Abstract
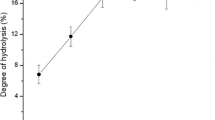
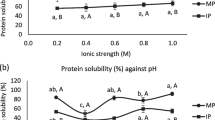
The chemical composition of palm heart (cultivar Piarom) and solubility kinetics of its protein was investigated under different salt concentrations and pHs. Palm heart protein isolate (PHPI) was prepared using alkaline extraction and acidic precipitation and its functional properties (emulsifying properties and emulsion stability, foam capacity, and water holding and fat absorption capacity) and thermal properties were determined. It was revealed that palm heart had high nutritional value and contains high protein content. By increasing pH up to 3, solubility was decreased and then significantly increased by elevating pH to 9 (p < 0.05). Salt addition significantly decreased palm heart protein (PHP) solubility. Considering solubility kinetics, pH 9 and salt concentration of 0.25 M was determined as the best protein extraction condition. Denaturation temperature and enthalpy changes of PHPI were 108.63 °C and 143.1 J/g; suggesting high thermal stability of this product. Regarding its suitable functional, physicochemical and thermal properties, PHP can be considered as an ideal substitution for animal protein sources in the food industry.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakhshi Moghadam F, Milani E, Mortazavi SA, Meshkani SM (2013) Effect of extraction methods on functional properties of chickpea protein isolated. Iran J Food Sci Tec 10:11–20
Bildstein M, Lohmann M, Hennigs C, Krause A, Hilz H (2008) An enzyme-based extraction process for the purification and enrichment of vegetable proteins to be applied in bakery products. Eur Food Res Technol 228:177–186
Borde B, Bizot H, Vigier G, Buleon A (2002) Calorimetric analysis of the structural relaxation in partially hydrated amorphous polysaccharides. I. Glass transition and fragility. Carbohyd Polym 48:83–96
Boye J, Aksay S, Roufik S, Ribéreau S, Mondor M, Farnworth E, Rajamohamed S (2010) Comparison of the functional properties of pea, chickpea and lentil protein concentrates processed using ultrafiltration and isoelectric precipitation techniques. Food Res Int 43:537–546
Chandi GK, Sogi D (2007) Functional properties of rice bran protein concentrates. J Food Eng 79:592–597
Denavi G, Tapia-Blácido DR, Añón MC, Sobral PJA, Mauri AN, Menegalli FC (2009) Effects of drying conditions on some physical properties of soy protein films. J Food Eng 90:341–349
Farahnaky A, Badii F, Farhat IA, Mitchell JR, Hill SE (2005) Enthalpy relaxation of bovine serum albumin and implications for its storage in the glassy state. Biopolymers 78:69–77
Garba U, Kaur S (2014) Protein isolates: production, functional properties and application. Int J Cur Res Rev 6:35–45
Ghumman A, Kaur A, Singh N (2016) Functionality and digestibility of albumins and globulins from lentil and horse gram and their effect on starch rheology. Food Hydrocoll 61:843–850
Hassan HM, Afify A, Basyiony A, Ahmed GT (2010) Nutritional and functional properties of defatted wheat protein isolates. Aust J Basic Appl Sci 4:348–358
Heywood A, Myers D, Bailey T, Johnson L (2002) Functional properties of extruded-expelled soybean flours from value-enhanced soybeans. J Am Oil Chem Soc 79:699–702
Johnson EA, Brekke C (1983) Functional properties of acylated pea protein isolates. J Food Sci 48:722–725
Kaur M, Singh N (2005) Studies on functional, thermal and pasting properties of flours from different chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) cultivars. Food Chem 91:403–411
Kaur M, Singh N (2007) Characterization of protein isolates from different Indian chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) cultivars. Food Chem 102:366–374
Khosravi Y, Keramat J, Hosaini E, Keshavarz HA, Mahmodi E (2013) Functional properties of Iranian legume flour. J Food Technol Nutr 10:73–80
Lawal O, Adebowale K, Ogunsanwo B, Sosanwo O, Bankole S (2005) On the functional properties of globulin and albumin protein fractions and flours of African locust bean (Parkia biglobossa). Food Chem 92:681–691
Liu C, Wang X, Ma H, Zhang Z, Gao W, Xiao L (2008) Functional properties of protein isolates from soybeans stored under various conditions. Food Chem 111:29–37
Liu S, Elmer C, Low NH, Nickerson MT (2010) Effect of pH on the functional behaviour of pea protein isolate–gum Arabic complexes. Food Res Int 43:489–495
Marco C, Rosell CM (2008) Functional and rheological properties of protein enriched gluten free composite flours. J Food Eng 88:94–103
Martínez KD, Carrera Sánchez C, Rodríguez Patino JM, Pilosof AMR (2009) Interfacial and foaming properties of soy protein and their hydrolysates. Food Hydrocoll 23:2149–2157
Mirarab RS, Mohebbi M, Haddad Khodaparast MH, Koocheki A (2014) Comparisons of some sensory, physical and textural characteristics of chocolate dessert containing different amounts of albumin, sodium caseinat, whey protein concentrate. J Res Innov Food Sci Tech 3:375–388
Movahed A, Mohammadi MM, Akbarzadeh S, Nabipour I, Ramezanian N, Hajian N (2011) The heart of date palm: its nutritional and functional constituents. Iran S Med J 14:100–105
Ogungbenle HN (2008) Effects of salt concentrations on the functional properties of some legume flours. Pak J Nutr 7:453–458
Papalamprou EM, Doxastakis GI, Kiosseoglou V (2010) Chickpea protein isolates obtained by wet extraction as emulsifying agents. J Sci Food Agric 90:304–313
Rahbari M, Aalami M, Maghsoudlou Y, Kashaninejad M (2013) Evaluation of solubility properties and electrophoretic patterns of wheat germ proteins. J Food Process Pres 2:71–86
Roccia P, Ribotta PD, Pérez GT, León AE (2009) Influence of soy protein on rheological properties and water retention capacity of wheat gluten. LWT Food Sci Technol 42:358–362
Salvi J, Katewa S (2014) Preliminary assessment of nutritional value of palm heart of Phoenix sylvestris (Roxb.). Int Food Res J 21:2141–2144
Shahrabi A, Badii F, Ehsani M, Maftoonazad N, Sarmadizadeh D (2011) Functional and thermal properties of chickpea and soy-protein concentrates and isolates. Iran J Nutr Sci Food Tec 6:49–58
Shevkani K, Singh N, Kaur A, Rana JC (2014) Physicochemical, pasting, and functional properties of Amaranth seed flours: effects of lipids removal. J Food Sci 79:1271–1277
Shevkani K, Kaur A, Kumar S, Singh N (2015a) Cowpea protein isolates: functional properties and application in gluten-free rice muffins. LWT Food Sci Technol 63:927–933
Shevkani K, Singh N, Kaur A, Rana JC (2015b) Structural and functional characterization of kidney bean and field pea protein isolates: a comparative study. Food Hydrocoll 43:679–689
Singh BP, Vij S, Hati S (2014) Functional significance of bioactive peptides derived from soybean. Peptides 54:171–179
Sun J, Li X, Xu X, Zhou G (2011) Influence of various levels of flaxseed gum addition on the water-holding capacities of heat-induced porcine myofibrillar protein. J Food Sci 76:C472–C478
Tang C-H, Sun X (2011) A comparative study of physicochemical and conformational properties in three vicilins from Phaseolus legumes: implications for the structure–function relationship. Food Hydrocoll 25:315–324
Xu L, Diosady L (2002) Removal of phenolic compounds in the production of high-quality canola protein isolates. Food Res Int 35:23–30
Zhang T, Jiang B, Wang Z (2007) Gelation properties of chickpea protein isolates. Food Hydrocoll 21:280–286
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hematian Sourki, A., Rahmanian, M. Kinetic studies on palm heart protein solubility and investigation of physicochemical, functional and thermal properties of palm heart protein isolate. J Food Sci Technol 56, 1820–1828 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03626-8
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03626-8