Abstract
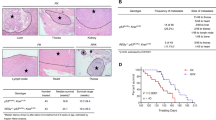
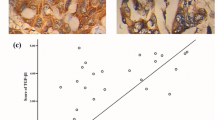
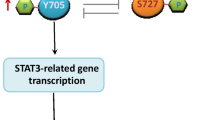
Smad ubiquitin regulatory factor 2 (Smurf2) is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that regulates transforming growth factor β (TGF-β)/Smad signaling and is implicated in a wide range of cellular responses. However, the exact mechanism whereby Smurf2 controls TGF-β-induced signaling pathways remains unknown. Here, we identified the relationship between the alternate TGF-β signaling pathways: TGF-β/PI3K/Akt/β-catenin and TGF-β/Smad2/3/FoxO1/PUMA and Smurf2. The results showed that TGF-β promoted proliferation, invasion, and migration of human pancreatic carcinoma (PANC-1) cells through the PI3K/Akt/β-catenin pathway. Inhibiting the PI3K/Akt signal transformed the TGF-β-induced cell response from promoting proliferation to Smad2/3/FoxO1/PUMA-mediated apoptosis. The activation of Akt inhibited the phosphorylation/activation of Smad3 and promoted the phosphorylation/inactivation of FoxO1, inhibiting the nuclear translocation of both Smad3 and FoxO1 and inhibiting the expression of PUMA, a key apoptotic mediator. However, downregulation of Smurf2 in PANC-1 cells removed Akt-mediated suppression of Smad3 and FoxO1, allowing TGF-β-induced phosphorylation/activation of Smad2/3, dephosphorylation/activation of FoxO1, nuclear translocation of both factors, and activation of PUMA-mediated apoptosis. Downregulation of Smurf2 also decreased invasion and migration in TGF-β-induced PANC-1 cells. The in vivo experiments also revealed that downregulation of Smurf2 delayed the growth of xenograft tumors originating from PANC-1 cells especially when treated with TGF-β. Taken together, these results indicate that expression of Smurf2 plays a central role in the determination and activation/inhibition of particular cellular pathways and the ultimate fate of cells induced by TGF-β. An increased understanding of the intricacies of the TGF-β signaling pathway may provide a new anti-cancer therapeutic target.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heldin CH, Miyazono K, ten Dijke P. TGF-beta signalling from cell membrane to nucleus through SMAD proteins. Nature. 1997;390:465–71.
Massague J. TGF-beta signal transduction. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:753–91.
Whitman M. Smads and early developmental signaling by the TGFbeta superfamily. Genes Dev. 1998;12:2445–62.
Massague J, Chen YG. Controlling TGF-beta signaling. Genes Dev. 2000;14:627–44.
Bean GR, Ganesan YT, Dong Y, et al. PUMA and BIM are required for oncogene inactivation-induced apoptosis. Sci Signal. 2013;6:ra20.
Wiener Z, Band AM, Kallio P, et al. Oncogenic mutations in intestinal adenomas regulate Bim-mediated apoptosis induced by TGF-beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111:E2229–36.
Zhu H, Kavsak P, Abdollah S, Wrana JL, Thomsen GHASMAD. Ubiquitin ligase targets the BMP pathway and affects embryonic pattern formation. Nature. 1999;400:687–93.
Kavsak P, Rasmussen RK, Causing CG, et al. Smad7 binds to Smurf2 to form an E3 ubiquitin ligase that targets the TGF beta receptor for degradation. Mol Cell. 2000;6:1365–75.
Lin X, Liang M, Feng XH. Smurf2 is a ubiquitin E3 ligase mediating proteasome-dependent degradation of Smad2 in transforming growth factor-beta signaling. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:36818–22.
Zhang Y, Chang C, Gehling DJ, Hemmati-Brivanlou A, Derynck R. Regulation of Smad degradation and activity by Smurf2, an E3 ubiquitin ligase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:974–9.
Fukuchi M, Fukai Y, Masuda N, et al. High-level expression of the Smad ubiquitin ligase Smurf2 correlates with poor prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2002;62:7162–5.
Loukopoulos P, Shibata T, Katoh H, et al. Genome-wide array-based comparative genomic hybridization analysis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: identification of genetic indicators that predict patient outcome. Cancer Sci. 2007;98:392–400.
Fukasawa H, Yamamoto T, Fujigaki Y, et al. Reduction of transforming growth factor-beta type II receptor is caused by the enhanced ubiquitin-dependent degradation in human renal cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:1517–25.
Tan R, He W, Lin X, Kiss LP, Liu Y. Smad ubiquitination regulatory factor-2 in the fibrotic kidney: regulation, target specificity, and functional implication. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008;294:F1076–83.
Tan R, Zhang J, Tan X, Zhang X, Yang J, Liu Y. Downregulation of SnoN expression in obstructive nephropathy is mediated by an enhanced ubiquitin-dependent degradation. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:2781–91.
David D, Jagadeeshan S, Hariharan R, Nair AS, Pillai RM. Smurf2 E3 ubiquitin ligase modulates proliferation and invasiveness of breast cancer cells in a CNKSR2 dependent manner. Cell Div. 2014;9:2.
Blank M, Tang Y, Yamashita M, Burkett SS, Cheng SY, Zhang YE. A Tumor suppressor function of Smurf2 associated with controlling chromatin landscape and genome stability through RNF20. Nat Med. 2012;18:227–34.
Lo RS, Massague J. Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of TGF-β activated smad2. Nat Cell Biol. 1999;1:472–8.
Gao S, Alarcon C, Sapkota G, Rahman S, Chen PY, Goerner N, Macias MJ, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Massague J. Ubiquitin ligase Nedd4L targets activated Smad2/3 to limit TGF-β signaling. Mol Cell. 2009;36:457–68.
David D, Nair SA, Pillai MR. Smurf E3 ubiquitin ligases at the cross roads of oncogenesis and tumor suppression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1835:119–28.
Li H, Seth A. An RNF11: Smurf2 complex mediates ubiquitination of the AMSH protein. Oncogene. 2004;23:1801–8.
Schwamborn JC, Muller M, Becker AH, Puschel AW. Ubiquitination of the GTPase Rap1B by the ubiquitin ligase Smurf2 is required for the establishment of neuronal polarity. EMBO J. 2007;26:1410–22.
Tang LY, Yamashita M, Coussens NP, et al. Ablation of Smurf2 reveals an inhibition in TGF-beta signalling through multiple mono-ubiquitination of Smad3. EMBO J. 2011;30:4777–89.
Osmundson EC, Ray D, Moore FE, Gao Q, Thomsen GH, Kiyokawa H. The HECT E3 ligase Smurf2 is required for Mad2-dependent spindle assembly checkpoint. J Cell Biol. 2008;183(2):267–77.
Moore FE, Osmundson EC, Koblinski J, Pugacheva E, Golemis EA, Ray D, Kiyokawa H. The WW-HECT protein Smurf2 interacts with the docking protein NEDD9/HEF1 for aurora a activation. Cell Div. 2010;5:22.
Dadke D, Jarnik M, Pugacheva EN, Singh MK, Golemis EA. Deregulation of HEF1 impairs M-phase progression by disrupting the RhoA activation cycle. Mol Biol Cell. 2006;17(3):1204–17.
Xie P, Tang Y, Shen S, Wang Y, Xing G, Yin Y, He F, Zhang L. Smurf1 ubiquitin ligase targets Kruppel-like factor KLF2 for ubiquitination and degradation in human lung cancer H1299 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;407(1):254–9.
Du JX, Hagos EG, Nandan MO, Bialkowska AB, Yu B, Yang VW. The E3 ubiquitin ligase SMAD ubiquitination regulatory factor 2 negatively regulates Krüppel-like factor 5 protein. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(46):40354–64.
Huang C. Roles of E3 ubiquitin ligases in cell adhesion and migration. Cell Adhes Migr. 2010;4(1):10–8.
Jin C, Yang YA, Anver MR, Morris N, Wang X, Zhang YE. Smad ubiquitination regulatory factor 2 promotes metastasis of breast cancer cells by enhancing migration and invasiveness. Cancer Res. 2009;69(3):735–40.
Nie J, Xie P, Liu L, Xing G, Chang Z, Yin Y, Tian C, He F, Zhang L. Smad ubiquitylation regulatory factor 1/2 (Smurf1/2) promotes p53 degradation by stabilizing the E3 ligase MDM2. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(30):22818–30.
Nie J, Liu L, Wu M, Xing G, He S, Yin Y, Tian C, He F, Zhang L. HECT Ubiquitin ligase Smurf1 targets the tumor suppressor ING2 for ubiquitination and degradation. FEBS Lett. 2010;584(14):3005–12.
Zhang H, Teng Y, Kong Y, Kowalski PE, Cohen SN. Suppression of human tumor cell proliferation by Smurf2-induced senescence. J Cell Physiol. 2008;215:613–20.
Scheffner M, Staub O. HECT E3s and human disease. BMC Biochem. 2007;8(Suppl 1):S6.
Lakshmanan M, Bughani U, Duraisamy S, Diwan M, Dastidar S, Ray A. Molecular targeting of E3 ligases—a therapeutic approach for cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2008;12(7):855–70.
Sun Y. E3 ubiquitin ligases as cancer targets and biomarkers. Neoplasia. 2006;8(8):645–54.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Additional information
Bo Wu and Bo-Min Guo have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, B., Guo, B., Kang, J. et al. Downregulation of Smurf2 ubiquitin ligase in pancreatic cancer cells reversed TGF-β-induced tumor formation. Tumor Biol. 37, 16077–16091 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5432-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5432-0