Abstract
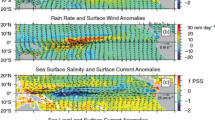
For the application of soil moisture and ocean salinity (SMOS) remotely sensed sea surface salinity (SSS) products, SMOS SSS global maps and error characteristics have been investigated based on quality control information. The results show that the errors of SMOS SSS products are distributed zonally, i.e., relatively small in the tropical oceans, but much greater in the southern oceans in the Southern Hemisphere (negative bias) and along the southern, northern and some other oceanic margins (positive or negative bias). The physical elements responsible for these errors include wind, temperature, and coastal terrain and so on. Errors in the southern oceans are due to the bias in an SSS retrieval algorithm caused by the coexisting high wind speed and low temperature; errors along the oceanic margins are due to the bias in a brightness temperature (TB) reconstruction caused by the high contrast between L-band emissivities fromice or land and from ocean; in addition, some other systematic errors are due to the bias in TB observation caused by a radio frequency interference and a radiometer receivers drift, etc. The findings will contribute to the scientific correction and appropriate application of the SMOS SSS products.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boutin J, Yin Xiaobin, Martin N, et al. 2011. Sea surface salinity from SMOS satellite and in situ observations: surface autonomous drifters in the tropical Atlantic Ocean. http://earth.eo.esa.int/workshops/smos_science_workshop/SESSION_3_OCEAN_SALINITY/J.Boutin_SMOS_Satellite_Sea_Surface_Salinity_situ.pdf
Brassington Gary B, Divakaran Prasanth. 2009. The theoretical impact of remotely sensed sea surface salinity observations in a multivariate assimilation system. Ocean Modelling, 27: 70–81
CP34. 2008. Detailed Processing Model for SMOS CP34 OS L3 Processors. http://www.cp34-users.cmima.csic.es/light_web/documentation
Font J, Boutin J, Reul N, et al. 2011. Status of sea surface salinity product provided by SMOS. http://earth.eo.esa.int/workshops/smos_science_workshop/SESSION_3_OCEAN_SALINITY/J.Font_SMOS_Status_Sea_Surface_Salinity.pdf
Gourrion J, Ballabrera J, Aretxabaleta A L, et al. 2010. Preliminary validation of SMOS products (Levels 3 and 4). IGARSS 2010 Proceedings. Honolulu USA: IEEE International, 3170–3173
Jordà Gabriel, Gomis Damià. 2010. Accuracy of SMOS Level 3 SSS products related to observational errors. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens, 48(4): 1694–1701
Jordà Gabriel, Gomis Damià, Talone Marco. 2011. The SMOS L3 mapping algorithm for sea surface salinity. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens, 49(3): 1032–1051
Kainulainen Juha, Martin-Neira Manuel, Closa Josep, et al. 2011. Performance and stability of the SMOS reference radiometers-status of investigations after 20 months of operation. http://earth.eo.esa.int/workshops/smos_science_workshop/SESSION_1_INSTRUMENTS/J.Kainulainen_SMOS_perfomance_stability_reference_radiometers.pdf
Kerr Yann H, Wigneron Jean-Pierre, Boutin Jacqueline, et al. 2010. The SMOS mission: new tool for monitoring key elements of the global water cycle. Proceedings of the IEEE, 98(5): 666–687
Martin-Neira M, Corbella I, Torres F, et al. 2011. Overview: MIRAS instrument performance and status of RFI. http://earth.eo.esa.int/workshops/smos_science_workshop/SESSION_1_INSTRUMENTS/M.M.Neira_Overview_MIRAS_Instrument_Status_RFI.pdf
Reul Nicolas, Tenerelli J, Boutin J, et al. 2011. First SSS products from SMOS generated at the Centre Aval des Donnees SMOS. http://earth.eo.esa.int/workshops/smos_science_workshop/SESSION_3_OCEAN_SALINITY/N.Reul_SMOS_1st_SSS_Products.pdf
Sabia Roberto, Camps Adriano, Talone Marco, et al. 2010. Determination of the sea surface salinity error budget in the soil moisture and ocean salinity mission. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens, 48(4): 1684–1693
Snyder J P. 1992. An equal-area map projection for polyhedral globes. Cartographica, 29(1): 10–21
Tenerelli Joseph E, Reul Nicolas. 2010. Analysis of SMOS brightness temperatures obtained from March through May 2010. http://argans.co.uk/smos/docs/papers/067-D3_jtenerelli.pdf
Yin Xiaobin, Boutin J, Martin N, et al. 2011. Sea surface roughness and foam signature onto SMOS brightness temperature and salinity. http://earth.eo.esa.int/workshops/smos_science_workshop/SESSION_3_OCEAN_SALINITY/X.Yin_SMOS_brightness_temperature_salinity.pdf
Yin Xiaobin, Liu Yuguang, Zhang Hande, et al. 2005. Microwave remote sensing of sea surface salinityĺCa study on microwave radiation theory of calm sea surface. Chinese High Technology Letters (in Chinese), 15(8): 86–90
Zine Sonia, Boutin Jacqueline, Font Jordi, et al. 2008. Overview of the SMOS sea surface salinity prototype processor. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens, 46(3): 621–664
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: The National Natural Science Fund of China under contact No. 41276088; and the National Natural Science Fund for Young Scholars of China under contact Nos 41206002 and 41306010.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Zhang, R., Wang, H. et al. An analysis on the error structure and mechanism of soil moisture and ocean salinity remotely sensed sea surface salinity products. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 33, 48–55 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-014-0427-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-014-0427-4