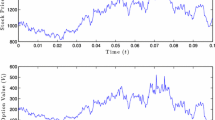
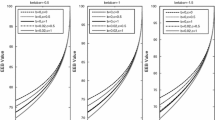
Abstract
In this paper, we present a simple numerical method to determine the optimal exercise boundary for American put option with jump risk. Our intermediate function obtained by the partial integro-differential equation can easily determine the optimal exercise boundary. We use finite difference method characterized by explicit scheme in continuation region and extrapolation near optimal exercise boundary. Finally, we present several numerical results which illustrate comparison to other methods.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almendral, A., Oosterlee, C.W.: Accurate evaluation of European and American options under the CGMY process. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 29, 93–117 (2007)
Amin, K.: Jump diffusion option valuation in discerete time. J. Financ. 48, 1833–1863 (1993)
Andersen, L., Andreasen, J.: Jump-diffusion processes: volatility smile fitting and numerical methods for option pricing. Rev. Deriv. Res. 4, 231–262 (2000)
Ball, C., Torous, W.: On jumps in common stock prices and their impact on call option pricing. J. Financ. 40, 155–173 (1985)
Ballestra, L.V., Cecere, L.: A numerical method to estimate the parameters of the CEV model implied by American option prices: evidence from NYSE. Chaos Solitons Fract. 88, 100–106 (2016)
Black, F., Scholes, M.: The pricing of options and corporate liabilities. J. Polit. Econ. 81, 637–659 (1973)
Carr, P., Geman, H., Madan, D.B., Yor, M.: The fine structure of asset returns: an empirical investigation. J. Bus. 75, 305–332 (2002)
Chockalingam, A., Muthuraman, K.: Pricing American options when asset prices jump. Oper. Res. Lett. 38, 82–86 (2010)
Cont, R., Voltchkova, E.: A finite difference scheme for option pricing in jump diffusion and exponential Levy models. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 43, 1596–1626 (2005)
Deng, G.: Pricing American put option on zero-coupon bond in a jump-extended CIR model. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 22, 186–196 (2015)
d’Halluin, Y., Forsyth, P.A., Labahn, G.: A penalty method for American options with jump diffusion processes. Numer. Math. 97, 321–352 (2004)
Gukhal, C.R.: Analytical valuation of American options on jump-diffusion processes. Math. Financ. 11, 97–115 (2001)
Jarrow, R.A., Rosenfeld, E.: Jump risks and the intertemporal capital asset pricing model. J. Bus. 57, 337–351 (1984)
Jorion, P.: On jump processes in the foreign exchange and stock markets. Rev. Financ. Study 1, 427–455 (1998)
Kim, B.J., Ahn, C., Choe, H.J.: Direct computation for American put option and free boundary using finite difference method. Jpn J. Ind. Appl. Math. 30, 21–37 (2013)
Kou, S.G.: A jump-diffusion model for option pricing. Manag. Sci. 48, 1086–1101 (2002)
Kou, S.G., Petrella, G., Wang, H.: Pricing path-dependent options with jump risk via Laplace transforms. Kyoto Econ. Rev. 74, 1–23 (2005)
Kou, S.G., Wang, H.: Option pricing under a double exponential jump diffusion model. Manag. Sci. 50, 1178–1192 (2004)
Merton, R.: Theory of rational option pricing. Bell J. Econ. Manag. Sci. 4, 141–183 (1973)
Merton, R.: Option pricing when the underlying stock returns are discontinuous. J. Financ. Econ. 3, 125–144 (1976)
Simonato, J.G.: Computing American option prices in the lognormal jump-diffusion framework with a Markov chain. Financ. Res. Lett. 8, 220–226 (2011)
Zhang, X.L.: Numerical analysis of American option pricing in a jump-diffusion model. Math. Oper. Res. 22, 668–690 (1997)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the research grant of the Kongju National University in 2015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, B.J., Ma, YK. & Choe, H.J. Optimal exercise boundary via intermediate function with jump risk. Japan J. Indust. Appl. Math. 34, 779–792 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13160-017-0261-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13160-017-0261-0