Abstract
Introduction
Cellulose microfibril is a major cell wall polymer that plays an important role in the growth and development of plants. The gene cellulose synthase A (CesA), encoding cellulose synthases, is involved in the synthesis of cellulose microfibrils. However, the regulatory mechanism of CesA gene expression is not well understood, especially during the early developmental stages.
Objective
To identify factor(s) that regulate the expression of CesA genes and ultimately control seedling growth and development.
Methods
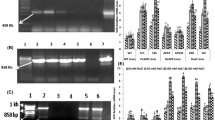
The presence of cis-elements in the promoter region of the eight CesA genes identified in flax (Linum usitatissimum L. ‘Nike’) seedlings was verified, and three kinds of ethylene-responsive cis-elements were identified in the promoters. Therefore, the effect of ethylene on the expression of four selected CesA genes classified into Clades 1 and 6 after treatment with 10−4 and 10−3 M 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC) was examined in the hypocotyl of 4–6-day-old flax seedlings.
Results
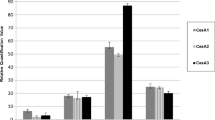
ACC-induced ethylene either up- or down-regulated the expression of the CesA genes depending on the clade to which these genes belonged, age of seedlings, part of the hypocotyl, and concentration of ACC.
Conclusion
Ethylene might be one of the factors regulating the expression of CesA genes in flax seedlings.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas M, Alabadi D, Blázquez MA (2013) Differential growth at the apical hook: all roads lead to auxin. Front Plant Sci 4:441
Burton RA, Shirley NJ, King BJ, Harvey AJ, Fincher GB (2004) The CesA gene family of barley. Quantitative analysis of transcripts reveals two groups of co-expressed genes. Plant Physiol 134:224–236
Chang WC, Lee TY, Huang HD, Huang HY, Pan RL (2008) PlantPAN: Plant promoter analysis navigator, for identifying combinatorial cis-regulatory elements with distance constraint in plant gene groups. BMC Genom 9:561
Chantreau M, Chabbert B, Billiard S, Hawkins S, Neutelings G (2015) Functional analyses of cellulose synthase genes in flax (Linum usitatissimum) by virus-induced gene silencing. Plant Biotechnol J. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12350
Chow CN, Zheng HQ, Wu NY, Chien CH, Huang HD, Lee TY, Chiang-Hsieh YF, Hou PF, Yang TY, Chang WC (2016) PlantPAN 2.0: an update of plant promoter analysis navigator for reconstructing transcriptional regulatory networks in plants. Nucl Acids Res 44:D1154–D1160
Clark AF, Villemez CL (1972) The formation of ß, 1 → 4 glucan from UDP-α-d-glucose catalyzed by a Phaseolus aureus enzyme. Plant Physiol 50:371–374
Doblin MS, Kurek I, Jacob-Wilk D, Delmer DP (2002) Cellulose biosynthesis in plants: from genes to rosettes. Plant Cell Physiol 43:1407–1420
Endres MW, Gregory BD, Gao Z, Foreman AW, Mlotshwa S, Ge X, Pruss GJ, Ecker JR, Bowman LH, Vance V (2010) Two plant viral suppressors of silencing require the ethylene-inducible host transcription factor RAV2 to block RNA silencing. PLoS Pathog 6:e1000729
Feng Y, Xu P, Li B, Li P, Wen X, An F, Gong Y, Xin Y, Zhu Z, Wang Y, Guo H (2017) Ethylene promotes root hair growth through coordinated EIN3/EIL1 and RHD6/RSL1 activity in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114:13834–13839
Goodstein DM, Shu S, Howson R, Neupane R, Hayes RD, Fazo J, Mitros T, Dirks W, Hellsten U, Putnam N, Rokhsar DS (2012) Phytozome: a comparative platform for green plant genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 40:D1178–D1186
Hamann T, Osborne E, Youngs HL, Misson J, Nussaume L, Somerville C (2004) Global expression analysis of CESA and CSL genes in Arabidopsis. Cellulose 11:279–286
Held MA, Penning B, Brandt AS, Kessans SA, Yong W, Scofield SR (2008) Small-interfering RNAs from natural antisense transcripts derived from a cellulose synthase gene modulate cell wall biosynthesis in barley. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:20534–20539
Higo K, Ugawa Y, Iwamoto M, Korenaga T (1999) Plant cis-acting regulatory DNA elements (PLACE) database: 1999. Nucleic Acids Res 27:297–300
Holland N, Holland D, Helentjaris T, Dhugga KS, Xoconostle-Cazares B, Delmer DP (2000) A comparative analysis of the plant cellulose synthase (CesA) gene family. Plant Physiol 123:1313–1323
Huang D, Wang S, Zhang B, Shang-Guan K, Shi Y, Zhang D, Liu X, Wu K, Xu Z, Fu X, Zhou Y (2015) A gibberellin-mediated DELLA-NAC signaling cascade regulates cellulose synthesis in rice. Plant Cell 27:1681–1696
Kagaya Y, Ohmiya K, Hattori T (1999) RAV1, a novel DNA-binding protein, binds to bipartite recognition sequence through two distinct DNA-binding domains uniquely found in higher plants. Nucleic Acids Res 27:470–478
Kim WC, Kim JY, Ko JH, Kim J, Han KH (2013) Transcription factor MYB46 is an obligate component of the transcriptional regulatory complex for functional expression of secondary wall-associated cellulose synthases in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Plant Physiol 170:1374–1378
Kumar M, Thammannagowda S, Buline V, Chiang V, Han KH, Joshi CP, Mansfield SD, Mellerowicz E, Sundberg B, Teeri T, Ellis BE (2009) An update on the nomenclature for the cellulose synthase genes in Populus. Trends Plant Sci 14:248–254
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the \({2^{-\Delta \Delta {\text{C}_\text{T}}}}\) method. Methods 25:402–408
Mokshina N, Gorshkova T, Deyholos MK (2014) Chitinase-like (CTL) and cellulose synthase (CESA) gene expression in gelatinous-type cellulosic walls of flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) bast fibers. PLoS One 9:e97949
Muday GK, Rahman A, Binder BM (2012) Auxin and ethylene: collaborators or competitors? Trends Plant Sci 17:181–195
Ohme-Takagi M, Suzuki K, Shinshi H (2000) Regulation of ethylene-induced transcription of defense genes. Plant Cell Physiol 41:1187–1192
Paek SH, Oh SE (2012) Cloning and characterization of cellulose synthase genes involved in primary cell wall synthesis in flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) In: Book of Abstracts for 10th International Congress on Plant Molecular Biology, Jeju, Korea, pp. 268
Peng J, Li Z, Wen X, Li W, Shi H, Yang L, Zhu H, Guo H (2014) Salt-induced stabilization of EIN3/EIL1 confers salinity tolerance by deterring ROS accumulation in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet 10:e1004664
Petti C, Hirano K, Stork J, DeBolt S (2015) Mapping of cellulose-deficient mutant named dwarf1-1 in Sorghum bicolor to the green revolution gene gibberellin20-oxidase reveals a positive regulatory association between gibberellin and cellulose biosynthesis. Plant Physiol 169:705–716
Raz V, Ecker JR (1999) Regulation of differential growth in the apical hook of Arabidopsis. Development 126:3661–3668
Richmond TA, Somerville CR (2001) Integrative approaches to determining Csl function. Plant Mol Biol 47:131–143
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson R (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5463–5467
Stanke M, Morgenstern B (2005) AUGUSTUS: a web server for gene prediction in eukaryotes that allows user-defined constraints. Nucleic Acids Res 33:W465–W467
Tanaka K, Murata K, Yamazaki M, Onosato K, Miyao A, Hirochika H (2003) Three distinct rice cellulose synthase catalytic subunit genes required for cellulose synthesis in the secondary wall. Plant Physiol 133:73–83
Taylor NG, Howells RM, Huttly AK, Vickers K, Turner SR (2003) Interactions among three distinct CesA proteins essential for cellulose synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:1450–1455
Tournier B, Sanchez-Ballesta MT, Jones B, Pesquet E, Regad F, Latché A, Pech JC, Bouzayen M (2003) New members of the tomato ERF family show specific epression pattern and diverse DNA-binding capacity to the GCC box element. FEBS Lett 550:149–154
Vandenbussche F, Petrášek J, Žádníková P, Hoyerová K, Pešek B, Raz V, Swarup R, Bennett M, Zažímalová E, Benková E, Van Der Straeten D (2010) The auxin influx carriers AUX1 and LAX3 are involved in auxin-ethylene interactions during apical hook development in Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings. Development 137:597–606
Wróbel M, Zebrowski J, Szopa J (2004) Polyhydroxybutyrate synthesis in transgenic flax. J Biotechnol 107:41–54
Wróbel-Kwiatkowska M, Turnau K, Góralska K, Anielska T, Szopa J (2012) Effects of genetic modifications to flax (Linum usitatissimum) on arbuscular mycorrhiza and plant performance. Mycorrhiza 22:493–499
Xie L, Yang C, Wang X (2011) Brassinosteroids can regulate cellulose biosynthesis by controlling the expression of CESA genes in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 62:4495–4506
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor Dr. Grzegorz Spychalski from the Institute of Natural Fibres and Medicinal Plants for providing the seeds of flax.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, H., Paek, SH. & Oh, SE. Effect of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC)-induced ethylene on cellulose synthase A (CesA) genes in flax (Linum usitatissimum L. ‘Nike’) seedlings. Genes Genom 40, 1237–1248 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-018-0720-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-018-0720-2