Abstract
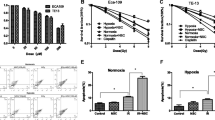
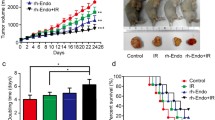
Radiation therapy is widely used in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Promoting radiation sensitivity is important. Recent studies have shown that fenofibrate can inhibit the growth of several cancer lines and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) expression in MCF-7 cells. However, few studies on the radiosensitive effect of fenofibrate on ESCCs under hypoxic condition have been conducted. In this study, we assessed the radiosensitive effects of fenofibrate on human ESCC cells. In vitro experiments showed the inhibition of cytotoxic effects after ionizing irradiation. We measured cell viability and clonogenic survival rate. Flow cytometry showed that fenofibrate pretreatment promoted apoptosis. The in vivo data also suggest that fenofibrate had radiosensitizing effects in ECA-109 cells xenografted into nude mice. Western blot and immunohistochemical analyses revealed that the HIF-1α and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) protein content decreased by fenofibrate. Thus, the inhibition of HIF-1α and VEGF expression in ESCC cells contributed to the radiosensitive effect. These data suggest that fenofibrate may be a potential radiosensitive drug.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee H, Park HC, Lee JA, et al. The efficacy of high-dose 3-dimensional conformal radiation therapy in patients with small hepatocellular carcinoma not eligible for other local modalities[J]. Am J Clin Oncol. 2013;36:162–6.
Dewas S, Mirabel X, Kramar A, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for liver primary and metastases: the Lille experience [J]. Cancer Radiother. 2012;16:58–69.
Brown LM, Devesa SS. Epidemiologic trends in esophageal and gastric cancer in the United States[J]. Surg Oncol Clin NAm. 2002;11:235–56.
Belozerov VE, Van Meir EG. Hypoxia inducible factor-1: a novel target for cancer therapy[J]. Anti-Cancer Drugs. 2005;16:901–9.
Yang Y, Sun M, Wang L, Jiao B. HIFs, angiogenesis, and cancer[J]. J Cell Biochem. 2013;114:967–74.
Meijer TW, Kaanders JH, et al. Targeting hypoxia, HIF-1, and tumor glucose metabolism to improve radiotherapy efficacy. J Clin Cancer Res: Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2012;18:5585–94.
Tanaka T, Kohno H, et al. Ligands for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors α andγinhibit chemically induced colitis and formation of aberrant crypt foci in rats[J]. Cancer Res. 2001;61:2424–8.
Maggiora M, Bologna M, et al. An overview of the effect of linoleic and conjugated-linoleic acids on the growth of several human tumor cell lines[J]. Int J Cancer. 2001;112:909–19.
Saidi SA, Holland CM, Charnock-Jones DS, et al. In vitro and in vivo effects of the PPARα agonists fenofibrate and retinoic acid in endometrial cancer[J]. Mol Cancer. 2006;5:13.
Thuillier P, Anchiraico GJ, Nickel KP, et al. Activators of peroxisome proliferator-activated-α partially inhibit mouse skin tumor promotion [J]. Mol Carcinog. 2000;29:134–42.
Zhou J, Zhang S, Xue J, et al. Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) suppresses hypoxia-inducible factor-1α(HIF-1α) signaling in cancer cells [J]. J Biol Chem. 2012;12:35161–9.
Greer SN, Metcalf JL, Wang Y, et al. The updated biology of hypoxia-inducible factor[J]. EMBO J. 2012;31:2448–60.
Vamesu S. Angiogenesis and tumor histologic type in primary breast cancer patients: an analysis of 155 needle core biopsies[J]. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2008;49:181–8.
Vermeulen PB, van Golen KL, Dirix LY. Angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, growth pattern, and tumor emboli in inflammatory breast cancer: a review of the current knowledge [J]. Cancer. 2010;116:2748–54.
Grabacka M, Placha W, Plonka PM, et al. Inhibition of melanoma metastases by fenofibrate[J]. Arch Dermatol Res. 2004;296:54–8.
Grabacka M, Plonka PM, Urbanska K, et al. Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha activation decreases metastatic potential of melanoma cells in vitro via down-regulation of Akt[J]. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:3028–36.
Tanaka T, Kohno H, Yoshitani S, et al. Ligands for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors α andγinhibit chemically induced colitis and formation of aberrant crypt foci in rats[J]. Cancer Res. 2001;61:2424–8.
Maggiora M, Bologna M, Cerù MP, et al. An overview of the effect of linoleic and conjugated-linoleic acids on the growth of several human tumor cell lines[J]. Int J Cancer. 2001;112:909–19.
Zhang J, Lu A, Beech D, et al. Suppression of breast cancer metastasis through the inhibition of VEGF-mediated tumor angiogenesis[J]. Cancer Ther. 2007;5:273–86.
Forsythe JA, Jiang BH, Iyer NV, et al. Activation of vascular endothelial growth factor gene transcription by hypoxia-inducible factor 1 [J]. Mol Cell Biol. 1996;16:4604–13.
Han JY, Oh SH, Morgillo F, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha and antiangiogenic activity of farnesyltransferase inhibitor SCH66336 in human aerodigestive tract cancer [J]. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97:1272–86.
Wang GL, Jiang BH, Rue EA, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92:5510–4.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD) (JX10231801), grants from Key Academic Discipline of Jiangsu Province “Medical Aspects of Specific Environments.”
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yangyang Ge, Jia Liu, and Xi Yang contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ge, Y., Liu, J., Yang, X. et al. Fenofibrate enhances radiosensitivity of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by suppressing hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression. Tumor Biol. 35, 10765–10771 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2149-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2149-9