Abstract
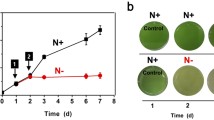
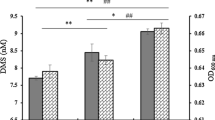
Sulfolobus species can grow on a variety of organic compounds as carbon and energy sources. These species degrade glucose to pyruvate by the modified branched Entner–Doudoroff pathway. We attempted to determine the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) under sugar-limited and sugar-rich conditions. RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) was used to quantify the expression of the genes and identify those DEGs between the S. acidocaldarius cells grown under sugar-rich (YT with glucose) and sugar-limited (YT only) conditions. The functions and pathways of the DEGs were examined using gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analyses. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was performed to validate the DEGs. Transcriptome analysis of the DSM 639 strain grown on sugar-limited and sugar-rich media revealed that 853 genes were differentially expressed, among which 481 were upregulated and 372 were downregulated under the glucose-supplemented condition. In particular, 70 genes showed significant changes in expression levels of ≥ twofold. GO and KEGG enrichment analyses revealed that the genes encoding components of central carbon metabolism, the respiratory chain, and protein and amino acid biosynthetic machinery were upregulated under the glucose condition. RNA-seq and qRT-PCR analyses indicated that the sulfur assimilation genes (Saci_2197–2204) including phosphoadenosine phosphosulfate reductase and sulfite reductase were significantly upregulated in the presence of glucose. The present study revealed metabolic networks in S. acidocaldarius that are induced in a glucose-dependent manner, improving our understanding of biomass production under sugar-rich conditions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berg IA, Ramos-Vera WH, Petri A, Huber H, Fuchs G (2010) Study of the distribution of autotrophic CO2 fixation cycles in Crenarchaeota. Microbiology 156:256–269
Borirak O, Rolfe MD, de Koning LJ, Hoefsloot HC, Bekker M, Dekker HL, Roseboom W, Green J, de Koster CG, Hellingwerf KJ (2015) Time-series analysis of the transcriptome and proteome of Escherichia coli upon glucose repression. Biochim Biophys Acta 1854:1269–1279
Brasen C, Esser D, Rauch B, Siebers B (2014) Carbohydrate metabolism in Archaea: current insights into unusual enzymes and pathways and their regulation. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 78:89–175
Brock TD, Brock KM, Belly RT, Weiss RL (1972) Sulfolobus: a new genus of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria living at low pH and high temperature. Arch Mikrobiol 84:54–68
Chen L, Brugger K, Skovgaard M, Redder P, She Q, Torarinsson E, Greve B, Awayez M, Zibat A, Klenk HP et al (2005) The genome of Sulfolobus acidocaldarius, a model organism of the Crenarchaeota. J Bacteriol 187:4992–4999
De Rosa M, Gambacorta A, Nicolaus B, Giardina P, Poerio E, Buonocore V (1984) Glucose metabolism in the extreme thermoacidophilic archaebacterium Sulfolobus solfataricus. Biochem J 224:407–414
Elferink MG, Albers SV, Konings WN, Driessen AJ (2001) Sugar transport in Sulfolobus solfataricus is mediated by two families of binding protein-dependent ABC transporters. Mol Microbiol 39:1494–1503
Ettema TJ, Ahmed H, Geerling AC, van der Oost J, Siebers B (2008) The non-phosphorylating glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPN) of Sulfolobus solfataricus: a key-enzyme of the semi-phosphorylative branch of the Entner–Doudoroff pathway. Extremophiles 12:75–88
Franchini AG, Egli T (2006) Global gene expression in Escherichia coli K-12 during short-term and long-term adaptation to glucose-limited continuous culture conditions. Microbiology 152:2111–2127
Gleissner M, Kaiser U, Antonopoulos E, Schafer G (1997) The archaeal SoxABCD complex is a proton pump in Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. J Biol Chem 272:8417–8426
Gogliettino M, Balestrieri M, Pocsfalvi G, Fiume I, Natale L, Rossi M, Palmieri G (2010) A highly selective oligopeptide binding protein from the archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus. J Bacteriol 192:3123–3131
Grogan DW (1989) Phenotypic characterization of the archaebacterial genus Sulfolobus: comparison of five wild-type strains. J Bacteriol 171:6710–6719
Hiller A, Henninger T, Schafer G, Schmidt CL (2003) New genes encoding subunits of a cytochrome bc1-analogous complex in the respiratory chain of the hyperthermoacidophilic crenarchaeon Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. J Bioenerg Biomembr 35:121–131
Huber H, Prangishvili D (2006) Sulfolobales. In: Falkow S, Rosenberg E, Dworkin M, Stackenbrandt E (eds) The prokaryotes. Springer, New York, pp 23–51
Huber G, Spinnler C, Gambacorta A, Stetter KO (1989) Metallosphaera sedula gen, and sp. nov. represents a new genus of aerobic, metal-mobilizing, thermoacidophilic archaebacteria. Syst Appl Microbiol 12:38–47
Komorowski L, Verheyen W, Schafer G (2002) The archaeal respiratory supercomplex SoxM from S. acidocaldarius combines features of quinole and cytochrome c oxidases. Biol Chem 383:1791–1799
Koning SM, Albers SV, Konings WN, Driessen AJ (2002) Sugar transport in (hyper) thermophilic archaea. Res Microbiol 153:61–67
Kouril T, Esser D, Kort J, Westerhoff HV, Siebers B, Snoep JL (2013) Intermediate instability at high temperature leads to low pathway efficiency for an in vitro reconstituted system of gluconeogenesis in Sulfolobus solfataricus. FEBS J 280:4666–4680
Lamble HJ, Heyer NI, Bull SD, Hough DW, Danson MJ (2003) Metabolic pathway promiscuity in the archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus revealed by studies on glucose dehydrogenase and 2-keto-3-deoxygluconate aldolase. J Biol Chem 278:34066–34072
Lamble HJ, Milburn CC, Taylor GL, Hough DW, Danson MJ (2004) Gluconate dehydratase from the promiscuous Entner–Doudoroff pathway in Sulfolobus solfataricus. FEBS Lett 576:133–136
Lamble HJ, Theodossis A, Milburn CC, Taylor GL, Bull SD, Hough DW, Danson MJ (2005) Promiscuity in the part-phosphorylative Entner–Doudoroff pathway of the archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus. FEBS Lett 579:6865–6869
Littlechild JA, Isupov M (2001) Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase from Sulfolobus solfataricus. Methods Enzymol 331:105–117
Lubben M, Kolmerer B, Saraste M (1992) An archaebacterial terminal oxidase combines core structures of two mitochondrial respiratory complexes. EMBO J 11:805–812
Lubben M, Arnaud S, Castresana J, Warne A, Albracht SP, Saraste M (1994a) A second terminal oxidase in Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. Eur J Biochem 224:151–159
Lubben M, Warne A, Albracht SP, Saraste M (1994b) The purified SoxABCD quinol oxidase complex of Sulfolobus acidocaldarius contains a novel haem. Mol Microbiol 13:327–335
Mortazavi A, Williams BA, McCue K, Schaeffer L, Wold B (2008) Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-SEq. Nat Methods 5:621–628
Purschke WG, Schmidt CL, Petersen A, Schafer G (1997) The terminal quinol oxidase of the hyperthermophilic archaeon Acidianus ambivalens exhibits a novel subunit structure and gene organization. J Bacteriol 179:1344–1353
Qureshi R, Sacan A (2013) Weighted set enrichment of gene expression data. BMC Syst Biol 7:S10
Ramos-Vera WH, Berg IA, Fuchs G (2009) Autotrophic carbon dioxide assimilation in Thermoproteales revisited. J Bacteriol 191:4286–4297
Reimann J, Esser D, Orell A, Amman F, Pham TK, Noirel J, Lindas AC, Bernander R, Wright PC, Siebers B et al (2013) Archaeal signal transduction: impact of protein phosphatase deletions on cell size, motility, and energy metabolism in Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. Mol Cell Proteomics 12:3908–3923
Schafer G, Engelhard M, Muller V (1999) Bioenergetics of the Archaea. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63:570–620
Selig M, Xavier KB, Santos H, Schonheit P (1997) Comparative analysis of Embden–Meyerhof and Entner–Doudoroff glycolytic pathways in hyperthermophilic archaea and the bacterium Thermotoga. Arch Microbiol 167:217–232
Simon G, Walther J, Zabeti N, Combet-Blanc Y, Auria R, van der Oost J, Casalot L (2009) Effect of O2 concentrations on Sulfolobus solfataricus P2. FEMS Microbiol Lett 299:255–260
Snijders AP, Walther J, Peter S, Kinnman I, de Vos MG, van de Werken HJ, Brouns SJ, van der Oost J, Wright PC (2006) Reconstruction of central carbon metabolism in Sulfolobus solfataricus using a two-dimensional gel electrophoresis map, stable isotope labelling and DNA microarray analysis. Proteomics 6:1518–1529
Ulas T, Riemer SA, Zaparty M, Siebers B, Schomburg D (2012) Genome-scale reconstruction and analysis of the metabolic network in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus. PLoS One 7:e43401
Wang L, Feng Z, Wang X, Wang X, Zhang X (2009) DEGseq: an R package for identifying differentially expressed genes from RNA-seq data. Bioinformatics 26:136–138
Wolf J, Stark H, Fafenrot K, Albersmeier A, Pham TK, Muller KB, Meyer BH, Hoffmann L, Shen L, Albaum SP et al (2016) A systems biology approach reveals major metabolic changes in the thermoacidophilic archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus in response to the carbon source L-fucose versus D-glucose. Mol Microbiol 102:882–908
Yang JW, Zheng DJ, Cui BD, Yang M, Chen YZ (2016) RNA-seq transcriptome analysis of a Pseudomonas strain with diversified catalytic properties growth under different culture medium. MicrobiologyOpen 5:626–636
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (NRF-2016R1A2B4011554) to J. Cha.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Jungwook Park declares that he has no conflict of interest. Areum Lee declares that she has no conflict of interest. Hyun-Hee Lee declares that she has no conflict of interest. Inmyoung Park declares that she has no conflict of interest. Young-Su Seo declares that he has no conflict of interest. Jaeho Cha declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Research involving human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, J., Lee, A., Lee, HH. et al. Profiling of glucose-induced transcription in Sulfolobus acidocaldarius DSM 639. Genes Genom 40, 1157–1167 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-018-0675-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-018-0675-3