Abstract
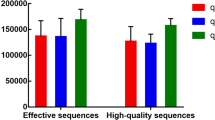
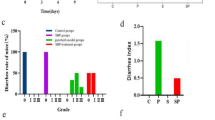
The objective of this study is to investigate the regulation effects of the active ingredients in Gegenqinlian Decoction (GD) on the intestinal mucosal flora of mice with diarrhea induced by high temperature and humidity based on systems pharmacology approach. Fifteen mice were randomly assigned to three equal groups of five mice, namely control (ctcm) group, model (ctmm) group and treatment (cttm) group. Mice in the cttm group were given 20 mL/kg of GD and sterile water was used as a placebo control twice a day for four consecutive days. We used the third-generation molecular high-throughput sequencing technology to measure the intestinal mucosal flora changes in mice. Combined with network pharmacology to predict the medicinal substances and action targets of GD against diarrhea. Results showed that Operational Taxonomic Unit (OTU) number and Alpha diversity in the intestinal mucosal flora of cttm group recovered and higher than that of the ctcm group. There were differences in the community structure between the ctmm and cttm groups in the Principal Coordinates Analysis (PCoA). The relative abundance results indicated dominant bacteria species (such as Lactobacillus crispatus, Muribaculum intestinal, Neisseria mucosa) in the intestinal mucosa of the three groups. Moreover, we screened out 146 active ingredients in GD corresponding to 252 component targets, and 328 disease targets in diarrhea to obtain 31 drug–disease common targets. Protein–protein interaction (PPI) networks mainly involved the core proteins such as Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and Interleukin-6 (IL-6). Enrichment analyses showed that GD played a role in the treatment of diarrhea by regulating the hypoxia inducible factor-1 (HIF-1), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and adipocytokine signaling pathways and so on. In brief, the active ingredients of GD could intervene from oxidative stress and inflammatory response through multiple targets and multiple channels to adjust the balance of intestinal mucosa flora, thereby playing a role in the treatment of diarrhea.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
This study was approved by the Animal Ethics and Welfare Committee of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine.
References
Bindea G, Mlecnik B, Hackl H, Charoentong P, Tosolini M, Kirilovsky A, Fridman W, Pages F, Trajanoski Z, Galon J (2009) ClueGO: a Cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks. Bioinformatics 25(8):1091–1093. https://doi.org/10.1116/1.581038
Boulangé CL, Neves AL, Chilloux J, Nicholson JK, Dumas ME (2016) Impact of the gut microbiota on inflammation, obesity, and metabolic disease. Genome Med 8(1):42. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmicrobiol.2016.215
Brugiroux S, Beutler M, Pfann C, Garzetti D, Ruscheweyh HJ, Ring D, Diehl M, Herp S, Lötscher Y, Hussain S, Bunk B, Pukall R, Huson DH, Münch PC, McHardy AC, McCoy KD, Macpherson AJ, Loy A, Clavel T, Berry D, Stecher B (2016) Genome-guided design of a defined mouse microbiota that confers colonization resistance against Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Nat Microbiol 2:16215. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmicrobiol.2016.215
Cao SL, Zhang XK (2020) Study progress on mechanism of hypoglycemic action of gegen qinlian decoction. Shandong J Tradit Chin Med 39(1):87–92. https://doi.org/10.16295/j.cnki.0257-358x.2020.01.021
Dao MC, Clément K (2018) Gut microbiota and obesity: concepts relevant to clinical care. Eur J Intern Med 48:18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejim.2017.10.005
Donal SMB, Fergus SMD (2017) The gut microbiota in inflammatory bowel disease, Gastroenterol. Clin N Am 46(1):143–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gtc.2016.09.011
Feng XR, Cui YS, He ZT, Cui XP, Wang L, Pan QY, Qi L (2019) Advance of research on biological function of tumor necrosis factor α. J Jilin Med Univ 40(1):66–68. https://doi.org/10.13845/j.cnki.issn1673-2995.2019.01.030
Guo LN, Wang DD, Pei Y, Wang R, Chen XP, Tian HD, Zhang R (2019) Investigating main components and action mechanism of Pueraria lobata based on pharmacology network. Drug Eval Res 42(09):1741–1748. https://doi.org/10.7501/j.issn.1674-6376.2019.09.006
Guo X, Ji JY, Feng ZT, Hou XQ, Luo YN, Mei ZG (2020) A network pharmacology approach to explore the potential targets underlying the effect of sinomenine on rheumatoid arthritis. Intern Immunopharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106201
He YS, Tang Y, Peng MJ, Xie GZ, Li WG, Tan ZJ (2019) Influence of Debaryomyces hansenii on bacterial lactase gene diversity in intestinal mucosa of mice with antibiotic-associated diarrhea. PLoS ONE 4(12):e022580. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0225802
Hellwig-Bürgel T, Stiehl DP, Wagner AE, Metzen E, Jelkmann W (2005) Review Review: hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1): a novel transcription factor in immune reactions. J Interferon Cytokine Res 25(6):297–310. https://doi.org/10.1089/jir.2005.25.297
Hidalgo-Cantabrana C, Goh YJ, Pan M, Sanozky-Dawes R, Barrangou R (2019) Genome editing using the endogenous type I CRISPR-Cas system in Lactobacillus crispatus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116(32):15774–15783. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1905421116
Hirota SA, Beck PL, MacDonald JA (2009) Targeting hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) signaling in therapeutics: implications for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov 3(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.2174/187221309787158434
Hirota SA, Fines K, Ng J (2010) Hypoxia-inducible factor signaling provides protection in clostridium difficile-induced intestinal injury. Gastroenterology 139(1):259–269. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2010.03.045
Huang C, Zheng CL, Li Y, Wang YH, Lu AP, Yang L (2014) Systems pharmacology in drug discovery and therapeutic insight for herbal medicines. Brief Bioinformatics 15(5):710–733. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbt035
Jaisinghani RN (2017) Antibacterial properties of quercetin. Microb Res. https://doi.org/10.4081/mr.2017.6877
Jin SF (2013) Pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment principles of antibiotic-related diarrhea. J Med Theory Pract 26(23):3112–3114. https://doi.org/10.19381/j.issn.1001-7585.2013.23.014
Li ZH, Wang J, Cai RL, Wang YW, Hu JP, Jiang AJ (2012) Effect of shenling baizhu powder on superoxide dismutase and malondialdehyde in ulcerative colitis rats. J Tradit Chin Med 53(20):1764–1767. https://doi.org/10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2012.20.025
Li JS, Zhao P, Li Y, Tian YG, Wang YH (2015) Systems pharmacologybased dissection of mechanisms of Chinese medicinal formula Bufei Yishen as an effective treatment for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Sci Rep 5:15290. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep15290
Liu CS, Liang X, Wei XH, Jin Z, Chen FL, Tang QF, Tan XM (2019a) Gegen qinlian decoction treats diarrhea in piglets by modulating gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acids. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00825
Liu JJ, Li Y, Zhang YL, Huo MQ, Sun XL, Xu ZX (2019b) A network pharmacology approach to explore the mechanisms of Qishen granules in heart failure. Med Sci Monit 25:7735–7745. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.919768
Lv GH, Bao YX, Sun XL, Cao Y, Zhu CH, Wang LD, Jia JL, Du G (2017) Effects of Kuijie Decoction on Expressions of EGFR and MUC2 in Colonic Mucosa of Patients with Refractory Ulcerative Colitis. Chin Archives Tradit Chin Med 35(8):2128–2130. https://doi.org/10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2017.08.056
Malara B, Jośko J, Tyrpień M, Malara P, Steplewska K (2005) Dynamics of changes in vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression and angiogenesis in stress-induced gastric ulceration in rats. J Physiol Pharmacol 56(2):259–271. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00127.2004
Malik HM, Nfn A, Sabira B, Saqib AS, Bina SS, Anwarul-Hassan G (2014) Pharmacological basis for the medicinal use of Carissa carandas in constipation and diarrhea. J Ethnopharmacol 153(2):359–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2014.02.024
Max F, Lopes CT, Gerardo H, Yue D, Onur S, Gary BD (2016) Cytoscape.Js: a graph theory library for visualisation and analysis. Bioinformatics 32(2):309–311. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv557
Mehmood MH, Anila N, Begum S, Syed SA, Siddiqui BS, Gilani AH (2014) Pharmacological basis for the medicinal use of Carissa carandas in constipation and diarrhea. J Ethnopharmacol 153(2):359–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2014.02.024
Persad R, Huyh HQ, Hao L, Ha JR, Sergi C, Srivastava R, Persad S (2012) Angiogenic remodeling in pediatric EoE is associated with increased levels of VEGF-A, angiogenin, IL-8, and activation of the TNF-α-NF-κB pathway. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 55(3):251–260. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0b013e31824b6391
Robinson A, Keely S, Karhausen J, Gerich ME, Furuta GT, Colgan SP (2008) Mucosal protection by hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibition. Gastroenterology 134(1):145–155. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2007.09.033
Ru JL, Li P, Wang JN, Zhou W, Li BH (2014) TCMSP: a database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J Cheminformatics 6(1):13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-6-13
Sekirov I, Russell SL, Antunes LCM, Finlay BB (2010) Gut microbiota in health and disease. Physiol Rev 90(3):859–904. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00045.2009
Shamala S, Baskaran G, Noor AS, Siti AA, Mohd YS, Senthil KV (2014) Venugopal Antiartherosclerotic effects of plant flavonoids. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/480258
Singhal R, Shah YM (2020) Oxygen battle in the gut: hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factors in metabolic and inflammatory responses in the intestine. J Biol Chem 295(30):10493–10505. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.REV120.011188
Sun BQ, Zhou Y, Liu WD, Wu CR (2015) Effects of different formulated Qiwei Baizhu powder on intestinal flora and tight junction protein in diarrhea mice. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res 26(12):2835–2837. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2015.12.007
Szklarczyk D, Morris JH, Cook H, Kuhn M, Wyder S, Simonovic M, Santos A, Doncheva NT, Roth A, Bork P, Jensen LJ, vonMering C (2017) The STRING database in 2017: quality-controlled protein–protein association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic Acids Res 45:D362–D368. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw937
Tang Y, Li M, Wang J, Pan Y, Wu FX (2015) CytoNCA: a cytoscape plug in for centrality analysis and evaluation of protein interaction networks. Biosystems 127:67–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystems.2014.11.005
Wang Y (2017) Expression and significance of HIF-1-VEGF pathway in intestinal tissue of SMVT rats. Master. North China University of Technology, Wuhan
Wang W, Cui LH (2016) Advances in intestinal microecology and its therapeutic effect on diarrhea. Acad J Chin PLA Med Sch 37:813–815. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.2095-5227.2016.07.037
Wang YF, Duan XY, Liu XX, Liu YJ, Fan H, Xu M (2020) Rho kinase blockade ameliorates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis in mice through dual inhibition of the NF-κB and IL-6/STAT3 pathways. Inflammation 40:66–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-019-01171-2
Wen QY, Yao WL, Yang CL, Ma Q, Zhang XS, Ji P, Hua YL, Wei YM (2017) Effects of Yujin Powder on gastrointestinal hormone in serum and intestinal tissue of large intestine dampness-heat syndrome rat model. Chin J Anim Vet Sci 48(06):1140–1149. https://doi.org/10.1184/j.issn.0366-6964.2017.06.019
Wu WQ, Wang LL, Zhao JX, Zhang H, Chen W (2019) Research progress on physiological characteristics and health benefits of Lactobacillus plantarum. Food Ferment Ind 45(01):1–13. https://doi.org/10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.019602
Xiao L, Jiaywei T, Ginsenoside R (2019) Ginsenoside Rg3 decreases NHE1 expression via inhibiting EGF-EGFR-ERK1/2-HIF-1α pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma: a novel antitumor mechanism. Am J Chin Med 46(08):1915–1931. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0192415X18500969
Xiong SP, Zhang CH, Deng YB, Sheng JQ, Tu XY, Yu M, Wei XX (2016) Experimental study of Gegen Qinlian decoction on improving glucose and lipid metabolism in KK-Ay diabetic mice. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res 27:2090–2092. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2016.09.015
Xu C, Zhong M, Ma ZJ, Jiang S, Xie JD, Liang LJ, Wang XD, Zhao KQ (2015) Research status of Gegen Qinlian decoction. Jilin J Tradit Chin Med 35(6):629–632. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpn.13283
Xu YL, Mao HL, Yang CM, Du HH, Wang HF (2020) Effects of chitosan nanoparticle supplementation on growth performance, humoral immunity, gut microbiota and immune responses after lipopolysaccharide challenge in weaned pigs. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr 104:597–605. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpn.13283
Yao F, Zhou QY, Xiong Y, Guan S (2015) Protective effects of β-sitosterol on acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice. Chin Agric Sci Bul 31(02):55–61
Yao X, Wu GZ, Zhao HW, Jing F, Dong HJ (2020) Study advances on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Huangqin (Scutellaria baicalensis). Liaoning J Tradit Chin Med 47(07):215–220. https://doi.org/10.13192/j.issn.1000-1719.2020.07.060
Zhang SS, Wang QJ, Li YF, Wang N (2017) Expert consensus on diagnosis and treatment of diarrhea. J Tradit Chin Med 58(14):1256–1259. https://doi.org/10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2017.14.023
Zheng LS, Tai W, Lan XX, Liu DB, Chen CQ (2017) Research progress on traditional Chinese medicine against diabetes based on intestinal flora new targets. Drug Eval Res 40(8):1173–1181. https://doi.org/10.7501/j.issn.1674-6376.2017.08.029
Zhu CR, Ma XC (2016) Recognition and management of antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Chin J Pract Surg 36:168–170. https://doi.org/10.7504/CJPS.ISSN1005-2208.2016.02.14
Zhu WK, Liang HY, Ma PC, Zhang ZY, Liu SQ (2019) The study progress of the antiviral activity and mechanism of Chinese herbs. Jiangsu J Tradit Chin Med 51(06):86–89. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1672-397X.2019.06.030
Acknowledgments
We thank all the scholars who provided relevant guidance for the study.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No: 81874460) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2019JJ50452). The author of this paper was in charge of the project, and Professor Zhoujin Tan is the project leader. Funding body provided approval for the manuscript and had no role in design of the study, analysis and interpretation of data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XL performed network analysis and drafted the manuscript; CZ analyzed the data; HH guided the performance of animal experiment; ZT designed the study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. The decision to submit the manuscript for publication was made by all the authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Institutional animal care and use committee statement
This study was approved by the Animal Ethics and Welfare Committee of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Zhang, C., Hui, H. et al. Effect of Gegenqinlian decoction on intestinal mucosal flora in mice with diarrhea induced by high temperature and humidity treatment. 3 Biotech 11, 83 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02628-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02628-0