Abstract
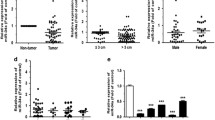
Nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a commonly occurring lung cancer. A combination of molecular biological treatments with regular chemotherapy may result in improved therapeutic outcome. Here, we reported significantly higher levels of fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) and significantly lower levels of miR-100 in the NSCLC specimen, compared to the paired NSCLC-adjacent normal lung tissues. Moreover, the levels of FGFR3 and miR-100 were inversely correlated. Bioinformatics analyses followed by luciferase reporter assay showed that miR-100 bound to the 3′-UTR of FGFR3 messenger RNA (mRNA) to inhibit its translation. Overexpression of miR-100 in NSCLC cells decreased FGFR3 protein levels, whereas inhibition of miR-100 increased FGFR3 protein levels, without affecting FGFR3 mRNA levels. Furthermore, overexpression of miR-100 suppressed cancer growth, migration, and chemosensitivity in NSCLC cells, while inhibition of miR-100 significantly facilitated them. Taken together, our data demonstrate that miR-100 may inhibit NSCLC through FGFR3.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caramori G, Casolari P, Cavallesco GN, Giuffre S, Adcock I, Papi A. Mechanisms involved in lung cancer development in COPD. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011;43:1030–44.
Buttery RC, Rintoul RC, Sethi T. Small cell lung cancer: the importance of the extracellular matrix. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2004;36:1154–60.
Jian H, Zhao Y, Liu B, Lu S. SEMA4b inhibits MMP9 to prevent metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:11051–6.
Jian H, Zhao Y, Liu B, Lu S. SEMA4b inhibits growth of non-small cell lung cancer in vitro and in vivo. Cell Signal. 2015;27:1208–13.
Pei J, Lou Y, Zhong R, Han B. MMP9 activation triggered by epidermal growth factor induced FoxO1 nuclear exclusion in non-small cell lung cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:6673–8.
Niu H, Wu B, Jiang H, Li H, Zhang Y, Peng Y, et al. Mechanisms of RhoGDI2 mediated lung cancer epithelial-mesenchymal transition suppression. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;34:2007–16.
Xiong Y, Ye T, Wang M, Xia Y, Wang N, Song X, et al. A novel cinnamide YLT26 induces breast cancer cells apoptosis via ROS-mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in vitro and inhibits lung metastasis in vivo. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;34:1863–76.
Yun M, Kim EO, Lee D, Kim JH, Kim J, Lee H, et al. Melatonin sensitizes H1975 non-small-cell lung cancer cells harboring a T790M-targeted epidermal growth factor receptor mutation to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;34:865–72.
Sun LX, Li WD, Lin ZB, Duan XS, Li XF, Yang N, et al. Protection against lung cancer patient plasma-induced lymphocyte suppression by Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;33:289–99.
Sicard F, Gayral M, Lulka H, Buscail L, Cordelier P. Targeting miR-21 for the therapy of pancreatic cancer. Mol Ther. 2013;21:986–94.
Tavano F, di Mola FF, Piepoli A, Panza A, Copetti M, Burbaci FP, et al. Changes in miR-143 and miR-21 expression and clinicopathological correlations in pancreatic cancers. Pancreas. 2012;41:1280–4.
Ali S, Ahmad A, Banerjee S, Padhye S, Dominiak K, Schaffert JM, et al. Gemcitabine sensitivity can be induced in pancreatic cancer cells through modulation of miR-200 and miR-21 expression by curcumin or its analogue CDF. Cancer Res. 2010;70:3606–17.
Deng W, Yan M, Yu T, Ge H, Lin H, Li J, et al. Quantitative proteomic analysis of the metastasis-inhibitory mechanism of miR-193a-3p in non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;35:1677–88.
Chen S, Li P, Li J, Wang Y, Du Y, Chen X, et al. MiR-144 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis and autophagy in lung cancer cells by targeting TIGAR. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;35:997–1007.
Zhang L, Qian J, Qiang Y, Huang H, Wang C, Li D, et al. Down-regulation of miR-4500 promoted non-small cell lung cancer growth. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;34:1166–74.
Hu X, Zhang F, Liu XR, Wu YT, Ni YM. Efficacy and potential microRNA mechanism for computed tomography-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of primary lung cancer and lung metastasis from liver cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;33:1261–71.
Wu N, Zhang C, Bai C, Han YP, Li Q. MiR-4782-3p inhibited non-small cell lung cancer growth via USP14. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;33:457–67.
Cortez MA, Valdecanas D, Zhang X, Zhan Y, Bhardwaj V, Calin GA, et al. Therapeutic delivery of miR-200c enhances radiosensitivity in lung cancer. Mol Ther. 2014;22:1494–503.
Pacurari M, Addison JB, Bondalapati N, Wan YW, Luo D, Qian Y, et al. The microRNA-200 family targets multiple non-small cell lung cancer prognostic markers in H1299 cells and BEAS-2B cells. Int J Oncol. 2013;43:548–60.
Jeon YJ, Middleton J, Kim T, Lagana A, Piovan C, Secchiero P, et al. A set of NF-kappaB-regulated microRNAs induces acquired TRAIL resistance in lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112:E3355–64.
Xiao F, Bai Y, Chen Z, Li Y, Luo L, Huang J, et al. Downregulation of HOXA1 gene affects small cell lung cancer cell survival and chemoresistance under the regulation of miR-100. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50:1541–54.
Liu J, Lu KH, Liu ZL, Sun M, De W, Wang ZX. MicroRNA-100 is a potential molecular marker of non-small cell lung cancer and functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting polo-like kinase 1. BMC Cancer. 2012;12:519.
Feng B, Wang R, Chen LB. MiR-100 resensitizes docetaxel-resistant human lung adenocarcinoma cells (SPC-A1) to docetaxel by targeting Plk1. Cancer Lett. 2012;317:184–91.
Soundararajan P, Fawcett JP, Rafuse VF. Guidance of postural motoneurons requires MAPK/ERK signaling downstream of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1. J Neurosci. 2010;30:6595–606.
Kuslak SL, Marker PC. Fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling through MEK-ERK is required for prostate bud induction. Differentiation. 2007;75:638–51.
Williamson AJ, Dibling BC, Boyne JR, Selby P, Burchill SA. Basic fibroblast growth factor-induced cell death is effected through sustained activation of p38MAPK and up-regulation of the death receptor p75NTR. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:47912–28.
An SJ, Liu P, Shao TM, Wang ZJ, Lu HG, Jiao Z, et al. Characterization and functions of vascular adventitial fibroblast subpopulations. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;35:1137–50.
Qi HP, Wang Y, Zhang QH, Guo J, Li L, Cao YG, et al. Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) through NF-kappaB/Brg1 and TGF-beta1 pathways attenuates cardiac remodeling in pressure-overloaded rat hearts. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;35:899–912.
Wang J, Liu W, Peng Y, Li W, Cheng T, Gao C, et al. Synergetic effect of alpha-lipoic acid with keratinocyte growth factor on protecting alveolar epithelial type II cells of rat fetus from hyperoxia-induced injury. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;33:953–66.
Kang J, Lee SY, Lee SY, Kim YJ, Park JY, Kwon SJ, et al. MicroRNA-99b acts as a tumor suppressor in non-small cell lung cancer by directly targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor 3. Exp Ther Med. 2012;3:149–53.
Giard DJ, Aaronson SA, Todaro GJ, Arnstein P, Kersey JH, Dosik H, et al. In vitro cultivation of human tumors: establishment of cell lines derived from a series of solid tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973;51:1417–23.
Liang CC, Park AY, Guan JL. In vitro scratch assay: a convenient and inexpensive method for analysis of cell migration in vitro. Nat Protoc. 2007;2:329–33.
Coronnello C, Benos PV. ComiR: combinatorial microRNA target prediction tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41:W159–64.
Dienstmann R, Rodon J, Prat A, Perez-Garcia J, Adamo B, Felip E, et al. Genomic aberrations in the FGFR pathway: opportunities for targeted therapies in solid tumors. Ann Oncol. 2014;25:552–63.
Yin Y, Betsuyaku T, Garbow JR, Miao J, Govindan R, Ornitz DM. Rapid induction of lung adenocarcinoma by fibroblast growth factor 9 signaling through FGF receptor 3. Cancer Res. 2013;73: 5730–41.
Imielinski M, Berger AH, Hammerman PS, Hernandez B, Pugh TJ, Hodis E, et al. Mapping the hallmarks of lung adenocarcinoma with massively parallel sequencing. Cell. 2012;150:1107–20.
Liao RG, Jung J, Tchaicha J, Wilkerson MD, Sivachenko A, Beauchamp EM, et al. Inhibitor-sensitive FGFR2 and FGFR3 mutations in lung squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2013;73:5195–205.
Brooks AN, Kilgour E, Smith PD. Molecular Pathways. Fibroblast growth factor signaling: a new therapeutic opportunity in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18:1855–62.
Ai X, Jia ZM, Wang J, DI GP, Zhang XU, Sun F, et al. Bioinformatics analysis of the target gene of fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 in bladder cancer and associated molecular mechanisms. Oncol Lett. 2015;10:543–9.
Langle YV, Belgorosky D, Prack Mc, Cormick B, Sahores A, Góngora A, et al. FGFR3 down-regulation is involved in BCG-induced bladder tumor growth inhibition. J Urol. 2015;S0022-5347:04308–6.
Li Z, Li X, Yu C, Wang M, Peng F, Xiao J, et al. MicroRNA-100 regulates pancreatic cancer cells growth and sensitivity to chemotherapy through targeting FGFR3. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:11751–9.
Paur J, Nika L, Maier C, Moscu-Gregor A, Kostka J, Huber D, et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 isoforms: novel therapeutic targets for hepatocellular carcinoma? Hepatology. 2015. doi:10.1002/hep.28023.
Wesche J, Haglund K, Haugsten EM. Fibroblast growth factors and their receptors in cancer. Biochem J. 2011; 437:199–213.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Jie Luo and Bin Chen contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, J., Chen, B., Ji, XX. et al. Overexpression of miR-100 inhibits cancer growth, migration, and chemosensitivity in human NSCLC cells through fibroblast growth factor receptor 3. Tumor Biol. 37, 15517–15524 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3850-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3850-z