sillin LF, Jones C, Peters JH (2007) Gastrectomy as a remedial operation for failed fundoplication. J Gastrointest Surg 11(1):29–35
Treitl D, Nieber D, Ben-David K (2017) Operative treatments for reflux after bariatric surgery: current and emerging management options. J Gastrointest Surg 21(3):577–582. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-017-3361-x (Epub 2017 Jan 13)
Peters JH, DeMeester TR, Crookes P, Oberg S, de Vos Shoop M, Hagen JA, Bremner CG (1998) The treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease with laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: prospective evaluation of 100 patients with “typical” symptoms. Ann Surg 228(1):40–50
Gasper WJ, Sweet MP, Hoopes C, Leard LE, Kleinhenz ME, Hays SR, Golden JA, Patti MG (2008) Antireflux surgery for patients with end-stage lung disease before and after lung transplantation. Surg Endosc 22(2):495–500
Acknowledgements
We are indebted to Ms. Debora Gallegos for illustrating the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
No informed consent is required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herbella, F.A.M., Schlottmann, F. & Patti, M.G. Pathophysiology of gastroesophageal reflux disease: how an antireflux procedure works (or does not work). Updates Surg 70, 343–347 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13304-018-0562-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13304-018-0562-0