Abstract
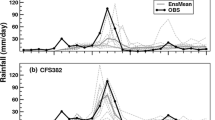
During the transition period between the Jianghuai Meiyu and North China rainy seasons in 2016, there was a high-impact rainstorm event, connecting these two rainy seasons. However, both the short and medium range forecasts predicted a rain band that was too far south; this error can have serious implications for flood preparedness. This study discusses the causes of the forecast error using the ECMWF deterministic and ensemble models. The results show that the prediction of a too-weak westerly trough at the 500-hPa level is the dominant factor. Specifically, a weaker predicted 500-hPa westerly trough reduces the strength of the low vortex at 850 hPa; correspondingly, the shear line to the east of the vortex and the Meiyu front are weaker and farther south, and the monsoon is also weaker, which causes the large area of humidity convergence to be shifted southward. Finally, the heavy rainfall is located farther south with weaker intensity. And vice visa, when a stronger westerly trough is predicted, the location of rain band will be northward. This conclusion may be useful for meteorological decision making in medium range and will help to improve capabilities of risk reduction.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bougeault, P., Toth, Z., Bishop, C., Brown, B., Burridge, D., Chen, D.H., Ebert, B., Fuentes, M., Hamill, T.M., Mylne, K., Nicolau, J., Paccagnella, T., Park, Y.Y., Parsons, D., Raoult, B., Schuster, D., Dias, P.S., Swinbank, R., Takeuchi, Y., Tennant, W., Wilson, L., Worley, S.: The THORPEX interactive grand global ensemble. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 91, 1059–1072 (2010)
Ding, Y.H.: Summer monsoon rainfall in China. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan. 70, 373–396 (1992)
Ding, Q., Wang, B.: Circumglobal teleconnection in the northern hemisphere summer. J. Clim. 18, 3483–3503 (2005)
Ding, Y.H., Zhang, Y., et al.: Analysis of the large scale circulation features and synoptic systems in East Asia during the intensive observation period of GAME/HUBEX. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan. 79, 277–300 (2001)
Ding, Y., Liu, J., Sun, Y., et al.: A study of the synoptic climatology of the Meiyu system in East Asia. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 31, 1082–1101 (2007)
Gao, Y., Xu, S., Guo, Q., et al.: Some Problems about East Asian Monsoon (in Chinese). Science Press, Beijing (1962)
Gentiloni, F., Johansson E., Greenall T., et al.: Final Report on 1998 Floods in the People's Republic of China, UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (1998)
Gu, W., Wang, L., Hu, Z., et al.: Interannual variations of the first rainy season precipitation over South China. J. Clim. 31, 623–640 (2018)
Huang, R., Chen, J., Wang, L., Lin, Z.: Characteristics, processes, and causes of the spatio-temporal variabilities of the east Asian monsoon system. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 29, 910–942 (2012)
Kang, Z., Ma, J.: Influence of the circulation at middle and high level on the position of Meiyu rainbelt. The 9th National Conference on disaster weather forecast technology (2012)
Liu, H., He, M., Wang, B., et al.: Advances in low-level jet research and future prospects. Acta Meteor. Sinica. 72, 191–206 (2014)
Miller, M., Buizza, R., Haseler, J., et al.: Increased resolution in the ECMWF deterministic and ensemble prediction systems. ECMWF Newsletter. 124, 10–16 (2010)
Si, D., Ding, Y., Liu, Y.: Decadal northward shift of the Meiyu belt and the possible cause. Chin. Sci. Bull. 55, 68–73 (2010)
Su, T., Xue, F.: The intraseasonal variation of summer monsoon circulation and rainfall in East Asia (in Chinese). Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 34, 611–628 (2010)
Swinbank, R., Kyouda, M., Buchanan, P., Froude, L., Hamill, T.M., Hewson, T.D., Keller, J.H., Matsueda, M., Methven, J., Pappenberger, F., Scheuerer, M., Titley, H.A., Wilson, L., Yamaguchi, M.: The TIGGE project and its achievements. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 97, 49–67 (2016)
Tanaka, M.: Intraseasonal oscillation and the onset and retreat dares of the summer monsoon over east, Southeast Asia and the western Pacific region using GMS high cloud amount data. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan. 70, 613–629 (1992)
Tao, S.: Some questions in the study of Monsoon. In: Review and Prospects of the Developments Of Atmospheric Sciences, pp. 35–36. China Meteorological Press, Beijing (1996)
Tao, S., Chen, L.: A review of recent research on the East Asian summer monsoon in China. In: Chang, C.P., Krishnamurti, T.N. (eds.) Monsoon Meteorology, pp. 60–92. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1987)
Wang, B.: The Asian Monsoon, p. 845. Springer, New York (2006)
Wang, Y., Ma, J., Dai, K.: Ensemble-based analysis of medium-range forecast change and uncertainty for the 20 July 2016 severe heavy rainfall over North China. Meteorol. Monogr. 44, 53–56 (2018)
Xu, W., Jiang, J.: Characteristics of the Rainbelt of Meiyu between interannual and interdecadal climate variations. Journal of Nanjing University (Nat. Sci.). 40, 292–303 (2004)
Yin, S., Ma, J.: Application research of big data in heavy rainfall forecast model in Meiyu season. In: Sun, S., Fu, M., Xu, L. (eds.) Signal and Information Processing, Networking and Computers. ICSINC 2018. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol. 550. Springer, Singapore (2019)
Zhao, H.: The rainy season in North China (in Chinese). Meteorol. Monogr. 20, 3–8 (1994)
Zhao, X., Wei, J., Zhu, D.: Analysis about function of jet of the persistent Meiy rainstorm. J. Meteor. Sci. 31, 211–216 (2011)
Zhu, K.: Southeast monsoon and rainfall in China (in Chinese). Chin. J. Geogr. Soc. 1, 1–27 (1934)
Acknowledgements
This work was jointly supported by the National Key Technology Research and Development Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2015BAC03B04), and the National Program on Global Change and Air-Sea Interaction (GASI-IPOVAI-03). We thanks Prof. Fuqing Zhang for constructive suggestion and comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jie Ma and Ruiqiang Ding designed the research. Zhiping Zong performed the data analysis, prepared all figures and led the writing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Kyong-Hwan Seo.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, J., Zong, Z., Jianping, L. et al. Assessment Based on the Forecast Error for the Transition Period between the Jianghuai Meiyu and North China Rainy Seasons in 2016. Asia-Pacific J Atmos Sci 57, 467–477 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-020-00208-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-020-00208-z