Abstract
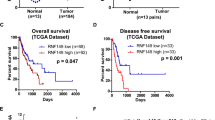
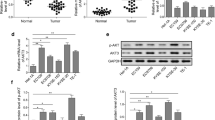
The incidence of esophageal carcinoma is increasing throughout the world. A major obstacle to its treatment is acquired multidrug resistance (MDR) which results in the failure of chemotherapy and patient relapse. Here, we identified that ouabain is capable of reversing MDR to cisplatin (CDDP) in EC109/CDDP cells and explore the possible mechanisms of action. The parental and the MDR cell lines were both sensitive to ouabain with 50 % inhibitory concentration (IC50) values of 258.11 and 710.63 nM, respectively. Cisplatin cytotoxicity increased in the EC109/CDDP cells by the addition of ouabain which helps promote CDDP-induced apoptosis. Ouabain at 20 nM effectively reduced the IC50 of CDDP in EC109/CDDP cells from 36.54 to 3.39 μM. This represents a 10.78-fold increase in sensitization to CDDP. We also found that ouabain was capable of down regulating the expression of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and Bcl-2 in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Finally, the results indicated that ouabain suppressed Wnt luciferase report (TOPFlash) activity obviously in EC109/CDDP and depressed the translocation of β-catenin into the nucleus. Moreover, ouabain showed reversal effect of MDR to CDDP in nude mouse xenograft model, and reduced the protein level of β-catenin (Y333) in tumor tissue of CDDP plus ouabain group. All data proved that ouabain has a potent β-catenin-dependent anti-MDR effect.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM. International variation. Oncogene. 2004;23:6329–40.
HB e-S. The epidemic of esophageal adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterol Clin N Am. 2002;31:421–40 viii.
Jemal A, Tiwari RC, Murray T, Ghafoor A, Samuels A, Ward E, Feuer EJ, Thun MJ, American Cancer S. Cancer statistics, 2004. CA Cancer J Clin. 2004;54:8–29.
Enzinger PC, Mayer RJ. Esophageal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:2241–52.
Tew WP, Kelsen DP, Ilson DH. Targeted therapies for esophageal cancer. Oncologist. 2005;10:590–601.
Rajasekaran AK, Rajasekaran SA. Role of Na-K-ATPase in the assembly of tight junctions. American Journal of Physiology Renal Physiology. 2003;285:F388–96.
Callaghan R, Ford RC, Kerr ID. The translocation mechanism of p-glycoprotein. FEBS Lett. 2006;580:1056–63.
Zandvliet M, Teske E, Schrickx JA. Multi-drug resistance in a canine lymphoid cell line due to increased p-glycoprotein expression, a potential model for drug-resistant canine lymphoma. Toxicology In Vitro: an International Journal Published in Association with BIBRA. 2014;28:1498–506.
Holland JD, Klaus A, Garratt AN, Birchmeier W. Wnt signaling in stem and cancer stem cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013;25:254–64.
Mizushima T, Nakagawa H, Kamberov YG, Wilder EL, Klein PS, Rustgi AK. Wnt-1 but not epidermal growth factor induces beta-catenin/t-cell factor-dependent transcription in esophageal cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2002;62:277–82.
Nakanishi Y, Ochiai A, Akimoto S, Kato H, Watanabe H, Tachimori Y, Yamamoto S, Hirohashi S. Expression of e-cadherin, alpha-catenin, beta-catenin and plakoglobin in esophageal carcinomas and its prognostic significance: Immunohistochemical analysis of 96 lesions. Oncology. 1997;54:158–65.
Hockenbery D, Nunez G, Milliman C, Schreiber RD, Korsmeyer SJ. Bcl-2 is an inner mitochondrial membrane protein that blocks programmed cell death. Nature. 1990;348:334–6.
Hsu PC, Hung HC, Liao YF, Liu CC, Tsay GJ, Liu GY. Ornithine decarboxylase attenuates leukemic chemotherapy drugs-induced cell apoptosis and arrest in human promyelocytic hl-60 cells. Leuk Res. 2008;32:1530–40.
Nelson WJ, Nusse R. Convergence of Wnt, beta-catenin, and cadherin pathways. Science. 2004;303:1483–7.
Teodori E, Dei S, Martelli C, Scapecchi S, Gualtieri F. The functions and structure of abc transporters: implications for the design of new inhibitors of pgp and mrp1 to control multidrug resistance (mdr). Curr Drug Targets. 2006;7:893–909.
Breier A, Stetka J, Bohacova V, Macejova D, Brtko J, Sulova Z. Effect of 9-cis retinoic acid and all-trans retinoic acid in combination with verapamil on p-glycoprotein expression in l1210 cells. Neoplasma. 2014;61:553–65.
Chearwae W, Anuchapreeda S, Nandigama K, Ambudkar SV, Limtrakul P. Biochemical mechanism of modulation of human p-glycoprotein (abcb1) by curcumin i, ii, and iii purified from turmeric powder. Biochem Pharmacol. 2004;68:2043–52.
Di Pietro A, Conseil G, Perez-Victoria JM, Dayan G, Baubichon-Cortay H, Trompier D, Steinfels E, Jault JM, de Wet H, Maitrejean M, Comte G, Boumendjel A, Mariotte AM, Dumontet C, McIntosh DB, Goffeau A, Castanys S, Gamarro F, Barron D. Modulation by flavonoids of cell multidrug resistance mediated by p-glycoprotein and related abc transporters. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences: CMLS. 2002;59:307–22.
Infed N, Smits SH, Dittrich T, Braun M, Driessen AJ, Hanekop N, Schmitt L. Analysis of the inhibition potential of zosuquidar derivatives on selected bacterial and fungal abc transporters. Mol Membr Biol. 2013;30:217–27.
Kelly RJ, Draper D, Chen CC, Robey RW, Figg WD, Piekarz RL, Chen X, Gardner ER, Balis FM, Venkatesan AM, Steinberg SM, Fojo T, Bates SE. A pharmacodynamic study of docetaxel in combination with the p-glycoprotein antagonist tariquidar (xr9576) in patients with lung, ovarian, and cervical cancer. Clinical Cancer Research: an Official Journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2011;17:569–80.
Kuppens IE, Witteveen EO, Jewell RC, Radema SA, Paul EM, Mangum SG, Beijnen JH, Voest EE, Schellens JH. A phase i, randomized, open-label, parallel-cohort, dose-finding study of elacridar (gf120918) and oral topotecan in cancer patients. Clinical Cancer Research: an Official Journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2007;13:3276–85.
Morschhauser F, Zinzani PL, Burgess M, Sloots L, Bouafia F, Dumontet C. Phase i/ii trial of a P-glycoprotein inhibitor, Zosuquidar.3HCl trihydrochloride (ly335979), given orally in combination with the CHOP regimen in patients with non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Leukemia & Lymphoma. 2007;48:708–15.
Ramirez-Ortega M, Maldonado-Lagunas V, Melendez-Zajgla J, Carrillo-Hernandez JF, Pastelin-Hernandez G, Picazo-Picazo O, Ceballos-Reyes G. Proliferation and apoptosis of hela cells induced by in vitro stimulation with digitalis. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006;534:71–6.
Kulikov A, Eva A, Kirch U, Boldyrev A, Scheiner-Bobis G. Ouabain activates signaling pathways associated with cell death in human neuroblastoma. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1768;2007:1691–702.
Ramu A, Ramu N, Gorodetsky R. Reduced ouabain-sensitive potassium entry as a possible mechanism of multidrug-resistance in p388 cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991;42:1699–704.
Fiebig HH, Berger DP, Winterhalter BR, Plowman J. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of US-NCI compounds in human tumor xenografts. Cancer Treat Rev. 1990;17:109–17.
Lin CF, Wan SW, Chen MC, Lin SC, Cheng CC, Chiu SC, Hsiao YL, Lei HY, Liu HS, Yeh TM, Lin YS. Liver injury caused by antibodies against dengue virus nonstructural protein 1 in a murine model. Laboratory Investigation; a Kournal of Technical Methods and Pathology. 2008;88:1079–89.
Stewart DJ. Mechanisms of resistance to cisplatin and carboplatin. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2007;63:12–31.
Ding XW, Wu JH, Jiang CP. Abcg2: a potential marker of stem cells and novel target in stem cell and cancer therapy. Life Sci. 2010;86:631–7.
Podolski-Renic A, Andelkovic T, Bankovic J, Tanic N, Ruzdijic S, Pesic M. The role of paclitaxel in the development and treatment of multidrug resistant cancer cell lines. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & Pharmacotherapie. 2011;65:345–53.
Chen J, Wang R, Zhang K, Chen LB. Long non-coding RNAs in non-small cell lung cancer as biomarkers and therapeutic targets. J Cell Mol Med. 2014;18:2425–36.
Wang TH, Wan JY, Gong X, Li HZ, Cheng Y. Tetrandrine enhances cytotoxicity of cisplatin in human drug-resistant esophageal squamous carcinoma cells by inhibition of multidrug resistance-associated protein 1. Oncol Rep. 2012;28:1681–6.
Jansson L, Kim GS, Cheng AG. Making sense of Wnt signaling-linking hair cell regeneration to development. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015;9:66.
Logan CY, Nusse R. The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2004;20:781–810.
Rosano L, Cianfrocca R, Spinella F, Di Castro V, Nicotra MR, Lucidi A, Ferrandina G, Natali PG, Bagnato A. Acquisition of chemoresistance and emt phenotype is linked with activation of the endothelin a receptor pathway in ovarian carcinoma cells. Clinical Cancer Research: an Official Journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2011;17:2350–60.
Rosano L, Cianfrocca R, Tocci P, Spinella F, Di Castro V, Caprara V, Semprucci E, Ferrandina G, Natali PG, Bagnato A. Endothelin a receptor/beta-arrestin signaling to the Wnt pathway renders ovarian cancer cells resistant to chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 2014;74:7453–64.
Zhang H, Jing X, Wu X, Hu J, Zhang X, Wang X, Su P, Li W, Zhou G. Suppression of multidrug resistance by rosiglitazone treatment in human ovarian cancer cells through downregulation of fzd1 and mdr1 genes. Anti-Cancer Drugs. 2015;26:706–15.
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by Jiangsu Provincial Special Program of Clinical Medical Science (BL2014040), Suzhou Science and Technology Development Program (SZS201509), and Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (11KJB180010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All animal studies were carried out in compliance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of Nantong University, China.
Conflict of interest
None.
Additional information
Yucheng Shen and Qinghua Wang have contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, Y., Wang, Q. & Tian, Y. Reversal effect of ouabain on multidrug resistance in esophageal carcinoma EC109/CDDP cells by inhibiting the translocation of Wnt/β-catenin into the nucleus. Tumor Biol. 37, 15937–15947 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5437-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5437-8