Abstract
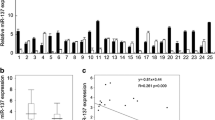
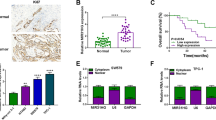
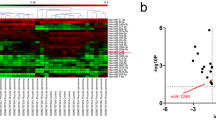
Thyroid carcinoma (TC) is a lethal cancer worldwide, whereas its carcinogenesis is not fully understood. Although growing evidence has demonstrated that dysregulation of microRNAs (miRNAs) contributes to the development of various cancers, the role of miRNAs in the pathogenesis of TC is poorly characterized. Here, we analyzed the levels of miR-449b in TC tissues and detected significantly lower miR-449b levels in TC tissues. Moreover, the low miR-449b levels were associated with poor survival. We then overexpressed miR-449b by miRNA mimic transfection and inhibited miR-449b by miRNA antisense transfection. Cell growth was analyzed by CCK-8 assay and MTT assay, and apoptosis and cell proliferation were analyzed by flow cytometry. Overexpression of miR-449b significantly inhibited cell growth, while depletion of miR-449b increased cell growth. Moreover, the effects of miR-449b on cell growth were through modulation of cell proliferation rather than through modulation of cell apoptosis. Targeted genes were predicted by a bioinformatics algorithm and confirmed by a dual luciferase reporter assay, showing that miR-449b binds to the 3′-UTR of MET (hepatocyte growth factor receptor) mRNA, to inhibit its expression in TC cells. MET levels were regulated by miR-449b in TT cells. Together, we show that reduced miR-449b levels in TT tissues may promote TC growth, through MET-mediated cell proliferation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang J, Wang Y, Li D, Jing S. Notch and TGF-beta/Smad3 pathways are involved in the interaction between cancer cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:379–85.
Chen J, Liu C, Yin L, Zhang W. The tumor-promoting function of ECRG4 in papillary thyroid carcinoma and its related mechanism. Tumour Biol. 2015;36:1081–9.
Deng X, Wu B, Xiao K, Kang J, Xie J, Zhang X, et al. Mir-146b-5p promotes metastasis and induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in thyroid cancer by targeting ZNRF3. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;35:71–82.
Ulbrich C, Pietsch J, Grosse J, Wehland M, Schulz H, Saar K, et al. Differential gene regulation under altered gravity conditions in follicular thyroid cancer cells: relationship between the extracellular matrix and the cytoskeleton. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2011;28:185–98.
Wang F, Wang P, Wang B, Fu ZJ, Yuan Y, Yan SL, et al. Association between TP53 Arg72Pro polymorphism and thyroid carcinoma risk. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:2723–8.
Wang H, Li YP, Chen JH, Yuan SF, Wang L, Zhang JL, et al. Prognostic significance of USP22 as an oncogene in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2013;34:1635–9.
Wan L, Zhu L, Xu J, Lu B, Yang Y, Liu F, et al. MicroRNA-409-3p functions as a tumor suppressor in human lung adenocarcinoma by targeting c-Met. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;34:1273–90.
Trusolino L, Bertotti A, Comoglio PM. Met signalling: principles and functions in development, organ regeneration and cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11:834–48.
Garouniatis A, Zizi-Sermpetzoglou A, Rizos S, Kostakis A, Nikiteas N, Papavassiliou AG. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptors 1,3 and caveolin-1 are implicated in colorectal cancer aggressiveness and prognosis—correlations with epidermal growth factor receptor, CD44v6, focal adhesion kinase, and c-Met. Tumour Biol. 2013;34:2109–17.
Liu H, Qian C, Shen Z. Anti-tumor activity of oridonin on SNU-5 subcutaneous xenograft model via regulation of c-Met pathway. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:9139–46.
Huang J, Dong B, Zhang J, Kong W, Chen Y, Xue W, et al. miR-199a-3p inhibits hepatocyte growth factor/c-Met signaling in renal cancer carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:5833–43.
Samadi AK, Cohen SM, Mukerji R, Chaguturu V, Zhang X, Timmermann BN, et al. Natural withanolide withaferin A induces apoptosis in uveal melanoma cells by suppression of Akt and c-MET activation. Tumour Biol. 2012;33:1179–89.
Li Y, Zhang S, Tang Z, Chen J, Kong W. Silencing of c-Met by RNA interference inhibits the survival, proliferation, and invasion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Tumour Biol. 2011;32:1217–24.
Grabellus F, Konik MJ, Worm K, Sheu SY, van de Nes JA, Bauer S, et al. MET overexpressing chordomas frequently exhibit polysomy of chromosome 7 but no MET activation through sarcoma-specific gene fusions. Tumour Biol. 2010;31:157–63.
Koo BS, Kim JM, Seo ST, Yoon YH, Kwon KR, Kim SH, et al. Upregulation of HGF and c-MET is associated with subclinical central lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014;21:2310–7.
Bentzien F, Zuzow M, Heald N, Gibson A, Shi Y, Goon L, et al. In vitro and in vivo activity of cabozantinib (XL184), an inhibitor of RET, MET, and VEGFR2, in a model of medullary thyroid cancer. Thyroid. 2013;23:1569–77.
Di Leva G, Croce CM. MiRNA profiling of cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2013;23:3–11.
Pereira DM, Rodrigues PM, Borralho PM, Rodrigues CM. Delivering the promise of miRNA cancer therapeutics. Drug Discov Today. 2013;18:282–9.
Mei Q, Li F, Quan H, Liu Y, Xu H. Busulfan inhibits growth of human osteosarcoma through miR-200 family microRNAs in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Sci. 2014;105:755–62.
Wang F, Xiao W, Sun J, Han D, Zhu Y. MiRNA-181c inhibits EGFR-signaling-dependent MMP9 activation via suppressing Akt phosphorylation in glioblastoma. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:8653–8.
Liu G, Jiang C, Li D, Wang R, Wang W. MiRNA-34a inhibits EGFR-signaling-dependent MMP7 activation in gastric cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:9801–6.
Bao J, Li D, Wang L, Wu J, Hu Y, Wang Z, et al. MicroRNA-449 and microRNA-34b/c function redundantly in murine testes by targeting E2F transcription factor-retinoblastoma protein (E2F-pRb) pathway. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:21686–98.
Yang X, Feng M, Jiang X, Wu Z, Li Z, Aau M, et al. miR-449a and miR-449b are direct transcriptional targets of E2F1 and negatively regulate pRb-E2F1 activity through a feedback loop by targeting CDK6 and CDC25A. Genes Dev. 2009;23:2388–93.
Scheffer AR, Holdenrieder S, Kristiansen G, von Ruecker A, Muller SC, Ellinger J. Circulating microRNAs in serum: novel biomarkers for patients with bladder cancer? World J Urol. 2014;32:353–8.
Fang Y, Gu X, Li Z, Xiang J, Chen Z. miR-449b inhibits the proliferation of SW1116 colon cancer stem cells through downregulation of CCND1 and E2F3 expression. Oncol Rep. 2013;30:399–406.
Dzikiewicz-Krawczyk A, Macieja A, Maly E, Januszkiewicz-Lewandowska D, Mosor M, Fichna M, et al. Polymorphisms in microRNA target sites modulate risk of lymphoblastic and myeloid leukemias and affect microRNA binding. J Hematol Oncol. 2014;7:43.
Chung TK, Lau TS, Cheung TH, Yim SF, Lo KW, Siu NS, et al. Dysregulation of microRNA-204 mediates migration and invasion of endometrial cancer by regulating FOXC1. Int J Cancer. 2012;130:1036–45.
Ostling P, Leivonen SK, Aakula A, Kohonen P, Makela R, Hagman Z, et al. Systematic analysis of microRNAs targeting the androgen receptor in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2011;71:1956–67.
Behr TM, Wulst E, Radetzky S, Blumenthal RD, Dunn RM, Gratz S, et al. Improved treatment of medullary thyroid cancer in a nude mouse model by combined radioimmunochemotherapy: doxorubicin potentiates the therapeutic efficacy of radiolabeled antibodies in a radioresistant tumor type. Cancer Res. 1997;57:5309–19.
Coronnello C, Benos PV. ComiR: combinatorial microRNA target prediction tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41:W159–164.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The Publisher and Editor retract this article in accordance with the recommendations of the Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE). After a thorough investigation we have strong reason to believe that the peer review process was compromised.
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s13277-017-5487-6.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Xu, L. & Wang, G. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Regulation of MET-mediated proliferation of thyroid carcinoma cells by miR-449b. Tumor Biol. 36, 8653–8660 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3619-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3619-4