Abstract
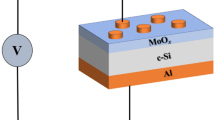
This paper studies the applicability of sputtered Molybdenum (Mo) thin films on silicon wafers (Mo–Si) to act as contact substrates for vertically structured Si quantum-dot (QD) solar cells. The compatibility of Mo–Si contact substrate with Si QD material under different annealing temperatures is examined. Cross sections of annealed samples show well-defined interfaces without metal penetration into the Si QD bilayer regions. Through comparing samples deposited on Mo–Si substrates with those on fused-silica substrates, we identified from Raman spectra that the presence of Mo is advantageous for the Si-crystallization process and in fact provide beneficial passivation effects on the Si QD material according to changes in photoluminescence intensity. This allows us to conclude that Mo thin films are compatible with the sputter–anneal process, and verify the feasibility of using the proposed Mo–Si contact scheme for future fabrication of Si QD solar cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker C, Ruske F, Sontheimer T, Gorka B, Bloeck U, Gall S, Rech B (2009) Microstructure and photovoltaic performance of polycrystalline silicon thin films on temperature-stable ZnO:Al layers. J Appl Phys 106(8):084506. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3240343
Chelvanathan P, Zakaria Z, Yusoff Y, Akhtaruzzaman M, Alam MM, Alghoul MA, Sopian K, Amin N (2015) Annealing effect in structural and electrical properties of sputtered Mo thin film. Appl Surf Sci 334(0):129–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.08.154
Cheylan S, Elliman RG (2001) Effect of hydrogen on the photoluminescence of Si nanocrystals embedded in a SiO2 matrix. Appl Phys Lett 78(9):1225–1227. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1338492
Conibeer G (2007) Third-generation photovoltaics. Mater Today 10(11):42–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1369-7021(07)70278-x
Conibeer G, Green MA, König D, Perez-Wurfl I, Huang S, Hao X, Di D, Shi L, Shrestha S, Puthen-Veetil B, So Y, Zhang B, Wan Z (2011) Silicon quantum dot based solar cells: addressing the issues of doping, voltage and current transport. Prog Photovoltaics Res Appl 19(7):813–824. https://doi.org/10.1002/pip.1045
Di D, Perez-Wurfl I, Gentle A, Kim D-H, Hao X, Shi L, Conibeer G, Green MA (2010) Impacts of post-metallisation processes on the electrical and photovoltaic properties of Si quantum dot solar cells. Nanoscale Res Lett 5(11):1762–1767. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11671-010-9707-x
Doğan İ, van de Sanden MCM (2013) Direct characterization of nanocrystal size distribution using Raman spectroscopy. J Appl Phys 114(13):134310. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4824178
Faraci G, Gibilisco S, Russo P, Pennisi AR, La Rosa S (2006) Modified Raman confinement model for Si nanocrystals. Phys Rev B 73(3):033307
Gordillo G, Grizález M, Hernandez LC (1998) Structural and electrical properties of DC sputtered molybdenum films. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 51(3–4):327–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-0248(97)00236-5
Guillén C, Herrero J (2003) Low-resistivity Mo thin films prepared by evaporation onto 30 cm × 30 cm glass substrates. J Mater Process Technol 143–144(0):144–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(03)00395-9
Hernández S, López-Vidrier J, López-Conesa L, Hiller D, Gutsch S, Ibáñez J, Estradé S, Peiró F, Zacharias M, Garrido B (2014) Determining the crystalline degree of silicon nanoclusters/SiO2 multilayers by Raman scattering. J Appl Phys 115(20):203504. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4878175
Hiller D, Goetze S, Zacharias M (2011) Rapid thermal annealing of size-controlled Si nanocrystals: dependence of interface defect density on thermal budget. J Appl Phys 109(5):054308. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3556449
Houben L, Luysberg M, Hapke P, Carius R, Finger F, Wagner H (1998) Structural properties of microcrystalline silicon in the transition from highly crystalline to amorphous growth. Philos Mag A 77(6):1447–1460. https://doi.org/10.1080/01418619808214262
Ivanda M, Hohl A, Montagna M, Mariotto G, Ferrari M, Crnjak Orel Z, Turković A, Furić K (2006) Raman scattering of acoustical modes of silicon nanoparticles embedded in silica matrix. J Raman Spectrosc 37(1–3):161–165
Jia X, Zhang P, Lin Z, Anthony R, Kortshagen U, Huang S, Puthen-Veettil B, Conibeer G, Perez-Wurfl I (2015) Accurate determination of the size distribution of Si nanocrystals from PL spectra. RSC Adv 5(68):55119–55125. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA02805A
Jia X, Lin Z, Zhang T, Puthen-Veettil B, Yang T, Nomoto K, Ding J, Conibeer G, Perez-Wurfl I (2017) Accurate analysis of the size distribution and crystallinity of boron doped Si nanocrystals via Raman and PL spectra. RSC Adv 7(54):34244–34250. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA04472K
Kaneko T, Wakagi M, Onisawa KI, Minemura T (1994) Change in crystalline morphologies of polycrystalline silicon films prepared by radio-frequency plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition using SiF4 + H2 gas mixture at 350 °C. Appl Phys Lett 64(14):1865–1867. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.111781
Lee DN (2000) Strain energy release maximization model for evolution of recrystallization textures. Int J Mech Sci 42(8):1645–1678. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7403(99)00095-8
Lin Z, Perez-Wurfl I, Wu L, Jia X, Zhang T, Puthen-Veettil B, Zhang H, Di D, Conibeer G (2013) Investigation in feasibility of Molybdenum as a back contact layer for Silicon based quantum dot solar cells. In: Proc. SPIE 8620, Physics, Simulation, and Photonic Engineering of Photovoltaic Devices II, San Francisco, United States, pp 86201W-86201W-86207. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2003504
Lin Z, Wu L, Jia X, Zhang T, Puthen-Veettil B, Yang TC-J, Conibeer G, Perez-Wurfl I (2015) Boron doped Si rich oxide/SiO2 and silicon rich nitride/SiNx bilayers on molybdenum-fused silica substrates for vertically structured Si quantum dot solar cells. J Appl Phys 118(4):045303. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4927514
Miura S, Nakamura T, Fujii M, Inui M, Hayashi S (2006) Size dependence of photoluminescence quantum efficiency of Si nanocrystals. Phys Rev B 73(24):245333
Perez-Wurfl I, Hao X, Gentle A, Kim D-H, Conibeer G, Green MA (2009) Si nanocrystal p-i-n diodes fabricated on quartz substrates for third generation solar cell applications. Appl Phys Lett 95(15):153506. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3240882
Repins I, Contreras MA, Egaas B, DeHart C, Scharf J, Perkins CL, To B, Noufi R (2008) 19·9%-efficient ZnO/CdS/CuInGaSe2 solar cell with 81·2% fill factor. Prog Photovoltaics Res Appl 16(3):235–239. https://doi.org/10.1002/pip.822
Scofield JH, Duda A, Albin D, Ballard BL, Predecki PK (1995) Sputtered molybdenum bilayer back contact for copper indium diselenide-based polycrystalline thin-film solar cells. Thin Solid Films 260(1):26–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-6090(94)06462-8
Scragg JJ, Ericson T, Fontané X, Izquierdo-Roca V, Pérez-Rodríguez A, Kubart T, Edoff M, Platzer-Björkman C (2014) Rapid annealing of reactively sputtered precursors for Cu2ZnSnS4 solar cells. Prog Photovoltaics Res Appl 22(1):10–17. https://doi.org/10.1002/pip.2265
Terry Chien-Jen Y, Keita N, Binesh P-V, Ziyun L, Lingfeng W, Tian Z, Xuguang J, Gavin C, Ivan P-W (2017) Properties of silicon nanocrystals with boron and phosphorus doping fabricated via silicon rich oxide and silicon dioxide bilayers. Mater Res Express 4(7):075004
Tong J, Luo H-L, Xu Z-A, Zeng H, Xiao X-D, Yang C-L (2013) The effect of thermal annealing of Mo film on the CuInSe2 layer texture and device performance. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 119(0):190–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2013.06.039
Tuschel DD, Lavine JP (1999) Micro-Raman characterization of unusual defect structure in arsenic-implanted silicon. MRS Online Proc Library. https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-588-227
Voutsas AT, Hatalis MK, Boyce J, Chiang A (1995) Raman spectroscopy of amorphous and microcrystalline silicon films deposited by low-pressure chemical vapor deposition. J Appl Phys 78(12):6999–7006. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.360468
Wu C-L, Lin G-R (2012) Inhomogeneous linewidth broadening and radiative lifetime dispersion of size dependent direct bandgap radiation in Si quantum dot. AIP Adv 2(4):042162. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4769362
Yang TC-J, Kauffmann Y, Wu L, Lin Z, Jia X, Puthen-Veettil B, Zhang T, Conibeer G, Perez-Wurfl I, Rothschild A (2014) In-situ high resolution transmission electron microscopy observation of silicon nanocrystal nucleation in a SiO2 bilayered matrix. Appl Phys Lett 105(5):053116. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4892658
Zhang T, Simonds B, Nomoto K, Veettil BP, Lin Z, Wurfl IP, Conibeer G (2016) Pulsed KrF excimer laser dopant activation in nanocrystal silicon in a silicon dioxide matrix. Appl Phys Lett 108(8):083103. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4942466
Zoppi G, Beattie N, Major J, Miles R, Forbes I (2011) Electrical, morphological and structural properties of RF magnetron sputtered Mo thin films for application in thin film photovoltaic solar cells. J Mater Sci 46(14):4913–4921. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-011-5404-0
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Australian Government through the Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA). Responsibility for the views, information or advice expressed herein is not accepted by the Australian Government. This work also was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant nos. 51272033, 51572037, 51335002, 91648109). The authors acknowledge the facilities, and the scientific and technical assistance of the Australian Microscopy & Microanalysis Research Facility at the Electron Microscope Unit at the University of New South Wales, as well as the Australian Centre for Microscopy & Microanalysis at the University of Sydney. The authors would also like to thank Fangyang Liu for his efforts in preparation of sputtered Mo thin films.
Funding
This study was supported by the Australian Government through the Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA). Responsibility for the views, information or advice expressed herein is not accepted by the Australian Government. This work also was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant nos. 51272033, 51572037, 51335002, 91648109).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, X., Lin, Z., Yang, T.CJ. et al. High-temperature annealing effects on molybdenum–silicon contact substrate for vertically structured silicon quantum-dot solar cells. Appl Nanosci 9, 135–142 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-018-0893-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-018-0893-7