Abstract
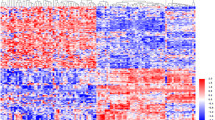
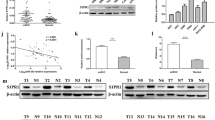
This study aimed to screen effective diagnosis or treatment biomarkers for renal cell carcinoma, especially for metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) based on microRNA (miRNA) and messenger RNA (mRNA) genechip, and their regulatory network. The differential expressions of miRNAs and mRNAs were examined by miRNA and mRNA gene-chip analyses, respectively, in patients with either localized renal cell carcinoma (lRCC) or mRCC, and a miRNA-mRNA regulatory network was established. Subsequently, the regulation of selected mRNAs by miRNAs was validated by reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) and dual-luciferase reporter gene assay. Thirty-one up-regulated miRNAs, 196 down-regulated miRNAs, 214 up-regulated mRNAs, and 156 down-regulated mRNAs were identified in patients with mRCC. In total, 1315 miRNA-mRNA pairs, involving 34 miRNAs and 225 mRNAs, were established. The expression profiles of four up-regulated miRNAs, hsa-miR-139-5p, hsa-miR-140-3p, hsa-miR-151a-3p, and hsa-miR-204-5p, and four down-regulated miRNAs, hsa-miR-409-3p, hsa-miR-671-3p, hsa-miR-1203, and hsa-miR-1290, were consistent with the results from the miRNA gene-chip analysis. The expression profiles of NEU2, MASP1, MCL1, ARHGAP11A, HOXA1, and CLDN8 were consistent with the results from the mRNA gene-chip analysis. In vitro, hsa-miR-140-3p bound to the 3′ untranslated region (3′-UTR) of the MASP1 mRNA and down-regulated its expression. Similarly, hsa-miR-151a-3p, hsa-miR-671-3p, and hsa-miR-1290 bound to the 3′-UTRs of the MCL1, HOXA1, and HOXA1 mRNAs, respectively, and down-regulated their expressions. However, binding by hsa-miR-140-3p, hsa-miR-671-3p, or hsa-miR-1290 did not down-regulate the expressions of NEU2, ARHGAP11A, and CLDN8, respectively. This study provides a significant reference of investigating the pathogenesis of mRCC and the subsequent screening of potential therapeutic targets.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108.
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:5–29.
Chow WH, Devesa SS, Warren JL, Fraumeni Jr JF. Rising incidence of renal cell cancer in the United States. JAMA. 1999;281:1628–31.
Fenaux P, Haase D, Sanz GF, Santini V, Buske C. Myelodysplastic syndromes: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2014;25(Suppl 3):iii57–69.
Glynne-Jones R, Nilsson PJ, Aschele C, Goh V, Peiffert D, Cervantes A, Arnold D. Anal cancer: ESMO-ESSO-ESTRO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2014;40:1165–76.
Gastrointestinal stromal tumours: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2014;25 Suppl 3:iii21–26.
Dreyling M, Ghielmini M, Marcus R, Salles G, Vitolo U, Ladetto M. Newly diagnosed and relapsed follicular lymphoma: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2014;25(Suppl 3):iii76–82.
Bozkurt O, Karaca H, Hacibekiroglu I, Kaplan MA, Duzkopru Y, Uysal M, Berk V, Inanc M, Duran AO, Ozaslan E, Ucar M, Ozkan M. Is sunitinib-induced hypothyroidism a predictive clinical marker for better response in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients? J Chemother. 2015;1973947815Y0000000039.
Diekstra MH, Swen JJ, Boven E, Castellano D, Gelderblom H, Mathijssen RH, Rodriguez-Antona C, Garcia-Donas J, Rini BI, Guchelaar HJ. Cyp3a5 and abcb1 polymorphisms as predictors for sunitinib outcome in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2015.
Miyazaki A, Miyake H, Harada K, Fujisawa M. No significant correlation of clinical outcomes between first- and second-line tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2015;35:3067–73.
Laitinen M, Parry M, Ratasvuori M, Wedin R, Albergo JI, Jeys L, Abudu A, Carter S, Gaston L, Tillman R, Grimer R. Survival and complications of skeletal reconstructions after surgical treatment of bony metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2015.
Bodnar L, Stec R, Cierniak S, Synowiec A, Wcislo G, Jesiotr M, Koktysz R, Kozlowski W, Szczylik C. Clinical usefulness of PI3K/Akt/mTOR genotyping in companion with other clinical variables in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients treated with everolimus in the second and subsequent lines. Ann Oncol. 2015.
Abdallah AO, Vallurupalli S, Kunthur A. Pazopanib- and bevacizumab-induced reversible heart failure in a patient with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a case report. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2015.
Lamuraglia M, Raslan S, Elaidi R, Oudard S, Escudier B, Slimane K, Penna RR, Wagner M, Lucidarme O. mTOR-inhibitor treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: contribution of Choi and modified Choi criteria assessed in 2D or 3D to evaluate tumor response. Eur Radiol. 2015.
Wang CH, Zhao TX, Li M, Zhang C, Xing XH. Characterization of a novel acinetobacter baumannii xanthine dehydrogenase expressed in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Lett. 2015.
Wu D, Gantier MP. Normalization of affymetrix miRNA microarrays for the analysis of cancer samples. Methods Mol Biol. 2015.
Berezikov E, Guryev V, van de Belt J, Wienholds E, Plasterk RH, Cuppen E. Phylogenetic shadowing and computational identification of human microRNA genes. Cell. 2005;120:21–4.
Croce CM. Causes and consequences of microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 2009;10:704–14.
Juan D, Alexe G, Antes T, Liu H, Madabhushi A, Delisi C, Ganesan S, Bhanot G, Liou LS. Identification of a microRNA panel for clear-cell kidney cancer. Urology. 2010;75:835–41.
Yi Z, Fu Y, Zhao S, Zhang X, Ma C. Differential expression of miRNA patterns in renal cell carcinoma and nontumorous tissues. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2010;136:855–62.
Qiu ZL, Shen CT, Song HJ, Wei WJ, Luo QY. Differential expression profiling of circulation microRNAs in PTC patients with non-(131)i and (131)i-avid lungs metastases: a pilot study. Nucl Med Biol. 2015;42:499–504.
Zhang J, Liu Y, Liu Z, Wang XM, Yin DT, Zheng LL, Zhang DY, Lu XB. Differential expression profiling and functional analysis of microRNAs through stage I-III papillary thyroid carcinoma. Int J Med Sci. 2013;10:585–92.
Chow TF, Youssef YM, Lianidou E, Romaschin AD, Honey RJ, Stewart R, Pace KT, Yousef GM. Differential expression profiling of microRNAs and their potential involvement in renal cell carcinoma pathogenesis. Clin Biochem. 2010;43:150–8.
Butz H, Szabo PM, Khella HW, Nofech-Mozes R, Patocs A, Yousef GM. MiRNA-target network reveals miR-124as a key miRNA contributing to clear cell renal cell carcinoma aggressive behaviour by targeting CAV1 and FLOT1. Oncotarget. 2015;6:12543–57.
Wittekind C, Oberschmid B. TNM classification of malignant tumors 2010: general aspects and amendments in the general section. Pathologe. 2010;31:333–4 .336-338
Wittekind C. 2010 TNM system: on the 7th edition of TNM classification of malignant tumors. Pathologe. 2010;31:331–2.
Selbach M, Schwanhausser B, Thierfelder N, Fang Z, Khanin R, Rajewsky N. Widespread changes in protein synthesis induced by microRNAs. Nature. 2008;455:58–63.
Tili E, Michaille JJ, Wernicke D, Alder H, Costinean S, Volinia S, Croce CM. Mutator activity induced by microRNA-155 (miR-155) links inflammation and cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:4908–13.
Sinha S, Dutta S, Datta K, Ghosh AK, Mukhopadhyay D. Von Hippel-Lindau gene product modulates tis11b expression in renal cell carcinoma: impact on vascular endothelial growth factor expression in hypoxia. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:32610–8.
Majid S, Saini S, Dar AA, Hirata H, Shahryari V, Tanaka Y, Yamamura S, Ueno K, Zaman MS, Singh K, Chang I, Deng G, Dahiya R. MicroRNA-205 inhibits SRC-mediated oncogenic pathways in renal cancer. Cancer Res. 2011;71:2611–21.
Jung M, Mollenkopf HJ, Grimm C, Wagner I, Albrecht M, Waller T, Pilarsky C, Johannsen M, Stephan C, Lehrach H, Nietfeld W, Rudel T, Jung K, Kristiansen G. MicroRNA profiling of clear cell renal cell cancer identifies a robust signature to define renal malignancy. J Cell Mol Med. 2009;13:3918–28.
Tan X, Qin W, Zhang L, Hang J, Li B, Zhang C, Wan J, Zhou F, Shao K, Sun Y, Wu J, Zhang X, Qiu B, Li N, Shi S, Feng X, Zhao S, Wang Z, Zhao X, Chen Z, Mitchelson K, Cheng J, Guo Y, He J. A 5-microRNA signature for lung squamous cell carcinoma diagnosis and HSA-miR-31 for prognosis. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:6802–11.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81100483) and the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 program; no. 2012AA021100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jie Zhu and Xin Ma contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, J., Ma, X., Zhang, Y. et al. Establishment of a miRNA-mRNA regulatory network in metastatic renal cell carcinoma and screening of potential therapeutic targets. Tumor Biol. 37, 15649–15663 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5135-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5135-6