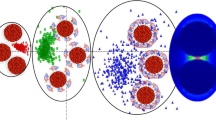
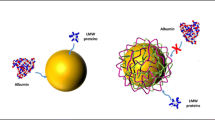
Abstract
Understanding the organization of self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) on gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) as protective coatings is a key role of biological applications of nanomaterials. Here, we report the influence on the stability of the surface coverage of three mercaptocarboxylic lingands onto AuNPs, mercaptopropanoic acid (MPA), mercaptoundecanoic acid (MUA) and mercaptopropionic acid (MHA) under different conditions. In addition, we optimized a bioconjugation route using bovine serum protein (BSA) as a protein model. AuNPs and successful binding of ligands and BSA on the AuNPs were analyzed by UV–Vis, TEM, FTIR, RAMAN, DLS and zeta potential. The size of as-synthesized AuNPs was 18 ± 1,2 nm with surface plasmon resonance (SPR) peak at 522 nm. The magnitude of the bathochromic shift of AuNPs with MPA, MUA and MHA was determined by UV–Vis and the SPR band position of AuNP shifts to 1.5, 3 and 5 nm longer. Moreover, the data show the influence of chain length on colloidal stability and covalent and non-covalent coupling steps with nanomaterials. We demonstrate a method for quantitative determination of the coatings on gold nanoparticles and open new perspectives in understanding the influence of monolayer thickness on the generation of nanobioconjugates for biological applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arruebo M, Valladares M, Gonzalez-Fernandez A (2009) Antibody-conjugated nanoparticles for biomedical applications. J Nanomater. https://doi.org/10.1155/2009/439389
Aslan K, Pérez-Luna VH (2002) Surface modification of colloidal gold by chemisorption of alkanethiols in the presence of a nonionic surfactant. Langmuir 18(16):6059–6065. https://doi.org/10.1021/la025795x
Bartczak D, Kanaras A (2011a) Preparation of peptide-functionalized gold nanoparticles using one pot EDC/Sulfo-NHS coupling. Langmuir 27:10119–10123
Bartczak D, Kanaras A (2011b) Preparation of peptide-functionalized gold nanoparticles using one pot EDC/sulfo-NHS coupling. Langmuir 27(16):10119–10123. https://doi.org/10.1021/la2022177
Briñas RP, Maetani M, Barchi JJ (2013) A survey of place-exchange reaction for the preparation of water-soluble gold nanoparticles. J Colloid Interface Sci 392:415–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2012.06.042
El-Sayed MA (2004) Small is different: shape-, size-, and composition-dependent properties of some colloidal semiconductor nanocrystals. Acc Chem Res 37(5):326–333. https://doi.org/10.1021/ar020204f
Feng AL, You ML, Tian L, Singamaneni S, Liu M, Duan Z, Lu TJ, Xu F, Lin M (2015) Distance-dependent plasmon-enhanced fluorescence of upconversion nanoparticles using polyelectrolyte multilayers as tunable spacers. Sci Rep 5:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep07779
Gasiorek F, Pouokam E, Diener M, Schlecht S, Wickleder MS (2015) Effects of multivalent histamine supported on gold nanoparticles: activation of histamine receptors by derivatized histamine at subnanomolar concentrations. Org Biomol Chem 13(39):9984–9992. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5OB01354B
Gole A, Murphy CJ (2008) Azide-derivatized gold nanorods: Functional materials for “Click” chemistry. Langmuir 24(1):266–272. https://doi.org/10.1021/la7026303
Haes AJ, Zou S, Schatz GC, Van Duyne RP (2004) A nanoscale optical biosensor: the long range distance dependence of the localized surface plasmon resonance of noble metal nanoparticles. J Phys Chem B 108(1):109–116. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0361327
Hermanson GT (1996) Bioconjugate techniques. Academic Press, New York
Hermanson GT (2008) Bioconjugate techniques, 2nd edn. Academic Press, San Diego
Jain PK, El-Sayed IH, El-Sayed MA (2007) Au nanoparticles target cancer. Nano Today 2(1):18–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1748-0132(07)70016-6
Jazayeri MH, Amani H, Pourfatollah AA, Pazoki-Toroudi H, Sedighimoghaddam B (2016) Various methods of gold nanoparticles (GNPs) conjugation to antibodies. Sensing Bio Sensing Res 9:17–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbsr.2016.04.002
Kumar S, Aaron J, Sokolov K (2008) Directional conjugation of antibodies to nanoparticles for synthesis of multiplexed optical contrast agents with both delivery and targeting moieties. Nat Protoc 3:314–320. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.1
Lacerda SHD, Park JJ, Meuse C, Pristinski D, Becker ML, Karim A, Douglas JF (2010) Interaction of gold nanoparticles with common human blood proteins. ACS Nano 4(1):365–379. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn9011187
Levy R, Wang ZX, Duchesne L, Doty RC, Cooper AI, Brust M, Fernig DG (2006) A generic approach to monofunctionalized protein-like gold nanoparticles based on immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography. Chembiochem 7(4):592–594. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.200500457
Lévy R, Thanh NT, Doty RC, Hussain I, Nichols RJ, Schiffrin DJ, Brust M, Fernig DG (2004) Rational and combinatorial design of peptide capping ligands for gold nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 126(32):10076–10084. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0487269
Li CH, Kuo TR, Su HJ, Lai WY, Yang PC, Chen JS, Wang DY, Wu YC, Chen CC (2015) Fluorescence-guided probes of aptamer-targeted gold nanoparticles with computed tomography imaging accesses forin vivo tumor resection. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep15675
Lin S-Y, Tsai Y-T, Chen C-C, Lin C-M (2004) C.-H. Chen. Two-step functionalization of neutral and positively charged thiols onto citrate-stabilized Au nanoparticles. J Phys Chem B 108(7):2134–2139. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp036310w
Lin Vien D, Colthup NB, Fateley WG, Graselli JG (1991) The handbook of infrared and Raman characteristic frequencies of organic molecules, 1st edn. Academic Press, San Diego
Lynch I, Dawson KA Protein-nanoparticle interactions. Nano Today 2008, 3(1–2):40–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1748-0132(08)70014-8
MacCuspie RI, Allen AJ, Hackley VA (2011) Dispersion stabilization of silver nanoparticles in synthetic lung fluid studied under in situ conditions. Nanotoxicology 5(2):140–156. https://doi.org/10.3109/17435390.2010.504311
Mak JSW, Rutledge SA, Abu-Ghazalah RM, Eftekhari F, Irizar TNCM, Zheng G, Helmy AS (2013) Recent developments in optofluidic-assisted Raman spectroscopy. Prog Quantum Electron 37(1):1–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pquantelec.2012.11.001
Mayya KS, Patil V, Sastry M (1997) On the stability of carboxylic acid derivatized gold colloidal particles: the role of colloidal solution pH studied by optical absorption spectroscopy. Langmuir 13(15):3944–3947. https://doi.org/10.1021/la962140l
Mulvaney P (1996) Surface plasmon spectroscopy of nanosized metal particles. Langmuir 12(3):788–800. https://doi.org/10.1021/la9502711
Oliveira JP, Prado AR, Keijok WJ, Pontes MJ, Ribeiro MRN, Nogueira BV, Guimarães MCC (2017) Arab J Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.04.003
Pease LF, Tsai DH, Zangmeister RA, Zachariah MR, Tarlov MJ (2007) Quantifying the surface coverage of conjugate molecules on functionalized nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 111(46):17155–17157. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp075571t
Peng G, Tisch U, Adams O, Hakim M, Shehada N, Broza YY, Bilan S, Abdah-Bortnyak R, Kuten A, Haick H (2009) Diagnosing lung cancer in exhaled breath using gold nanoparticles. Nat Nanotechonol 4(10):669–673. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2009.235
Prado AR, Oliveira JP, Pereira RH, Guimarães MC, Nogueira BV, Castro EV, Almeida LC, Ribeiro MR, Pontes MJ (2015) Surface-enhanced Raman plasmon in self-assembled sulfide-coated gold nanoparticle arrays. Plasmonics 10(5):1097–1103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-9909-2
Roeges PG (1995) A guide to the complete interpretation of infrared spectra of organic structures. J Chem Educ 72(4):A93. https://doi.org/10.1021/ed072pA93.4
Saha K, Agasti SS, Kim C, Li X, Rotello VM (2012) Gold nanoparticles in chemical and biological sensing. Chem Rev 112(5):2739–2779. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr2001178
Schroeder A, Heller DA, Winslow MM, Dahlman JE, Pratt GW, Langer R, Jacks T, Anderson DG (2012) Treating metastatic cancer with nanotechnology. Nat Rev Cancer 12(1):39–50. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3180
Silvia F, Sally P, David AR, Kim ES (2000) Self-assembled monolayers: a versatile tool for the formulation of the biosurfaces. Trends Anal Chem 19(9):530–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-9936(00)00032-7
Socrates G (1994) Infrared characteristic group frequencies, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Sperling RA, Rivera-Gil P, Zhang F, Zanella M, Parak WJ (2008) Biological applications of gold nanoparticles. Chem Soc Rev 37(9):1896–1908. https://doi.org/10.1039/b712170a
Stuart B (1997) Biological applications of infrared spectroscopy. ACOL Series, Wiley, Chichester
Stuchinskaya T, Moreno M, Cook MJ, Edwards DR, Russell DA (2011) Targeted photodynamic therapy of breast cancer cells using antibody–phthalocyanine–gold nanoparticle conjugates. Photochem Photobiol Sci 10(5):822–831. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1pp05014a
Sukhanova A, Even-Desrumeaux K, Kisserli A, Tabary T, Reveil B, Millot JM, Chames P, Baty D, Artemyev M, Oleinikov V, Pluot M, Cohen JHM, Nabiev I (2012) Oriented conjugates of single-domain antibodies and quantum dots: toward new generation of ultra-small diagnostic nanoprobes. Nanomedicine 8(4):516–525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2011.07.007
Tandford C (1962) The interpretation of hydrogen ion titration curves of proteins. Adv Protein Chem 17:69–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-3233(08)60052-2
Terentyuk GS, Maslyakova GN, Suleymanova LV, Khlebtsov NG, Khlebtsov BN, Akchurin GG, Maksimova IL, Tuchin VV (2009) Laser-induced tissue hyperthermia mediated by gold nanoparticles: toward cancer phototherapy. J Biomed Opt 14(2):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.3122371
Thobhani S, Attree S, Boyd R, Kumarswami N, Noble J, Szymanski M, Porter RA (2010) Bioconjugation and characterisation of gold colloid-labelled proteins. J Immunol Methods 356(1–2):60–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jim.2010.02.007
Tsai DH, Zangmeister RA, Pease LF, Tarlov MJ, Zachariah MR (2008) Gas-phase ion-mobility characterization of SAM-functionalized Au nanoparticles. Langmuir 24(16):8483–8490. https://doi.org/10.1021/la7024846
Weisbecker CS, Merritt MV, Whitesides GM (1996) Molecular self-assembly of aliphatic thiols on gold colloids. Langmuir 12(16):3763–3772. https://doi.org/10.1021/la950776r
Wilson R, Chen Y, Aveyard J (2004) One molecule per particle method for functionalising nanoparticles. Chem Commun 10:1156–1157. https://doi.org/10.1039/B402786H
Zargar B, Hatamie A (2013) A simple and fast colorimetric method for detection of hydrazine in water samples based on formation of gold nanoparticles as a colorimetric probe. Sens Actuators B 182:706–710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2013.03.036
Zhou Y, Dong H, Liu L, Li M, Xiao K, Xu M (2014) Selective and sensitive colorimetric sensor of mercury (II) based on gold nanoparticles and 4-mercaptophenylboronic acid. Sens Actuators B 196:106–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.01.060
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge financial support from the Brazilian Ministry of Science and Technology (CNPq Grant 483036/2011-0), the Ministry of Science and Technology (MCTI/FINEP/CT-INFRA grant PROINFRA 01/2006) and the Foundation Support Research and Innovation of Espírito Santo (Grant 006/2014). This work used the equipment facilities at the Laboratory of Cellular Ultrastructure Carlos Alberto Redins and the Laboratory of Biomolecular Analysis (LABIOM) at the Federal University of Espírito Santo, with thanks for providing the equipment and technical support for experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JPO conceived the project. JPO, ARP and WJK performed the characterizations and analysis. All authors contributed to discussions and writing of the manuscript. MCCG guided the research.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oliveira, J.P., Keijok, W.J., Prado, A.R. et al. Tracking the effect of binder length on colloidal stability and bioconjugation of gold nanoparticles. Appl Nanosci 8, 1781–1790 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-018-0843-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-018-0843-4