Abstract
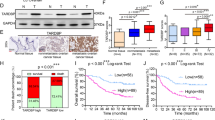
The malignancy of endometrial carcinoma (EC) largely results from its high invasive feature. The regulation of the mRNA splicing of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) is critical for EC-associated cancer vascularization and invasion. Recently, we have reported that poorly prognostic EC had high levels of YT521, a newly defined RNA splicing protein. However, whether YT521 may similarly regulate the splicing of VEGF-A in EC is unknown. Here, we showed that EC specimens contained significantly higher levels of YT521, compared to the adjacent non-tumor endometrial tissue. Higher levels of YT521 were detected in EC specimens with metastases. High-YT521 EC is associated with poor patient survival. In order to examine whether YT521 may regulate VEGF-A mRNA splicing in EC, we transfected an EC cell line HEC-1A with different doses of YT521 mimics. We found that YT521 dose-dependently increased the ratio of VEGF-165 vs VEGF-121 at both mRNA and protein level, suggesting that YT521 may promote VEGF-A mRNA splicing to favor a VEGF-165 isoform. Moreover, the increases in the ratio of VEGF-165 vs VEGF-121 by YT521 overexpression resulted in increases in EC cell invasion, while decreases in the ratio of VEGF-165 vs VEGF-121 by YT521 depletion resulted in decreases in EC cell invasion in a transwell cell migration assay. Further, overexpression of VEGF-165, but not overexpression of VEGF-121, increased EC cell invasiveness. Finally, a strong correlation was detected between the ratio of VEGF-165 vs VEGF-121 and the levels of YT521 in EC specimens. Together, these data suggest that YT521 may promote EC metastases by regulating mRNA splicing of VEGF-A.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wright JD, Barrena Medel NI, Sehouli J, Fujiwara K, Herzog TJ. Contemporary management of endometrial cancer. Lancet. 2012;379:1352–60.
Huo X, Li Y, Jiang Y, Sun X, Gu L, Guo W, et al. Inhibition of ocular neovascularization by co-inhibition of vegf-a and plgf. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;35:1787–96.
Jiang H, Wu X, Wang H, Huang C, Zhang L. Combined anti-plgf and anti-endostatin treatments inhibit ocular hemangiomas. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;36:930–6.
Zhou X, Qi Y. Larynx carcinoma regulates tumor-associated macrophages through plgf signaling. Sci Rep. 2015;5:10071.
Bu J, Bu X, Liu B, Chen F, Chen P. Inhibition of metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma by anti-plgf treatment. Tumour Biol. 2015;36:2695–701.
Chen B, Zhang C, Dong P, Guo Y, Mu N. Molecular regulation of cervical cancer growth and invasion by vegfa. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:11587–93.
Gong J, Zhu S, Zhang Y, Wang J. Interplay of vegfa and mmp2 regulates invasion of glioblastoma. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:11879–85.
Liu G, Xu S, Jiao F, Ren T, Li Q. Vascular endothelial growth factor b coordinates metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer. Tumour Biol. 2015;36:2185–91.
Mao D, Zhang Y, Lu H, Zhang H. Molecular basis underlying inhibition of metastasis of gastric cancer by anti-vegfa treatment. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:8217–23.
Zhou X, Qi Y. Plgf inhibition impairs metastasis of larynx carcinoma through mmp3 downregulation. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:9381–6.
Eichmann A, Simons M. Vegf signaling inside vascular endothelial cells and beyond. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2012;24:188–93.
Carmeliet P, Jain RK. Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature. 2011;473:298–307.
Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J. The biology of vegf and its receptors. Nat Med. 2003;9:669–76.
Xiao X, Prasadan K, Guo P, El-Gohary Y, Fischbach S, Wiersch J, et al. Pancreatic duct cells as a source of vegf in mice. Diabetologia. 2014;57:991–1000.
Xiao X, Guo P, Chen Z, El-Gohary Y, Wiersch J, Gaffar I, et al. Hypoglycemia reduces vascular endothelial growth factor a production by pancreatic beta cells as a regulator of beta cell mass. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:8636–46.
Imai Y, Matsuo N, Ogawa S, Tohyama M, Takagi T. Cloning of a gene, yt521, for a novel rna splicing-related protein induced by hypoxia/reoxygenation. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1998;53:33–40.
Nayler O, Hartmann AM, Stamm S. The er repeat protein yt521-b localizes to a novel subnuclear compartment. J Cell Biol. 2000;150:949–62.
Hirschfeld M, Zhang B, Jaeger M, Stamm S, Erbes T, Mayer S, et al. Hypoxia-dependent mrna expression pattern of splicing factor yt521 and its impact on oncological important target gene expression. Mol Carcinog. 2014;53:883–92.
Zhang B. zur Hausen A, Orlowska-Volk M, Jager M, Bettendorf H, Stamm S, Hirschfeld M, Yiqin O, Tong X, Gitsch G, Stickeler E: Alternative splicing-related factor yt521: an independent prognostic factor in endometrial cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2010;20:492–9.
Rafalska I, Zhang Z, Benderska N, Wolff H, Hartmann AM, Brack-Werner R, et al. The intranuclear localization and function of yt521-b is regulated by tyrosine phosphorylation. Hum Mol Genet. 2004;13:1535–49.
Stoss O, Olbrich M, Hartmann AM, Konig H, Memmott J, Andreadis A, et al. The star/gsg family protein rslm-2 regulates the selection of alternative splice sites. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:8665–73.
Kuramoto H, Tamura S, Notake Y. Establishment of a cell line of human endometrial adenocarcinoma in vitro. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1972;114:1012–9.
Acknowledgments
The project was supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC Nos. 81202045) and the Shanghai Science and Technology Committee Foundation (13ZR1432000).
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Bo Zhang and Xiaowen Shao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, B., Shao, X., Zhou, J. et al. YT521 promotes metastases of endometrial cancer by differential splicing of vascular endothelial growth factor A. Tumor Biol. 37, 15543–15549 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3908-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3908-y