Abstract
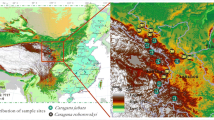
The effect of altitude on the composition and diversity of microbial communities have attracted highly attention recently but is still poorly understood. We used 16S rRNA gene clone library analyses to characterize the bacterial communities from the rhizosphere and roots of Stellera chamaejasme in the Tibetan Plateau. Our results revealed that Actinobacteria and Proteobacteria were dominant bacteria in this medicinal plant in the rhizosphere and root communities. The Shannon diversity index showed that the bacterial diversity of rhizosphere follows a small saddle pattern, while the roots possesses of a hump-backed trend. Significant differences in the composition of bacterial communities between rhizosphere and roots were detected based on multiple comparisons analysis. The community of Actinobacteria was found to be significantly negative correlated with soil available P (p < 0.01), while the phylum of Proteobacteria showed a positive relationship with available P (p < 0.05). Moreover, redundancy analysis indicated that soil phosphorus, pH, latitude, elevation and potassium positively correlated with bacterial communities associated with rhizosphere soils. Taken together, we provide evidence that bacterial communities associated with S. chamaejasme exhibited some certain elevational pattern, and bacterial communities of rhizosphere soil were regulated by environmental characteristics along elevational gradients in this alpine ecosystem.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson I, Abt B, Lykidis A, Klenk HP, Kyrpides N, Ivanova N (2012) Genomics of aerobic cellulose utilization systems in actinobacteria. PLoS One 7:e39331
Anwar S, Ali B, Sajid I (2016) Screening of rhizospheric actinomycetes for various in-vitro and in-vivo plant growth promoting (PGP) traits and for agroactive compounds. Front Microbiol 7:1334
Bodenhausen N, Horton MW, Bergelson J (2013) Bacterial communities associated with the leaves and the roots of Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS One 8:e56329
Bryant JA, Lamanna C, Morlon H, Kerkhoff AJ, Enquist BJ, Green JL (2008) Microbes on mountainsides: contrasting elevational patterns of bacterial and plant diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(Supplement 1):11505–11511
Cole JR, Wang Q, Fish JA, Chai B, McGarrell DM, Sun YN, Brown CT, Porras-Alfaro A, Kuske CR, Tiedje JM (2014) Ribosomal database project: data and tools for high throughput rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 42:633–642
Colwell RK, Lees DC (2000) The mid-domain effect: geometric constraints on the geography of species richness. Trends Ecol Evol 15:70–76
Compant S, Mitter B, Colli-Mull JG, Gangl H, Sessitsch A (2011) Endophytes of grapevine flowers, berries, and seeds: identification of cultivable bacteria, comparison with other plant parts, and visualization of niches of colonization. Microb Ecol 62:188–197
Corneo PE, Pellegrini A, Cappellin L, Roncador M, Chierici M, Gessler C, Pertot I (2013) Microbial community structure in vineyard soils across altitudinal gradients and in different seasons. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 84:588–602
Costa R, Götz M, Mrotzek N, Lottmann J, Berg G, Smalla K (2006) Effects of site and plant species on rhizosphere community structure as revealed by molecular analysis of microbial guilds. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 56:236–249
Cui HY, Jin H, Liu Q, Yan ZQ, Ding L, Qin B (2014) Nematicidal metabolites from roots of Stellera chamaejasme against Bursaphelenchus xylophilus and Bursaphelenchus mucronatus. Pest Manag Sci 70:827–835
Cui HY, Yang XY, Lu DX, Jin H, Yan ZQ, Chen JX, Li XZ, Qin B (2015) Isolation and characterization of bacteria from the rhizosphere and bulk soil of Stellera chamaejasme L. Can J Microbiol 61:171–181
Djukic I, Zehetner F, Mentler A, Gerzabek MH (2010) Microbial community composition and activity in different alpine vegetation zones. Soil Biol Biochem 42:155–161
Faoro H, Alves AC, Souza EM, Rigo LU, Cruz LM, Al-Janabi SM, Monteiro RA, Baura VA, Pedrosa FO (2010) Influence of soil characteristics on the diversity of bacteria in the southern Brazilian Atlantic forest. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:4744–4749
Fierer N, McCain CM, Meir P, Zimmermann M, Rapp JM, Silman MR, Knight R (2011) Microbes do not follow the elevational diversity patterns of plants and animals. Ecology 92:797–804
França L, Sannino C, Turchetti B, Buzzini P, Margesin R (2016) Seasonal and altitudinal changes of culturable bacterial and yeast diversity in alpine forest soils. Extremophiles 20:855–873
Galperin MY (2013) Genomic diversity of spore-forming Firmicutes. Microbiol Spectr 1: TBS-0015-2012
Gottel NR, Castro HF, Kerley M, Yang Z, Pelletier DA, Podar M, Karpinets T, Uberbacher E, Tuskan GA, Vilgalys R, Doktycz MJ, Schadt CW (2011) Distinct microbial communities within the endosphere and rhizosphere of Populus deltoides roots across contrasting soil types. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:5934–5944
Guo GX, Kong WD, Liu JB, Zhao JX, Du HD, Zhang XZ, Xia PH (2015a) Diversity and distribution of autotrophic microbial community along environmental gradients in grassland soils on the Tibetan plateau. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:8765–8776
Guo HR, Cui HY, Jin H, Yan ZQ, Ding L, Qin B (2015b) Potential allelochemicals in root zone soils of Stellera chamaejasme L. and variations at different geographical growing sites. Plant Growth Regul 77:335–342
Huber T, Faulkner G, Hugenholtz P (2004) Bellerophon: a program to detect chimeric sequences in multiple sequence alignments. Bioinformatics 20:2317–2319
Jin H, Yang XY, Yan ZQ, Liu Q, Li XZ, Chen JX, Zhang DH, Zeng LM, Qin B (2014) Characterization of rhizospere and endophytic bacterial communities from leaves, stems and roots of medicinal Stellera chamaejasme L. Syst Appl Microbiol 37:376–385
Jin H, Yang XY, Lu DX, Li CJ, Yan ZQ, Li XZ, Zeng LM, Qin B (2015) Phylogenic diversity and tissue specificity of fungal endophytes associated with the pharmaceutical plant, Stellera chamaejasme L. revealed by a cultivation independent approach. Anton Leeuw Int J G 108:835–850
Kan FL, Chen ZY, Wang ET, Tian CF, Sui XH, Chen WX (2007) Characterization of symbiotic and endophytic bacteria isolated from root nodules of herbaceous legumes grown in Qinghai-Tibet plateau and in other zones of China. Arch Microbiol 188:103–115
Khan AL, Waqas M, Kang SM, Al-Harrasi A, Hussain J, Al-Rawahi A, Al-Khiziri S, Ullah I, Ali L, Jung HY, Lee IJ (2014) Bacterial endophyte Sphingomonas sp. LK11 produces gibberellins and IAA and promotes tomato plant growth. J Microbiol 52:689–695
Kourteva PS, Ehrenfelda JG, Häggblom M (2003) Experimental analysis of the effect of exotic and native plant species on the structure and function of soil microbial communities. Soil Biol Biochem 35:895–905
Lane DJ (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley, New York, pp 115–175
Li XZ, Rui JP, Mao YJ, Yannarell A, Mackie R (2014) Dynamics of the bacterial community structure in the rhizosphere of a maize cultivar. Soil Biol Biochem 68:392–401
Li YC, Li Z, Li ZW, Jiang YH, Weng BQ, Lin WX (2016) Variations of rhizosphere bacterial communities in tea (Camellia sinensis L.) continuous cropping soil by high-throughput pyrosequencing approach. J Appl Microbiol 121:787–799
Lu RK (2000) Methods of soil and agro-chemistry. Chinese Agricultural Science and Technology Press, Beijing
Lugtenberg B, Kamilova F (2009) Plant-growth promoting rhizobacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 63:541–556
Männistö MK, Tiirola M, Häggblom MM (2007) Bacterial communities in Arctic fields of Finnish Lapland are stable but highly pH-dependent. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 59:452–465
Margesin R, Jud M, Tscherko D, Schinner F (2009) Microbial communities and activities in alpine and subalpine soils. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 67:208–218
Padda KP, Puri A, Chanway CP (2016) Effect of GFP tagging of Paenibacillus polymyxa P2b-2R on its ability to promote growth of canola and tomato seedlings. Biol Fertil Soils 52:377–387
Palaniyandi SA, Yang SH, Zhang L, Suh JW (2013) Effects of actinobacteria on plant disease suppression and growth promotion. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:9621–9636
Pragya R, Yasmin A, Anshula J (2012) An insight into agricultural properties of actinomycetes. Int J Res BioSci 1:7–12
Qiu J (2008) China: the third pole. Nature 454:393–396
Rosenblueth M, Martínez-Romero E (2006) Bacterial endophytes and their interactions with hosts. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 19:827–837
Ryan RP, Germaine K, Franks A, Ryan DJ, Dowling DN (2008) Bacterial endophytes: recent developments andapplications. FEMS Microbiol Lett 278:1–9
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ, Sahl JW, Stres B, Thallinger GG, van Horn DJ, Weber CF (2009) Introducing mothur: opensource, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7537–7541
Shen SY, Fulthorpe R (2015) Seasonal variation of bacterial endophytes in urban trees. Front Microbiol 6:427
Shen CC, Xiong JB, Zhang HY, Feng YZ, Lin XG, Li XY, Liang WJ, Chu HY (2013) Soil pH drives the spatial distribution of bacterial communities along elevation on Changbai Mountain. Soil Biol Biochem 57:204–211
Shen CC, Ni YY, Liang WJ, Wang JJ, Chu HY (2015) Distinct soil bacterial communities along a small-scale elevational gradient in alpine tundra. Front Microbiol 6:582
Singh D, Takahashi K, Kim M, Chun J, Adams JM (2012) A hump-backed trend in bacterial diversity with elevation on Mount Fuji, Japan. Microb Ecol 63:429–437
Singh D, Lee-Cruz L, Kim WS, Kerfahi D, Chun JH, Adams JM (2014) Strong elevational trends in soil bacterial community composition on Mt. Halla, South Korea. Soil Biol Biochem 68:140–149
Sundqvist MK, Liu ZF, Giesler R, Wardle DA (2014) Plant and microbial responses to nitrogen and phosphorus addition across an elevational gradient in subarctic tundra. Ecology 95:1819–1835
Tamreihao K, Ningthoujam DS, Nimaichand S, Singh ES, Reena P, Singh SH, Nongthomba U (2016) Biocontrol and plant growth promoting activities of a Streptomyces corchorusii strain UCR3-16 and preparation of powder formulation for application as biofertilizer agents for rice plant. Microbiol Res 192:260–270
Teixeira LCRS, Peixoto RS, Cury JC, Sul WJ, Pellizari VH, Tiedje J, Rosado AS (2010) Bacterial diversity in rhizosphere soil from Antarctic vascular plants of Admiralty Bay, maritime Antarctica. ISME J 4:989–1001
Terrazas RA, Giles C, Paterson E, Robertson-Albertyn S, Cesco S, Mimmo T, Pii Y, Bulgarelli D (2016) Plant-microbiota interactions as a driver of the mineral turnover in the rhizosphere. Adv Appl Microbiol 95:1–67
Ulrich K, Ulrich A, Ewald D (2008) Diversity of endophytic bacterial communities in poplar grown under field conditions. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 63:169–180
Wakelin S, Mander C, Gerard E, Jansa J, Erb A, Young S, Condron L, O'Callaghan M (2012) Response of soil microbial communities to contrasted histories of phosphorus fertilisation in pastures. Appl Soil Ecol 61:40–48
Wang JT, Cao P, Hu HW, Li J, Han LL, Zhang LM, Zheng YM, He JZ (2015) Altitudinal distribution patterns of soil bacterial and archaeal communities along Mt. Shegyla on the Tibetan Plateau. Microb Ecol 69:135–145
Wawrik B, Kerkhof L, Kukor J, Zylstra G (2005) Effect of different carbon sources on community composition of bacterial enrichments from soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:6776–6783
Wu ZX, Hao ZP, Zeng Y, Guo LP, Huang LQ, Chen BD (2015) Molecular characterization of microbial communities in the rhizosphere soils and roots of diseased and healthy Panax notoginseng. Anton Leeuw Int J G 108:1059–1074
Yao YX, Tang HZ, Su F, Xu P (2015) Comparative genome analysis reveals the molecular basis of nicotine degradation and survival capacities of Arthrobacter. Sci Rep UK 5:8642
Yuan YL, Si GC, Wang J, Luo TX, Zhang GX (2014) Bacterial community in alpine grasslands along an altitudinal gradient on the Tibetan Plateau. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 87:121–132
Zhang LM, Wang M, Prosser JI, Zheng YM, He JZ (2009) Altitude ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in soils of Mount Everest. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 70:208–217
Zhang C, Zhou SS, Feng LY, Zhang DY, Lin NM, Zhang LH, Pan JP, Wang JB, Li J (2013) In vitro anti-cancer activity of chamaejasmenin B and neochamaejasmin C isolated from the root of Stellera chamaejasme L. Acta Pharmacol Sin 34:262–270
Zhang BG, Zhang W, Liu GX, Chen T, Zhang GS, Wu XK, Chen XM, Chang SJ (2015) Variations in culturable terrestrial bacterial communities and soil biochemical characteristics along an altitude gradient upstream of the Shule river, Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Nat Environ Pollut Technol 14:839–846
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful the Professor Frank Stermitz for assistance with language editing. This work was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program (2017YFD0200804), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31772668, 21775154, 31560037 and 31570354), the Open Project Program of Breeding Base for State Key Laboratory of Land Degradation and Ecological Restoration of North-western China/Key Laboratory for Restoration and Reconstruction of Degraded Ecosystem in North-western China of Ministry of Education (2017KF009), the Open Project Program for State Key Laboratory of Grassland Agro-ecosystem of Lanzhou University (SKLGAE201704), Basic Research Program of Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (080423SYR1), the Youth Science Foundations of Gansu Province (1506RJYA294), and Around five top priorities program of “One-Three-Five” Strategic Planning of Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 1971 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, H., Yang, X., Liu, R. et al. Bacterial community structure associated with the rhizosphere soils and roots of Stellera chamaejasme L. along a Tibetan elevation gradient. Ann Microbiol 68, 273–286 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-018-1336-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-018-1336-0