Abstract
Data-driven computing in applied mechanics utilizes the material data set directly, and hence is free from errors and uncertainties stemming from the conventional material modeling. For data-driven computing in elasticity, this paper presents a simple heuristic that is robust against noise and outliers in a data set. For each structural element, we extract the material property from some nearest data points. Using the nearest neighbors reduces the influence of noise, compared with the existing method that uses a single data point. Also, the robust regression is adopted to reduce the influence of outliers. Numerical experiments on the static equilibrium analysis of trusses are performed to illustrate that the proposed method is robust against the presence of noise and outliers.











Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
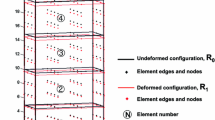
Since this example is a statically determinate truss, for any member strains there exists a compatible nodal displacement vector. What is meant to be explained here is that in the proposed method a solution is alway defined so as to satisfy the compatibility relation exactly.
References
Altman, N.S.: An introduction to kernel and nearest-neighbor nonparametric regression. Am Stat 46, 175–185 (1992)
Boyd, S., Vandenberghe, L.: Convex Optimization. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2004)
Bessa, M.A., Bostanabad, R., Liu, Z., Hu, A., Apley, D.W., Brinson, C., Chen, W., Liu, W.K.: A framework for data-driven analysis of materials under uncertainty: countering the curse of dimensionality. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 320, 633–667 (2017)
Chen, H., Chiang, R.H.L., Storey, V.C.: Business intelligence and analytics: from big data to big impact. MIS Q. Arch. 36, 1165–1188 (2012)
Clément, A., Soize, C., Yvonnet, J.: Computational nonlinear stochastic homogenization using a nonconcurrent multiscale approach for hyperelastic heterogeneous microstructures analysis. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Eng. 91, 799–824 (2012)
Cleveland, W.S.: Robust locally weighted regression and smoothing scatterplots. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 74, 829–836 (1979)
Cleveland, W.S., Devlin, S.J.: Locally weighted regression: an approach to regression analysis by local fitting. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 83, 596–610 (1988)
Conti, S., Müller, S., Ortiz, M.: Data-driven problems in elasticity. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 229, 79–123 (2018)
Fahad, A., Alshatri, N., Tari, Z., Alamri, A., Khalil, I., Zomaya, A.Y., Foufou, S., Bouras, A.: A survey of clustering algorithms for big data: taxonomy and empirical analysis. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Topics Comput. 2, 267–279 (2014)
Fan, W., Hu, C.: Big graph analyses: from queries to dependencies and association rules. Data Sci. Eng. 2, 36–55 (2017)
Flach, P.: Machine Learning: The Art and Science of Algorithms that Make Sense of Data. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2012)
Gupta, M.R., Garcia, E.K., Chin, E.: Adaptive local linear regression with application to printer color management. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 17, 936–945 (2008)
Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R., Friedman, J.: The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction, 2nd edn. Springer, New York (2009)
Huber, P.J.: Robust estimation of a location parameter. Ann. Math. Stat. 35, 73–101 (1964)
Huber, P.J., Ronchetti, E.M.: Robust Statistics, 2nd edn. Wiley, Hoboken (2009)
Ibañez, R., Abisset-Chavanne, E., Aguado, J.V., Gonzalez, D., Cueto, E., Chinesta, F.: A manifold learning approach to data-driven computational elasticity and inelasticity. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 25, 47–57 (2018)
Ibañez, R., Borzacchiello, D., Aguado, J.V., Abisset-Chavanne, E., Cueto, E., Ladeveze, P., Chinesta, F.: Data-driven non-linear elasticity: constitutive manifold construction and problem discretization. Comput. Mech. 60, 813–826 (2017)
Kirchdoerfer, T., Ortiz, M.: Data-driven computational mechanics. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 304, 81–101 (2016)
Kirchdoerfer, T., Ortiz, M.: Data driven computing with noisy material data sets. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 326, 622–641 (2017)
Kirchdoerfer, T., Ortiz, M.: Data-driven computing in dynamics. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Eng. 113, 1697–1710 (2018)
Klusemann, B., Ortiz, M.: Acceleration of material-dominated calculations via phase-space simplicial subdivision and interpolation. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Eng. 103, 256–274 (2015)
Lee, T., Ouarda, T.B.M.J., Yoon, S.: KNN-based local linear regression for the analysis and simulation of low flow extremes under climatic influence. Clim. Dyn. 49, 3493–3511 (2017)
Maronna, R., Martin, D., Yohai, V.: Robust Statistics: Theory and Methods. Wiley, Chichester (2006)
Mattmann, C.A.: Computing: a vision for data science. Nature 493, 473–475 (2013)
Miguel, E., Bradley, D., Thomaszewski, B., Bickel, B., Matusik, W., Otaduy, M.A., Marschner, S.: Data-driven estimation of cloth simulation models. Comput. Graph. Forum 31, 519–528 (2012)
Nguyen, L.T.K., Keip, M.-A.: A data-driven approach to nonlinear elasticity. Comput. Struct. 194, 97–115 (2018)
Prairie, J.R., Rajagopalan, B., Fulp, T.J., Zagona, E.A.: Statistical nonparametric model for natural salt estimation. J. Environ. Eng. 131, 130–138 (2005)
Ruiters, R., Schwartz, C., Klein, R.: Data driven surface reflectance from sparse and irregular samples. Comput. Graph. Forum 31, 315–324 (2012)
Siuly, S., Zhang, Y.: Medical big data: neurological diseases diagnosis through medical data analysis. Data Sci. Eng. 1, 54–64 (2016)
Temizer, İ., Wriggers, P.: An adaptive method for homogenization in orthotropic nonlinear elasticity. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 196, 3409–3423 (2007)
Temizer, İ., Zohdi, T.I.: A numerical method for homogenization in non-linear elasticity. Comput. Mech. 40, 281–298 (2007)
Terada, K., Kato, J., Hirayama, N., Inugai, T., Yamamoto, K.: A method of two-scale analysis with micro-macro decoupling scheme: application to hyperelastic composite materials. Comput. Mech. 52, 1199–1219 (2013)
Tsai, C.W., Lai, C.F., Chao, H.C., Vasilakos, A.V.: Big data analytics: a survey. J. Big Data 21, Article No. 21 (2015)
Wang, H., O’Brien, J.F., Ramamoorthi, R.: Data-driven elastic models for cloth: modeling and measurement. ACM Trans. Graph. 30, Article No. 71 (2011)
Acknowledgements
This work is partially supported by JSPS KAKENHI 17K06633 and 18K18898.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kanno, Y. Simple heuristic for data-driven computational elasticity with material data involving noise and outliers: a local robust regression approach. Japan J. Indust. Appl. Math. 35, 1085–1101 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13160-018-0323-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13160-018-0323-y