Abstract
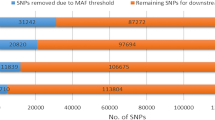
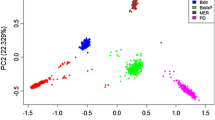
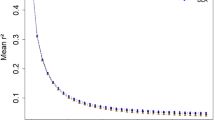
Knowledge of the extent of linkage disequilibrium (LD) between markers is crucial for determining the number of markers required for quantitative trait loci mapping, genome-wide association studies, and application of marker-assisted selection. In this study, we surveyed genome-wide LD using three genotyping BeadChips (9, 50, and 80 K) in 11 indigenous Ethiopian cattle populations and the Korean (Hanwoo) cattle breed. The overall mean r 2 values were 0.05 ± 0.12, 0.12 ± 0.20, and 0.20 ± 0.24 in the Ethiopian cattle populations for the 9, 50, and 80 K genotyping BeadChips, respectively. In Hanwoo cattle, these values were respectively 0.06 ± 0.13, 0.15 ± 0.23, and 0.15 ± 0.26. The level of LD was significantly affected by breed, genotyping BeadChip, and chromosome (P < 0.0001). For Ethiopian cattle populations, a moderate level of LD (r 2 = 0.22) extended at marker distances of 20–40 kb for the indicine-derived 80 K BeadChip, whereas it was only 0.14 for the 50 K BeadChip. As a consequence of the moderate r 2, genome-wide association studies in Ethiopian cattle populations require 75,000–150,000 indicine-derived SNPs (with a MAF ≥ 0.05). We suggest that indicine-derived SNPs maybe more suitable for genome-wide association studies and genomic selection in indigenous Ethiopian (or African) cattle populations.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arias JA, Keehan M, Fisher P, Coppieters W, Spelman R (2009) A high density linkage map of the bovine genome. BMC Genet 10:18
Boichard D, Chung H, Dassonneville R, David X, Eggen A, Fritz S, Gietzen KJ, Lawley CT, Sonstegard TS, Van Tassell CP et al (2012) Design of a bovine low-density SNP array optimized for imputation. PLoS One 7:e34130
Dadi H, Lee SH, Lee SS, Park C, Kim KS (2014) Inter- and Intra- population genetic divergence of East Asian cattle populations: focusing on Korean cattle. Genes Genom 36:261–265
Edea Z, Dadi H, Kim SW, Dessie T, Lee T, Kim H, Kim JJ, Kim KS (2013) Genetic diversity, population structure and relationships in indigenous cattle populations of Ethiopia and Korean Hanwoo breeds using SNP markers. Front Genet 4:35
Edea Z, Dadi H, Kim SW, Park JH, Shin GH, Dessie T, Kim KS (2014) Linkage disequilibrium and genomic scan to detect selective loci in cattle populations adapted to different ecological conditions in Ethiopia. J Anim Breed Genet 131:358–366
Edea Z, Bhuiyan MAS, Dessie T, Rothschild MF, Dadi H, Kim KS (2015) Genome-wide genetic diversity, population structure and admixture analysis in African and Asian cattle breeds. Animal 9:218–226
Espigolan R, Baldi F, Boligon AA, Souza RP, Gordo GM, Tonussi RL, Cardoso DF, Oliveira HN, Tonhati H, Sargolzaei M et al (2013) Study of whole genome linkage disequilibrium in Nellore cattle. BMC Genomics 14:305
Farnir F, Coppieters W, Arranz JJ (2000) Extensive genome-wide linkage disequilibrium in cattle. Genome Res 10:220–227
García-Gámez E, Sahana G, Gutiérrez-Gil B, Arranz JJ (2012) Linkage disequilibrium and inbreeding estimation in Spanish Churra sheep. BMC Genet 13:43
Goddard ME, Hayes BJ (2012) Genome-wide association studies and linkage disequilibrium in cattle. In: Womack JE (ed) Bovine genomics. Wiley-Blackwell, Oxford. doi:10.1002/9781118301739.ch13
Hayes BJ, Chamberlain AJ, Maceachern S, Savin K, McPartlan H, MacLeod I, Sethuraman L, Goddard ME (2009) A genome map of divergent artificial selection between Bos taurus dairy cattle and Bos Taurus beef cattle. Anim Genet 40:176–184
Hill WG, Robertson A (1986) Linkage disequilibrium in finite populations. Theor Appl Genet 38:226–231
Khatkar MS, Nicholas FW, Collins AR, Zenger KR, Cavanagh JA, Barris W, Schnabel RD, Taylor JF, Raadsma HW (2008) Extent of genome-wide linkage disequilibrium in Australian Holstein-Friesian cattle based on a high-density SNP panel. BMC Genomics 9:187
Kim ES, Berger PJ, Kirkpatrick BW (2009) Genome-wide scan for bovine twinning rate QTL using linkage disequilibrium. Anim Genet 40:300–307
Lee SH, Cho YM, Lim D, Kim HC, Choi BH, Park HS, Kim OH, Kim S, Kim TH, Yoon D et al (2011) Linkage disequilibrium and effective population size in Hanwoo Korean cattle. Asian-Aust J Anim Sci 24:1660–1665
Lee SH, Park BH, Sharma A, Dang CG, Lee SS, Choi TJ, Choy YH, Kim HC, Jeon KJ, Kim SD et al (2014) Hanwoo cattle: origin, domestication, breeding strategies and genomic selection. J Anim Sci Technol 56:2
Lu D, Sargolzaei M, Kelly M, Li C, Voort GV, Wang Z, Plastow G, Moore S, Miller SP (2012) Linkage disequilibrium in Angus, Charolais, and Crossbred beef cattle. Front Genet 3:152
Meuwissen TH, Hayes BJ, Goddard ME (2001) Prediction of total genetic value using genome-wide dense marker maps. Genetics 157:1819–1829
Porto-Neto LR, Kijas JW, Reverter A (2014) The extent of linkage disequilibrium in beef cattle breeds using high-density SNP genotypes. Genet Sel Evol 46:22
Prasad A, Schnabel RD, McKay SD, Murdoch B, Stothard P, Kolbehdari D, Wang Z, Taylor JF, Moore SS (2008) Linkage disequilibrium and signatures of selection on chromosomes 19 and 29 in beef and dairy cattle. Anim Genet 39:597–605
Qanbari S, Pimentel EC, Tetens J, Thaller G, Lichtner P, Sharifi AR, Simianer H (2010) The pattern of linkage disequilibrium in German Holstein cattle. Anim Genet 41:346–356
Tenesa A, Knott SA, Ward D, Smith D, Williams JL, Visscher PM (2003) Estimation of linkage disequilibrium in a sample of the United Kingdom dairy cattle population using unphased genotypes. J Anim Sci 81:617–623
The Bovine HapMap Consortium (2009) Genome-wide survey of SNP variation uncovers the genetic structure of cattle breeds. Science 324:528–532
Wiggans GR, Cooper TA, Vanraden PM, Olson KM, Tooker ME (2012) Use of the Illumina Bovine 3 K BeadChip in dairy genomic evaluation. J Dairy Sci 95:1552–1558
Zavattari P, Deidda E, Whalen M, Lampis R, Mulargia A, Loddo M, Eaves I, Mastio G, Todd JA, Cucca F (2000) Major factors influencing linkage disequilibrium by analysis of different chromosome regions in distinct populations: demography, chromosome recombination frequency and selection. Hum Mol Genet 9:2947–2957
Zhu M, Zhu B, Wang YH, Wu Y, Xu L, Guo LP, Yuan ZR, Zhang LP, Cao X, Gao HJ et al (2013) Linkage disequilibrium estimation of Chinese beef Simmental cattle using high-density SNP panels. Asian-Aust J Anim Sci 26:772–779
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the research grant of Chungbuk National University in 2013. The authors extend their gratitude to International Livestock Research (ILRI), Addis Ababa (Ethiopia), for providing logistical support. The indisputable cooperation of livestock officials, farmers and pastoralists during sampling is deeply acknowledged.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest
Ethics of animal experimentation
The research was conducted in the absence of any ethical issue on animal research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Edea, Z., Dadi, H., Dessie, T. et al. Genome-wide linkage disequilibrium analysis of indigenous cattle breeds of Ethiopia and Korea using different SNP genotyping BeadChips. Genes Genom 37, 759–765 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-015-0304-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-015-0304-3