Abstract
African legumes are an important protein source in the human diet. However, a long and often extended cooking process has been identified as a major challenge in the consumption and utilisation of these legumes. The application of infrared heating as a method of shortening the cooking-time of African legume seeds and flour, by increasing their water absorption rates and pasting viscosity is emphasised in literature. Structural changes caused by infrared heating of moisture-conditioned African legumes include microstructural, molecular and interaction of the biomolecules in the seeds. However, to the best of the authors’ our knowledge, no overview on elucidated mechanisms surrounding the microstructural and molecular changes of infrared heated African legumes has been done. The authors’ therefore, present current knowledge of these mechanisms including certain highlighted factors such as seed sizes, moisture, surface temperature and time, affecting the efficacy of the application of infrared heating to African legumes. In conclusion, infrared heating is a promising technology that provides a potential solution to the consumption and utilisation challenges of African legumes and flour from these legumes, to enhance their consumption in the food industry.


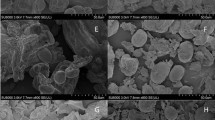
(Adapted from Ogundele 2017)

(Adapted from Mwangwela et al. 2006)

(Adapted from Ogundele et al. 2017)
Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
01 March 2023
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-023-05703-5
References
Adebowale YA, Schwarzenbolz U, Henle T (2011) Protein isolates from bambara groundnut (Voandzeia Subterranean L.): chemical characterisation and functional properties. Int J Food Prop 14:758–775
Andrejko D, Rydzak L, Slaska-Grzywna B, Goÿdziewska M, Kobus Z (2008) Influence of preliminary thermal processing applying infra-red radiation on pea seeds cooking process. Int Agrophys 22:17–20
Annan N, Plahar W, Swetman T (2002) Effect of kawe treatment on the water absorption and cooking characteristics of bambara groundnut varieties. FRI, Accra, p 15
Arce-Arce EE, Gallegos-Infante JA, Rocha-Guzmán NE, González-Laredo RF, Moreno-Jiménez R, Figueroa-Cárdenas JDD, Montelongo-Montelongo AN (2014) Effect of infrared heating on the physicochemical properties of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) flour. CyTA-J Food 12:242–248
Arntfield SD, Scanlon MG, Malcolmson LJ, Watts BM, Cenkowski S, Ryland D, Savoie V (2001) Reduction in lentil cooking time using micronisation: comparison of two micronisation temperatures. J Food Sci 66:500–505
Ashraf S, Saeed SMG, Sayeed SA, Ali R (2012) Impact of microwave treatment on the functionality of cereals and legumes. Int J Agric Biol 14:356–370
Bellido G, Arntfield SD, Cenkowski S, Scanlon M (2006) Effects of micronisation pretreatments on the physicochemical properties of navy and black beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). LWT Food Sci Technol 39:779–787
Bernal-Lugo I, Parra C, Portilla M, Peña-Valdivia CB, Moreno E (1997) Cotyledon thermal behavior and pectic solubility as related to cooking quality in common beans. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 50:141–150
Betancur- Ancona D, Segura-Campos M, Rosado-Rubio JG, Franco LS, Chel-Guerrero L (2012) Chemical composition and anti-nutritional factors in five tropical legume seeds. Nutr Consum Health, Beans, pp 117–141
Boye J, Zare F, Pletch A (2010) Pulse proteins: processing, characterisation, functional properties and applications in food and feed. Food Res Int 43:414–431
Cenkowski S, Sosulski F (1998) Cooking characteristics of split peas treated with infrared heat. Trans ASAE 41:715–720
Cenkowski S, Hong JT, Scanlon M, Arntfield S (2003) Development of a mathematical model for high-intensity infrared processing (micronisation) of peas. Trans ASAE 46:705–713
Cenkowski S, Arntfield S, Scanlon M (2007) Far infrared dehydration and processing. In: Hui YH, Clary C, Farid MM, Fasina OO, Noomhorm A, Welti-Chanes J (eds) Food drying science and technology: microbiology, chemistry, application. DEStech Publications, Lancaster, pp 157–201
Chandrasekaran S, Ramanathan S, Basak T (2013) Microwave food processing—a review. Food Res Int 52:243–261
De Mesa RY, Alavi S, Singh N, Shi NY, Dogan H, Sang Y (2009) Soy protein-fortified expanded extrudates: baseline study using corn starch. J Food Eng 90:262–270
Deepa C, Hebbar HU (2016) Effect of high-temperature short-time ‘Micronisation’ of grains on product quality and cooking characteristics. Food Eng Rev 8:1–13
Fasina O, Tyler RT, Pickard MD, Zheng GH (1999) Infrared heating of hull-less and pearled barley. J Food Process Preserv 23:135–151
Fasina O, Tyler B, Pickard M, Zheng GH, Wang N (2001) Effect of infrared heating on the properties of legume seeds. Int J Food Sci Technol 36:79–90
Food and Agriculture Organisation of United Nations (2004) Value of production: Bambara groundnut. http://faostat3.fao.org/crop/bambaragroundnut.htm. Accessed Sept 2016
Galiotou-Panayotou M, Kyriakidis NB, Margaris I (2008) Phytase–phytate–pectin hypothesis and quality of legumes cooked in calcium solutions. J Sci Food Agric 88:355–361
Ginzburg AS (1969) Application of infrared radiation in food processing. Chemical and process engineering series. Leonard Hill Books, London
Han H, Baik BK (2008) Antioxidant activity and phenolic content of lentils (Lens culinaris), chickpeas (Cicer arietinum L.), peas (Pisum sativum L.) and soybeans (Glycine max), and their quantitative changes during processing. Int J Food Sci Technol 43:1971–1978
Hebbar UH, Vishwanathan KH, Ramesh MN (2004) Development of combined infrared and hot air dryer for vegetables. J Food Eng 65:557–563
Hernandez-Infante M, Sousa V, Montalvo I, Tena E (1998) Impact of microwave heating on haemogglutenin, trypsin inhibitors and protein quality of selected legume seeds. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 52:199–208
Hohlberg AI, Stanley DW (1987) Hard-to-cook defect in black beans. Protein and starch considerations. J Agric Food Chem 35:571–576
Huma N, Anjum M, Sehar S, Khan MI, Hussain S (2008) Effect of soaking and cooking on nutritional quality and safety of legumes. Nutr Food Sci 38:570–577
Iqbal A, Khalil IA, Ateeq N, Sayyar-Khan M (2006) Nutritional quality of important food legumes. Food Chem 97:331–335
Jackson GM, Varriano-Marston E (1981) Hard-to-cook phenomenon in beans: effects of accelerated storage on water absorption and cooking time. J Food Sci 46:799–803
Jeevitha GC, Hebbar HU, Raghavarao KSMS (2013) Electromagnetic radiation-based dry blanching of red bell peppers: a comparative study. J Food Process Eng 36:663–674
Jun S, Irudayaraj J (2003) A dynamic fungal inactivation approach using selective infrared heating. Trans ASAE 46(5):1407–1412
Karr-Lilienthal LK, Grieshop CM, Merchen NR, Mahan DC, Fahey GC (2004) Chemical composition and protein quality comparisons of soybeans and soybean meals from five leading soybean-producing countries. J Agric Food Chem 52:6193–6199
Kayitesi E, Duodu KG, Minnaar A, De Kock HL (2012) Effect of micronisation of pre-conditioned cowpeas on cooking time and sensory properties of cooked cowpeas. J Sci Food Agric 93:838–845
Krishnamurthy K, Khurana HK, Soojin J, Irudayaraj J, Demirci A (2008) Infrared heating in food processing: an overview. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 7:2–13
Michael P, Ámingos D, Baghurst R (1991) Tilden lecture. Applications of microwave dielectric heating effects to synthetic problems in chemistry. Chem Soc Rev 20:1–47
Murevanhema YY, Jideani VA (2013) Potential of bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranea (L.) Verdc) milk as a probiotic beverage—a review. Crit Rev Food Sci 53:954–967
Mwangwela AM (2006) Physicochemical characteristics of conditioned and micronised cowpeas and functional properties of the resultant flours. University of Pretoria, Pretoria
Mwangwela AM, Waniska RD, Minnaar A (2006) Hydrothermal treatments of two cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp) varieties: effect of micronisation on physicochemical and structural characteristics. J Sci Food Agric 86:35–45
Mwangwela AM, Waniska RD, Minnaar A (2007a) Effect of micronisation temperature (130 and 170 °C) on functional properties of cowpea flour. Food Chem 104:650–657
Mwangwela AM, Waniska RD, Mcdonough C, Minnaar A (2007b) Cowpea cooking characteristics as affected by micronisation temperature: a study of the physicochemical and functional properties of starch. J Sci Food Agric 87:399–410
Ndungu KE, Emmambux MN, Minnaar A (2012) Micronisation and hot air roasting of cowpeas as pretreatments to control the development of hard-to-cook phenomenon. J Sci Food Agric 92:1194–1200
Nti CA (2009) Effects of bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranea) variety and processing on the quality and consumer appeal for its products. Int J Food Sci Technol 44:2234–2242
Oboh G (2006) Antioxidant properties of some commonly consumed and underutilised tropical legumes. Eur Food Res Technol 224:61–65
Ofuya Z, Akhidue V (2005) The role of pulses in human nutrition: a review. J Appl Sci Environ Manag 9:99–104
Ogundele OM (2017) Nutritional and functional properties of soaked and micronised Bambara groundnut seeds and their flours. PhD Thesis (Food Science). University of Pretoria, Pretoria
Ogundele OM, Emmambux MN (2018) Effect of infrared heating of pre-soaked whole and dehulled bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranea) seeds on their cooking characteristics and microstructure. LWT Food Sci Technol 97:581–587
Ogundele OM, Minnaar A, Emmambux MN (2017) Effects of micronisation and dehulling of pre-soaked bambara groundnut seeds on microstructure and functionality of the resulting flours. Food Chem 214:655–663
Padmashree A, Semwal A, Khan M, Govindaraj T, Sharma G (2016) Effect of infrared processing on functional, nutritional, antinutritional and rheological properties of mung bean (Phaseolus aereus) seeds. Int J Adv Res 4:606–613
Parmar N, Singh N, Kaur A, Thakur S (2017) Comparison of color, anti-nutritional factors, minerals, phenolic profile and protein digestibility between hard-to-cook and easy-to-cook grains from different kidney bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) accessions. J Food Sci Technol 54:1023–1034
Penicela L (2011) The Influence of seed coat and cotyledon structure on cooking characteristics of cowpea. M.Sc. dissertation. (Food Science). University of Pretoria, Pretoria, SA
Sadeghi AA, Fattah ANA, Chamani M (2010) The effects of micronisation on ruminal starch degradation of corn grain. World Appl Sci J 16:240–243
Sakai N, Hanzawa T (1994) Applications and advances in far-infrared heating in Japan. Trends Food Sci Technol 5:357–362
Sandu C (1986) Infrared radiative drying in food engineering: a process analysis. Biotechnol Prog 3:109–119
Sanginga N (2003) Role of biological nitrogen fixation in legume based cropping systems; a case study of West Africa farming systems. Plant Soil 252:25–39
Scanlon MG, Cenkowski S, Segall KI, Arntfield SD (2005) The physical properties of micronised lentils as a function of tempering moisture. Biosyst Eng 92:247–254
Sharma G (2009) Micronisation. Defence research and development organization, ministry of defence, government of India. Sci Spectrum 169–171
Sharma GP, Verma RC, Pathare PB (2005) Thin layer infrared radiation drying of onion slices. J Food Eng 67:361–366
Silva C, Bates R, Deng J (1981) Influence of soaking and cooking upon the softening and eating quality of black beans (Phaseolus vulgaris). J Food Sci 46:1716–1720
Singh R, Chung G, Nelson R (2007) Landmark research in legumes. Genome 50:525–537
Singh B, Singh JP, Shevkani K, Singh N, Kaur A (2017) Bioactive constituents in pulses and their health benefits. J Food Sci Technol 54:858–870
Taiwo KA, Akanbi C, Ajibola OO (1997) The effects of soaking and cooking time on the cooking properties of two cowpea varieties. J Food Eng 33:337–346
Tresina PS, Mohan VR (2011) Effect of gamma irradiation on physicochemical properties, proximate composition, vitamins and antinutritional factors of the tribal pulse Vigna unguiculata subsp. unguiculata. Int J Food Sci Technol 46:1739–1746
Vadivel V, Janardhanan K (2005) Nutritional and antinutritional characteristics of seven South Indian wild legumes. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 60:69–75
Van Zuilichem DJ, Van’t Riet K, Stolp W (1986) An overview of new infrared radiation processes for various agricultural products. In: Le Maguer M, Jelen P (eds) Food engineering and process applications, transport phenomena, vol 1. Elsevier, New York, pp 595–610
Vilakati N, Macintyre U, Oelofse A, Taylor JR (2015) Influence of micronisation (infrared treatment) on the protein and functional quality of a ready-to-eat sorghum-cowpea African porridge for young child-feeding. LWT Food Sci Technol 63:1191–1198
Wang N, Daun JK, Malcolmson LJ (2003) Relationship between physicochemical and cooking properties, and effects of cooking on antinutrients, of yellow field peas (Pisum sativum). J Sci Food Agric 83:1228–1237
Zhao Y (2000) The effects of treatment and micronization on the quality and cookability of lentils. Unpublished M.Sc. thesis. University of Manitoba, Department of Food Science, Winnipeg, Manitoba
Acknowledgements
The work was supported through the Global Excellence and Stature Funding (GES) of the University of Johannesburg granted to the main author (Ogundele O. M).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-023-05703-5
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ogundele, O.M., Kayitesi, E. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Influence of infrared heating processing technology on the cooking characteristics and functionality of African legumes: a review. J Food Sci Technol 56, 1669–1682 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03661-5
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03661-5