Abstract
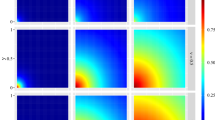
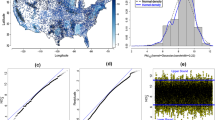
This article studies the dependence of spatial linear models using a slash distribution with a finite second moment. The parameters of the model are estimated with maximum likelihood by using the EM algorithm. To avoid identifiability problems, the cross-validation, the Trace and the maximum log-likelihood value are used to choose the parameter for adjusting the kurtosis of the slash distribution and the selection of the model to explain the spatial dependence. We present diagnostic techniques of global and local influences for exploring the sensibility of estimators and the presence of possible influential observations. A simulation study is developed to determine the performance of the methodology. The results showed the effectiveness of the choice criteria of the parameter for adjusting the kurtosis and for the selection of the spatial dependence model. It has also showed that the slash distribution provides an increased robustness to the presence of influential observations. As an illustration, the proposed model and its diagnostics are used to analyze an aquifer data. The spatial prediction with and without the influential observations were compared. The results show that the contours of the interpolation maps and prediction standard error maps showed low changes when we removed the influential observations. Thus, this model is a robust alternative in the spatial linear modeling for dependent random variables. Supplementary materials accompanying this paper appear online.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaike, H. (1974), “A new look at statistical model identification,” IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 19, 716–723.
Alcantara, I. C., and Cysneiros, F. J. A. (2013), “Linear regression models with slash-elliptical erros,” Computational Statistics and Data Analysis, 64, 153–164.
Anderson, J. F., Hardy, E. E., Roach, J. T., and Witmer, R. E. (1976), “A land use and land cover classification system for use with remote sensor data,” U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 964, Washington.
Assumpção, R. A. B., Uribe-Opazo, M. A. and Galea, M. (2014),“ Analysis of local influence in geostatistics using Student-t distribution,” Journal of Applied Statistics, 41, 2323–2341.
Belsley, D. A., Kuh, E., Weslsh, R. E. (1980) Regression diagnostics: identifying influential data and sources of collinearity John Wiley, New York.
Christensen, R., Johnson, W., and Pearson L. (1996), “Crediction diagnostics for spatial linear models,” Biometrika, 79, 583–591.
Cook, R. D. (1977), “Detection of influential observations in linear regression,” Technometrics, 19(1), 15–18.
Cook, R. D. (1986), “Assessment of local influence,” Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, B 48, 133–169.
De Bastiani, F., Mariz de Aquino Cysneiros, A. H., Uribe-Opazo, M. A., and Galea, M. (2015), “Influence diagnostics in elliptical spatial linear models,” TEST, 24 (2), 322–340.
Diggle, P. J., and Ribeiro Jr., P. J. (2007), Model-based Geostatistics Springer, New York.
Galea, M., Díaz-García, J. A., and Vilca, F. (2008), “Influence diagnostics in the capital asset pricing model under elliptical distributions,” Journal of Applied Statistics, 35, 179–192.
Genton, M., and Zhang, H., (2012), “Identifiability problems in some non-gaussian spatial random fields,” Chilean Journal of Statistics, 3 (2), 171–179.
Gradshteyn, I., and Ryzhik, I. (2000), Tables of Integrals, Series and Products Academic Press, New York.
Guedes, L.P.C., Uribe-Opazo, M., Ribeiro Jr., P. J. (2013), “Influence of incorporating geometric anisotropy on the construction of thematic maps of simulated data and chemical attributes of soil,” Chilean Journal of Agricultural Research, 73, 414–423.
Jamshidian, M. (2001), “A note on parameter and standard error estimation in adaptive robust regression,” Journal of Statistics Computation and Simulation, 71, 11–27.
Jones, R. (1989), “Fitting a stochastic partial differential equation to aquifer data,” Stoch Hydrol Hydraul, 3, 85–96.
Kano, Y., Berkane, M., and Bentler, P. M. (1993), “Statistical inference based on pseudo-maximum likelihood estimators in elliptical populations,” Journal of the American Statistical Association, 88 (421), 135–143.
Krippendorff, K. (2004), Content Analysis: an Introduction to its Methodology Sage, Thousand Oaks.
Lange, K., Little, R., and Taylor, J. (1989), “Robust statistical modeling using the t distribution,” Journal of the American Statistical Association, 84, 881–896.
Lange, K., and Sinsheimer, J. S. (1993), “Normal/independent distributions and their applications in robust regression,” Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 2, 175–198.
Magnus, J., and Neudecker, H. (1999), Matrix differential calculus with applications in statistics and econometrics John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Mardia, K., and Marshall, R. (1984), “Maximum likelihood estimation of models for residual covariance in spatial regression,” Biometrika, 71, 135–146.
Matérn, B. (1986) Lecture notes in statistics Springer, New York.
Matheron, G. (1963), “Principles of geostatistics,” Economic Geology, 58 (1), 1246–1266.
Militino, A., Palacius, M., and Ugarte, M. (2006), “Outliers detection in multivariate spatial linear models,” Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference, 136, 125–146.
Mitchell, A. (1989), “The information matrix, skewness tensor and ?-connections for the general multivariate elliptic distribution,” Annals of the Institute of Statistical Mathematics, 41, 289–304.
Osorio, F., Paula, G., and Galea, M. (2009), “On estimation and influence diagnostics for the grubbs model under heavy-tailed distributions,” Computational Statistics and Data Analysis, 53 (4), 1249–1263.
Pan, J., Fei, Y., and Foster, P. (2014), “Case-deletion diagnostics for linear mixed models,” Technometrics, 56 (3), 269–281.
Poon, W.,and Poon, Y. S. (1999), “Conformal normal curvature and assessment of local influence,” Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, B 61, 51–61.
Ribeiro Jr., P. J., and Diggle, P. J. (2001), “Geor: a package for geostatistical analysis,” R-NEWS 1 (2), 15–18.
R Development Core Team. (2016), R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria.
Uribe-Opazo, M., Borssoi, J., and Galea, M. (2012), “Influence diagnostics in gaussian spatial linear models,” Journal of Applied Statistics, 39 (3), 615–630.
Venables, W. N., and Ripley, B. D. (2002), Modern Applied Statistics with S Springer, New York.
Watanabe, M., and Yamaguchi, K. (2004), The EM algorithm and related statistical models Marcel Dekker, New York.
Zhang, H. (2004), “Inconsistent estimation and asymptotically equivalent interpolations in model based geostatistics,” Journal of the American Statistical Association, 99, 250–261.
Zhu, H., Ibrahim, J., Lee, S., and Zhang, H. (2007), “Perturbation selection and influence measures in local influence analysis,” Annals of Statistics, 35, 2565–2588.
Zhu, H. T., Lee, S. Y., Wei, B. C., and Zhou, J. (2001), “Case-deletion measures for models with incomplete data,” Biometrika, 88, 727–737.
Funding
Funding was provided by Capes, Fundação Araucária, CNPq Brazil, FONDECYT (Grant No. 1150325).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fagundes, R.S., Uribe-Opazo, M.A., Galea, M. et al. Spatial Variability in Slash Linear Modeling with Finite Second Moment. JABES 23, 276–296 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13253-018-0322-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13253-018-0322-0