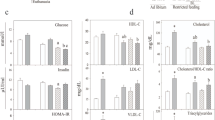
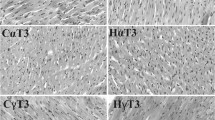
Abstract
High-sugar intake and senescence share common deleterious effects, in particular in liver, but combination of these two factors was little studied. Our aims were to examine the effect of a high-sucrose diet in liver of old rats and also the potential benefices of a polyphenol/micronutrient supplementation. Four groups of 22-month-old male rats fed during 5 months with a diet containing either 13 or 62% sucrose, supplemented or not with rutin, vitamin E, A, D, selenium, and zinc were compared. We measured liver macronutrient composition, glycation/oxidative stress, enzyme activities (lipogenesis, β-oxidation, fructokinase), gene expression (enzymes and transcription factors), in vivo protein synthesis rates and plasma parameters. Sucrose induced an increase in plasma and liver lipid content, and a stimulation of liver protein synthesis rates. Gene expression was little changed by sucrose, with lower levels for LXR-α and LXR-β. Polyphenol/micronutrient supplementation tended to limit liver triglyceride infiltration through variations in fatty acid synthase, acyl coA oxidase, and possibly ATP-citrate lyase activities. In conclusion, despite differences in enzymatic regulations, and blunted responses of gene expression, high-sucrose diet was still able to induce a marked increase in liver lipid content in old animals. However, it probably attenuated the positive impact of polyphenol/micronutrients.




Similar content being viewed by others

References
Bechmann LP, Hannivoort RA, Gerken G, Hotamisligil GS, Trauner M, Canbay A (2012) The interaction of hepatic lipid and glucose metabolism in liver diseases. J Hepatol 56:952–964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2011.08.025
Bertolotti M, Lonardo A, Mussi C, Baldelli E, Pellegrini E, Ballestri S, Romagnoli D, Loria P (2014) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and aging: epidemiology to management. World J Gastroenterol 20:14185–14204. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i39.14185
Chuffa LG, Fioruci-Fontanelli BA, Bordon JG, Pires RB, Braga CP, Seiva FR, Fernandes AA (2014) Rutin ameliorates glycemic index, lipid profile and enzymatic activities in serum, heart and liver tissues of rats fed with a combination of hypercaloric diet and chronic ethanol consumption. Indian J Biochem Biophys 51:215–222
Chypre M, Zaidi N, Smans K (2012) ATP-citrate lyase: a mini-review. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 422:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.04.144
Dekker MJ, Su Q, Baker C, Rutledge AC, Adeli K (2010) Fructose: a highly lipogenic nutrient implicated in insulin resistance, hepatic steatosis, and the metabolic syndrome. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 299:E685–E694. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00283.2010
Dong B, Kan CF, Singh AB, Liu J (2013) High-fructose diet downregulates long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase 3 expression in liver of hamsters via impairing LXR/RXR signaling pathway. J Lipid Res 54:1241–1254. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.M032599
Eliades M, Spyrou E (2015) Vitamin D: a new player in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease? World J Gastroenterol 21:1718–1727. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i6.1718
Faure P, Barclay D, Joyeux-Faure M, Halimi S (2007) Comparison of the effects of zinc alone and zinc associated with selenium and vitamin E on insulin sensitivity and oxidative stress in high-fructose-fed rats. J Trace Elem Med Biol 21:113–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2006.12.005
Ferramosca A, Conte A, Damiano F, Siculella L, Zara V (2014) Differential effects of high-carbohydrate and high-fat diets on hepatic lipogenesis in rats. Eur J Nutr 53:1103–1114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-013-0613-8
Giris M, Dogru-Abbasoglu S, Kumral A, Olgac V, Kocak-Toker N, Uysal M (2014) Effect of carnosine alone or combined with alpha-tocopherol on hepatic steatosis and oxidative stress in fructose-induced insulin-resistant rats. J Physiol Biochem 70:385–395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-014-0314-7
Hagopian K, Ramsey JJ, Weindruch R (2005) Fructose metabolizing enzymes from mouse liver: influence of age and caloric restriction. Biochim Biophys Acta 1721:37–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2004.10.001
Hsu CL, Wu CH, Huang SL, Yen GC (2009) Phenolic compounds rutin and o-coumaric acid ameliorate obesity induced by high-fat diet in rats. J Agric Food Chem 57:425–431. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf802715t
Hu QH, Zhang X, Pan Y, Li YC, Kong LD (2012) Allopurinol, quercetin and rutin ameliorate renal NLRP3 inflammasome activation and lipid accumulation in fructose-fed rats. Biochem Pharmacol 84:113–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2012.03.005
Jensen-Urstad AP, Semenkovich CF (2012) Fatty acid synthase and liver triglyceride metabolism: housekeeper or messenger? Biochim Biophys Acta 1821:747–753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2011.09.017
Lanaspa MA, Sanchez-Lozada LG, Choi YJ, Cicerchi C, Kanbay M, Roncal-Jimenez CA, Ishimoto T, Li N, Marek G, Duranay M, Schreiner G, Rodriguez-Iturbe B, Nakagawa T, Kang DH, Sautin YY, Johnson RJ (2012) Uric acid induces hepatic steatosis by generation of mitochondrial oxidative stress: potential role in fructose-dependent and -independent fatty liver. J Biol Chem 287:40732–40744. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.399899
Lustig RH (2013) Fructose: it’s “alcohol without the buzz”. Advances in nutrition: an international review. Journal 4:226–235. https://doi.org/10.3945/an.112.002998
Mayot G, Breuille D, Jarret AR, Obled C, Papet I (2008) Systemic low-grade inflammation does not decrease skeletal muscle mass and protein synthesis in old rats. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 8:410–417
Mosoni L, Gatineau E, Gatellier P, Migne C, Savary-Auzeloux I, Remond D, Rocher E, Dardevet D (2014) High whey protein intake delayed the loss of lean body mass in healthy old rats, whereas protein type and polyphenol/antioxidant supplementation had no effects. PLoS One 9:e109098. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0109098
Odbayar TO, Badamhand D, Kimura T, Takashi Y, Tsushida T, Ide T (2006) Comparative studies of some phenolic compounds (quercetin, rutin, and ferulic acid) affecting hepatic fatty acid synthesis in mice. J Agric Food Chem 54:8261–8265. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf061135c
Pagliassotti MJ, Prach PA, Koppenhafer TA, Pan DA (1996) Changes in insulin action, triglycerides, and lipid composition during sucrose feeding in rats. Am J Phys 271:R1319–R1326
Panchal SK, Poudyal H, Arumugam TV, Brown L (2011) Rutin attenuates metabolic changes, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, and cardiovascular remodeling in high-carbohydrate, high-fat diet-fed rats. J Nutr 141:1062–1069. https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.111.137877
Park SY, Kim YW, Kim JE, Kim JY (2006) Age-associated changes in fat metabolism in the rat and its relation to sympathetic activity. Life Sci 79:2228–2233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2006.07.014
Peng CH, Liu LK, Chuang CM, Chyau CC, Huang CN, Wang CJ (2011) Mulberry water extracts possess an anti-obesity effect and ability to inhibit hepatic lipogenesis and promote lipolysis. J Agric Food Chem 59:2663–2671. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf1043508
Poirier Y, Antonenkov VD, Glumoff T, Hiltunen JK (2006) Peroxisomal beta-oxidation—a metabolic pathway with multiple functions. Biochim Biophys Acta 1763:1413–1426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.08.034
Polakof S, Dardevet D, Lyan B, Mosoni L, Gatineau E, Martin JF, Pujos-Guillot E, Mazur A, Comte B (2016) Time course of molecular and metabolic events in the development of insulin resistance in fructose-fed rats. J Proteome Res 15:1862–1874. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.6b00043
Prakash P, Singh V, Jain M, Rana M, Khanna V, Barthwal MK, Dikshit M (2014) Silymarin ameliorates fructose induced insulin resistance syndrome by reducing de novo hepatic lipogenesis in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 727:15–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.01.038
Reeves PG, Nielsen FH, Fahey GC Jr (1993) AIN-93 purified diets for laboratory rodents: final report of the American Institute of Nutrition ad hoc writing committee on the reformulation of the AIN-76A rodent diet. J Nutr 123:1939–1951
Shafrir E, Orevi M (1984) Response of hepatic fructokinase to long-term sucrose diets and diabetes in spiny mice, albino mice and rats. Comp Biochem Physiol B 78:493–498
She P, Olson KC, Kadota Y, Inukai A, Shimomura Y, Hoppel CL, Adams SH, Kawamata Y, Matsumoto H, Sakai R, Lang CH, Lynch CJ (2013) Leucine and protein metabolism in obese Zucker rats. PLoS One 8:e59443. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0059443
Tappy L, Le KA (2012) Does fructose consumption contribute to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease? Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol 36:554–560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinre.2012.06.005
Vila L, Rebollo A, Adalsteisson GS, Alegret M, Merlos M, Roglans N, Laguna JC (2011) Reduction of liver fructokinase expression and improved hepatic inflammation and metabolism in liquid fructose-fed rats after atorvastatin treatment. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 251:32–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2010.11.011
Vitorica J, Satrustegui J, Machado A (1981) Metabolic implications of ageing: changes in activities of key lipogenic and gluconeogenic enzymes in the aged rat liver. Enzyme 26:144–152
Wu CH, Lin MC, Wang HC, Yang MY, Jou MJ, Wang CJ (2011) Rutin inhibits oleic acid induced lipid accumulation via reducing lipogenesis and oxidative stress in hepatocarcinoma cells. J Food Sci 76:T65–T72. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3841.2010.02033.x
Yang L, Zhang Y, Wang S, Zhang W, Shi R (2014) Decreased liver peroxisomal beta-oxidation accompanied by changes in brain fatty acid composition in aged rats. Neurol Sci 35:289–293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-013-1509-3
Zhang Y, Wang L, Zhang J, Li Y, He Q, Li H, Guo X, Guo J, Zhang H (2014) Probiotic Lactobacillus casei Zhang ameliorates high-fructose-induced impaired glucose tolerance in hyperinsulinemia rats. Eur J Nutr 53:221–232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-013-0519-5
Zhao S, Li R, Li Y, Chen W, Zhang Y, Chen G (2012) Roles of vitamin a status and retinoids in glucose and fatty acid metabolism. Biochem Cell Biol 90:142–152. https://doi.org/10.1139/o11-079
Acknowledgements
We thank Christophe Del’homme, Philippe Denis, Philippe Lhoste, and Arlette Cissoire for animal management and Nordine Hafnaoui and Brigitte Laillet for technical assistance.
This work was supported by Institut National de la Recherche Agronomique (INRA), France. Similar results as those of this study were published in a preliminary form in the result section of Gatineau Eva thesis on the following website: https://tel.archives-ouvertes.fr/tel-01491088/document.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gatineau, E., Capel, F., Dardevet, D. et al. Effect of high chronic intake of sucrose on liver metabolism in aging rats. Modulation by rutin and micronutrients. J Physiol Biochem 74, 569–577 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-018-0628-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-018-0628-y