Abstract
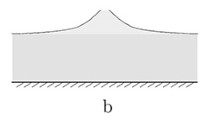
Consideration in this paper is the two-dimensional steady periodic rotational gravity waves with negative surface tension. Local curves of small amplitude solutions of the resulting problem are obtained by using the Crandall–Rabinowitz local bifurcation theory. By means of the global bifurcation theory combined with the Schauder theory of elliptic equations with the Venttsel boundary conditions, the curves of small amplitude solutions is extended to the global continuum of solutions. Furthermore, it is shown that those waves are necessarily symmetric about the crest under the assumption that their surface profiles are monotonic between troughs and crests and locally strictly monotonic near the troughs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berestycki, H., Nirenberg, L.: Monotonicity, symmetry and antisymmetry of solutions of semilinear elliptic equations. J. Geom. Phys. 5, 237–275 (1988)
Constantin, A.: Nonliear Water Waves with Applications to Wave-Current Interactions and Tsunamis, volume 81 of CBMS-NSF Conference Series in Applied Mathematics, vol. 81. SIAM, Philadelphia (2011)
Constantin, A.: On equatorial wind waves. Differ. Integr. Equ. 26, 237–252 (2013)
Constantin, A., Varvaruca, E.: Global bifurcation of steady gravity water waves with critical layers. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 199, 33–67 (2011)
Constantin, A., Ehrnström, M., Wahlén, E.: Symmetry of steady periodic gravity water waves with vorticity. Duke Math. J. 140(3), 591–603 (2007)
Constantin, A., Escher, J.: Symmetry of steady periodic surface water waves with vorticity. J. Fluid Mech. 498, 171–181 (2004)
Constantin, A., Escher, J.: Symmetry of steady deep-water waves with vorticity. Eur. J. Appl. Math. 15, 755–768 (2004)
Constantin, A., Strauss, W.: Exact steady periodic water waves with vorticity. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 57, 481–527 (2004)
Constantin, A., Strauss, W., Varvaruca, E.: Global bifurcation of steady gravity water waves with critical layers (2014). arXiv:1407.0092 (preprint)
Crandall, M., Rabinowitz, P.: Bifurcation from simple eigenvalues. J. Funct. Anal. 8, 321–340 (1971)
Craig, W., Sternberg, P.: Symmetry of solitary waves. Commun. Partial Differ. Equ. 13, 603–633 (1988)
Evans, L.C.: Partial Differential Equations. American Mathematical Society, Providence (1998)
Ehrnstoröm, M.: Deep-water waves with vorticity: symmetry and rotational behaviour. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. 19, 483–491 (2007)
Fraenkl, L.E.: Introduction to Maximum Principles and Symmetry in Elliptic Problems. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2000)
Garabedian, P.: Surface waves of finite depth. J. Anal. Math. 14, 161–169 (1965)
Gidas, B., Ni, W.M., Nirenberg, L.: Symmetry and related properties via the maximum principle. Commun. Math. Phys. 68, 209–243 (1979)
Henry, D., Matioc, A.-V.: On the symmetry of steady equatorial wind waves. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 18, 50–56 (2014)
Henry, D., Matioc, A.-V.: On the existence of equatorial wind waves. Nonlinear Anal. 101, 113–123 (2014)
Henry, D., Matioc, A.-V.: Global bifurcation of capillary-gravity stratified water waves. Proc. R. Soc. Edinb. Sect. A 144, 775–786 (2014)
Henry, D., Matioc, A.-V.: On the existence of steady periodic capillary-gravity stratified water waves. Ann. Sc. Norm. Super. Pisa Cl. Sci. (5) 12, 955–974 (2013)
Hur, V.M.: Symmetry of solitary water waves with vorticity. Math. Res. Lett. 15, 491–509 (2008)
Hur, V.M.: Symmetry of steady periodic water waves with vorticity. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 365, 2203–2214 (2007)
Luo, Y., Trudinger, N.: Linear second order elliptic equations with Venttsel boundary conditions. Proc. R. Soc. Edinb. Sect. A 118, 193–207 (1991)
Martin, C.-I.: Equatorial wind waves with capillary effects and stagnation points. Nonlinear Anal. 96, 1–17 (2014)
Matioc, A.-V., Matioc, B.-V.: Regularity and symmetry properties of rotational solitary water waves. J. Evol. Equ. 12, 481–494 (2012)
Matioc, A.-V., Matioc, B.-V.: On the symmetry of periodic gravity water waves with vorticity. Differ. Integr. Equ. 26, 129–140 (2013)
Okamoto, H., Shōji, M.: Two-dimensional, periodic, capillary-gravity waves with negative surface tension. In: Mielke, A., Kirchässner, K. (eds.) Structure and Dynamics of Nonlinear Waves in Fluids, pp. 363–369. World Scientific Publishing, River Edge (1995)
Okamoto, H., Shōji, M.: The Mathematical Theory of Permanent Progressive Water Waves. World Scientific Publishing, River Edge (2001)
Prandtl, L., Tietjens, O.G.: Fundamentals of Hydro- and Aerodynamics. Dover Publications, Mineola (1957)
Serrin, J.: A symmetry property in potential theory. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 43, 304–318 (1971)
Toland, J.F.: On the symmetry theory for Stokes waves of finite and infinite depth, In: Iooss, G., Guès, O., Nouri, A. (eds.) Trends in Applications of Mathematics to Mechanics (Nice, 1998), pp. 207–217. Chapman & Hall/CRC, Boca Raton, (2000)
Wahlén, E.: Steady periodic capillary-gravity waves with vorticity. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 38, 921–943 (2006)
Wahlén, E.: Steady periodic capillary waves with vorticity. Ark. Mat. 44, 367–387 (2006)
Wahlén, E.: On some nonlinear aspects of wave motion. PhD thesis, Lund University (2008)
Walsh, S.: Some criteria for the symmetry of stratified water waves. Wave Motion 46, 350–362 (2009)
Walsh, S.: Steady stratified periodic gravity waves with surface tension I: local bifurcation. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. 34, 3241–3285 (2014)
Walsh, S.: Steady stratified periodic gravity waves with surface tension II: global bifurcation. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. 34, 3287–3315 (2014)
Acknowledgements
The work of Gao is partially supported by the NSF-China Grant-11171158, National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program)-2013CB 834100, PAPD of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, and Jiangsu Center for Collaborative Innovation in Geographical Information Resource Development and Application. The authors are grateful to Ming Chen and Samuel Walsh for their valuable suggestions during preparation of the manuscript. The work of Fan is supported by Natural Science Foundation of Henan Normal University, Grant No. 2016QK03, and the Startup Foundation for Introducing Talent of Henan Normal University, Grant No. qd16150.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
For the sake of completeness, we present the maximum principles suitable for our setting in this section.
Theorem 5.1
[14] Let \(\Omega \subset \mathbb {R}^{2}\) be a rectangle, \(w \in C^{2} (\overline{\Omega })\), and suppose that \( \mathcal {L}w =0\) for some uniformly elliptic operator \(\mathcal {L}=\sum _{i,j=1}^{2}a_{ij}\partial _{ij}+\sum _{i=1}^{2}b_i\partial _i\) with continuous coefficients in \(\overline{\Omega }\). Then the following statements hold:
(i) [The maximum principle] If \(min_{\overline{\Omega }}w\) or \(max_{\overline{\Omega }}w\) is attained in the interior of \(\Omega \), then w is a constant in \(\overline{\Omega }\).
(ii) [The Hopf boundary-point lemma] Let A be a point on the smooth part of the boundary \(\partial \Omega \) such that \( w(A)< w(X)\) (or \( w(A)> w(X)\) ) for all \(X \in \Omega \). Then the outer normal derivative of w at A is strictly negative (positive).
(iii) [The Serrin edge point lemma] Let \(\Theta _0\) be a corner point of \(\partial \Omega \) such that \(w(\Theta _0)>w(\Theta )\) (or \(w(\Theta _0)<w(\Theta )\)) for all \(\Theta \in \Omega \). If \(a_{11}(\Theta _0)-0\), and \(\tau \) is a unit vector outward from \(\Omega \) at \(\Theta _0\), then either the first or the second derivative of w in the direction of \(\tau \) is strictly positive (negative).
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, L., Gao, H. Steady periodic rotational gravity waves with negative surface tension. Japan J. Indust. Appl. Math. 34, 531–554 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13160-017-0256-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13160-017-0256-x