Abstract
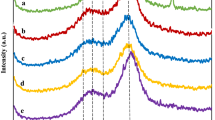
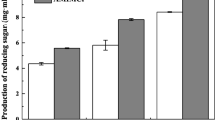
Ultrasound-assisted soaking in aqueous ammonia (USAA) pretreatment with 15 wt% aqueous ammonia under low temperature (~ 60 °C) and short-time (< 12 min) low-frequency (20 kHz, 60–650 W) ultrasound has been investigated for enhancement of enzymatic hydrolysis of corncob. Operational parameters of energy density (2.93–17.07 W/mL) and sonication time (0.34–11.66 min) that affect cellulose recovery, delignification, and sugar recovery yield were studied and optimized. The maximum cellulose recovery, delignification and sugar recovery yield determined at the optimum conditions (energy density 10 W/mL, sonication time 11.66 min) were 83.8, 84.7, and 77.6%, respectively. The corncob pretreated using USAA has a lower hemicellulose content (28.9% vs 31.8%), a slightly lower crystallinity index value (42.7% vs 43.7%), and a larger surface cavity diameter (> 36 μm vs < 20 μm) than that pretreated using soaking in aqueous ammonia (SAA) pretreatment. The USAA pretreatment was proved to be a reliable and effective method for corncob pretreatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bansal P, Hall M, Realff MJ, Lee JH, Bommarius AS (2010) Multivariate statistical analysis of X-ray data from cellulose: a new method to determine degree of crystallinity and predict hydrolysis rates. Bioresour Technol 101:4461–4471
Cheng K-K, Wang W, Zhang J-A, Zhao Q, Li J-P, Xue J-W (2011) Statistical optimization of sulfite pretreatment of corncob residues for high concentration ethanol production. Bioresour Technol 102:3014–3019
Chundawat SPS, Donohoe BS, Sousa LdC, Elder T, Agarwal UP, Lu F, Ralph J, Himmel ME, Balan V, Dale BE (2011) Multi-scale visualization and characterization of lignocellulosic plant cell wall deconstruction during thermochemical pretreatment. Energy Environ Sci 4:973–984
Du R, Su R, Li X, Tantai X, Liu Z, Yang J, Qi W, He Z (2012) Controlled adsorption of cellulase onto pretreated corncob by pH adjustment. Cellulose 19:371–380
Du R, Huang R, Su R, Zhang M, Wang M, Yang J, Qi W, He Z (2013) Enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulose: SEC-MALLS analysis and reaction mechanism. RSC Adv 3:1871–1877
Huang R, Qi W, Su R, He Z (2010) The optimization of fractionating lignocellulose by formic acid using response surface methodology. Energ Source Part A 32:1282–1292
Kahar P, Taku K, Tanaka S (2010) Enzymatic digestion of corncobs pretreated with low strength of sulfuric acid for bioethanol production. J Biosci Bioeng 110:453–458
Kim TH, Taylor F, Hicks KB (2008) Bioethanol production from barley hull using SAA (soaking in aqueous ammonia) pretreatment. Bioresour Technol 99:5694–5702
Lee J-W, Rodrigues RCLB, Jeffries TW (2009) Simultaneous saccharification and ethanol fermentation of oxalic acid pretreated corncob assessed with response surface methodology. Bioresour Technol 100:6307–6311
Lee J-W, Rodrigues RCLB, Kim HJ, Choi I-G, Jeffries TW (2010) The roles of xylan and lignin in oxalic acid pretreated corncob during separate enzymatic hydrolysis and ethanol fermentation. Bioresour Technol 101:4379–4385
Liu K, Lin X, Yue J, Li X, Fang X, Zhu M, Lin J, Qu Y, Xiao L (2010) High concentration ethanol production from corncob residues by fed-batch strategy. Bioresour Technol 101:4952–4958
Ramadoss G, Muthukumar K (2014) Ultrasound assisted ammonia pretreatment of sugarcane bagasse for fermentable sugar production. Biochem Eng J 83:33–41
Rollin JA, Zhu Z, Sathitsuksanoh N, Zhang Y-HP (2011) Increasing cellulose accessibility is more important than removing lignin: a comparison of cellulose solvent-based lignocellulose fractionation and soaking in aqueous ammonia. Biotechnol Bioeng 108:22–30
Shirkavand E, Baroutian S, Gapes DJ, Young BR (2016) Combination of fungal and physicochemical processes for lignocellulosic biomass pretreatment—A review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 54:217–234
Su R, Yang R, Jifeng Y, Du R, Huang R, Qi W, He Z (2017) Oscillating cellulase adsorption and enhanced lignocellulose hydrolysis upon ultrasound treatment. Trans Tianjin Univ 23:11–19
Tilman D, Socolow R, Foley JA, Hill J, Larson E, Lynd L, Pacala S, Reilly J, Searchinger T, Somerville C, Williams R (2009) Beneficial biofuels—the food, energy, and environment trilemma. Science 325:270–271
Wang GS, Lee J-W, Zhu JY, Jeffries TW (2011) Dilute acid pretreatment of corncob for efficient sugar production. Appl Biochem Biotech 163:658–668
Wu H, Dai X, Zhou S-L, Gan Y-Y, Xiong Z-Y, Qin Y-H, Ma J, Yang L, Wu Z-K, Wang T-L, Wang W-G, Wang C-W (2017) Ultrasound-assisted alkaline pretreatment for enhancing the enzymatic hydrolysis of rice straw by using the heat energy dissipated from ultrasonication. Bioresour Technol 241:70–74
Xu Q-Q, Zhao M-J, Yu Z-Z, Yin J-Z, Li G-M, Zhen M-Y, Zhang Q-Z (2017) Enhancing enzymatic hydrolysis of corn cob, corn stover and sorghum stalk by dilute aqueous ammonia combined with ultrasonic pretreatment. Ind Crops Prod 109:220–226
Yoo CG, Nghiem NP, Hicks KB, Kim TH (2013) Maximum production of fermentable sugars from barley straw using optimized soaking in aqueous ammonia (SAA) pretreatment. Appl Biochem Biotech 169:2430–2441
Zhang M, Qi W, Liu R, Su R, Wu S, He Z (2010) Fractionating lignocellulose by formic acid: characterization of major components. Biomass Bioenerg 34:525–532
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Research Project of Chongqing Education Commission (No. KJ1500632), Chongqing Technology and Business University (No. 1556035 and 20145601), and the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21776212).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, R., Su, R., Qi, W. et al. Enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis of corncob by ultrasound-assisted soaking in aqueous ammonia pretreatment. 3 Biotech 8, 166 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1186-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1186-2