Abstract
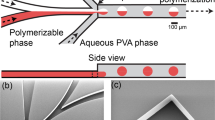
Controlling the merging of different microdroplets in a microfluidics system could generate a multitude of complex droplets because of their inherent surface tension, but poses a significant challenge because of their high surface tension. Here, a novel microfluidic merging technique is introduced using an asymmetric cross-junction geometry which increases the interfacial compression between two microdroplets. Microdroplets of two viscous polymer solutions, oxidized dextran (ODX) and N-carboxyethyl chitosan (N-CEC), which can undergo a crosslinking reaction via Schiff base formation, are allowed to merge at the asymmetric cross-junction without the assistance of additional merging schemes. The N-CEC and ODX microdroplets being formed at their orifices contact at a more favorable position to overcome their interfacial tension through this asymmetric geometry, until the interfacial layer breaks and pushes the former (with higher viscosity) into the latter. On the other hand, a typical symmetric cross-junction geometry cannot induce merging, because of insufficient interfacial compression generated by direct collision between two droplets. The merged N-CEC and ODX droplets soon become completely homogeneous via diffusion, ultimately leading to in situ microgel formation. Changing the concentration of ODX further controls the crosslinking density of the microgels. In addition, the viability of cells encapsulated within the microgels is well maintained, demonstrating the biocompatibility of the entire process. Taken together, the microfluidic merging technique introduced here could be broadly applicable for engineering cell-encapsulated microgels for biomedical applications.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Thorsen, R. W. Roberts, F. H. Arnold, and S. R. Quake, Phys. Rev. Lett., 86, 4163 (2001).
C. Cramer, P. Fischer, and E. J. Windhab, Chem. Eng. Sci., 59, 3045 (2004).
S. L. Anna, N. Bontoux, and H. A. Stone, Appl. Phys. Lett., 82, 364 (2003).
S. A. Nabavi, G. T. Vladisavljevic, and V. Manovic, Chem. Eng. J., 322, 140 (2017).
H. F. Chan, S. Ma, J. Tian, and K. W. Leong, Nanoscale, 9, 3485 (2017).
A. T. Tyowua, S. G. Yiase, and B. P. Binks, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 488, 127 (2017).
Q. Zhang, S. Savagatrup, P. Kaplonek, P. H. Seeberger, and T. M. Swager, ACS Cent. Sci., 3, 309 (2017).
S. Seiffert, M. B. Romanowsky, and D. A. Weitz, Langmuir, 26, 14842 (2010).
S. Y. Teh, R. Lin, L. H. Hung, and A. P. Lee, Lab Chip, 8, 198 (2008).
M. Sun, S. S. Bithi, and S. A. Vanapalli, Lab Chip, 11, 3949 (2011).
Y. C. Tan, Y. L. Ho, and A. P. Lee, Microfluid. Nanofluid., 3, 495 (2007).
C. H. Yang, Y. S. Lin, K. S. Huang, Y. C. Huang, E. C. Wang, J. Y. Jhong, and C. Y. Kuo, Lab Chip, 9, 145 (2009).
K. Liu, H. J. Ding, Y. Chen, and X. Z. Zhao, Microfluid. Nanofluid., 3, 239 (2007).
N. Bremond, A. R. Thiam, and J. Bibette, Phys. Rev. Lett., 100, 024501 (2008).
B. C. Lin and Y. C. Su, J. Micromech. Microeng., 18, 115005 (2008).
D. R. Link, S. L. Anna, D. A. Weitz, and H. A. Stone, Phys. Rev. Lett., 92, 054503 (2004).
Y. C. Tan, J. S. Fisher, A. I. Lee, V. Cristini, and A. P. Lee, Lab Chip, 4, 292 (2004).
H. Sato, H. Matsumura, S. Keino, and S. Shoji, J. Micromech. Microeng., 16, 2318 (2006).
B. Ziaie, A. Baldi, M. Lei, Y. Gu, and R. A. Siegel, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 56, 145 (2004).
S. Kim, J. Oh, and C. Cha, Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces, 147, 1 (2016).
P. C. Gach, K. Iwai, P. W. Kim, N. J. Hillson, and A. K. Singh, Lab Chip, 17, 3388 (2017).
E. Um and J. K. Park, Lab Chip, 9, 207 (2009).
G. F. Christopher, J. Bergstein, N. B. End, M. Poon, C. Nguyen, and S. L. Anna, Lab Chip, 9, 1102 (2009).
Y. C. Tan, Y. L. Ho, and A. P. Lee, Microfluid. Nanofluid., 3, 495 (2007).
S. Okushima, T. Nisisako, T. Torii, and T. Higuchi, Langmuir, 20, 9905 (2004).
L. Y. Chu, A. S. Utada, R. K. Shah, J. W. Kim, and D. A. Weitz, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 46, 8970 (2007).
V. Chokkalingam, B. Weidenhof, M. Krämer, S. Herminghaus, R. Seemann, and W. F. Maier, ChemPhysChem, 11, 2091 (2010).
V. Chokkalingam, B. Weidenhof, M. Krämer, W. F. Maier, S. Herminghaus, and R. Seemann, Lab Chip, 10, 1700 (2010).
B. J. Jin, Y. W. Kim, Y. Lee, and J. Y. Yoo, J. Micromech. Microeng., 20, 035003 (2010).
L. M. Fidalgo, C. Abell, and W. T. Huck, Lab Chip, 7, 984 (2007).
X. Niu, S. Gulati, J. B. Edel, and A. J. deMello, Lab Chip, 8, 1837 (2008).
J. Sivasamy, Y. C. Chim, T. N. Wong, N. T. Nguyen, and L. Yobas, Microfluid. Nanofluid., 8, 409 (2010).
H. Gu, M. H. G. Duits, and F. Mugele, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 12, 2572 (2011).
M. Lee, J. W. Collins, D. M. Aubrecht, R. A. Sperling, L. Solomon, J. W. Ha, G. R. Yi, D. A. Weitz, and V. N. Manoharan, Lab Chip, 14, 509 (2014).
M. Zagnoni and J. M. Cooper, Lab Chip, 9, 2652 (2009).
A. R. Guzman, H. S. Kim, P. de Figueiredo, and A. Han, Biomed. Microdevices, 17, 35 (2015).
V. B. Varma, A. Ray, Z. M. Wang, Z. P. Wang, and R. V. Ramanujan, Sci. Rep., 6, 37671 (2016).
J. Jung, K. Kim, S. C. Choi, and J. Oh, Biotechnol. Lett., 36, 1549 (2014).
L. Weng, A. Romanov, J. Rooney, and W. Chen, Biomaterials, 29, 3905 (2008).
J. Jung and J. Oh, Biomicrofluidics, 8, 036503 (2014).
J. Oh, K. Kim, S. Choi, and J. Jung, Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct., 9, 739 (2014).
J. D. Tice, H. Song, A. D. Lyon, and R. F. Ismagilov, Langmuir, 19, 9127 (2003).
J. D. Berry, M. J. Neeson, R. R. Dagastine, D. Y. C. Chan, and R. F. Tabor, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 454, 226 (2015).
S. Fordham, Proc. Royal Soc. A, 194, 1 (1948).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Acknowledgment: This work was supported by National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (2016R1C1B2014747, 2017R1A4A1015681, and 2017M3A9C6033875).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jang, Y., Cha, C., Jung, J. et al. Interfacial Compression-Dependent Merging of Two Miscible Microdroplets in an Asymmetric Cross-Junction for In Situ Microgel Formation. Macromol. Res. 26, 1143–1149 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-019-7013-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-019-7013-8