Abstract
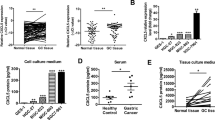
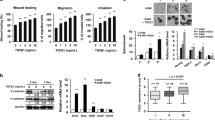
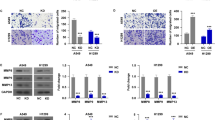
Epithelial neutrophil-activating peptide-78 (CXCL5), a member of the subgroup of CXC-type chemokine family, is an inflammatory factor involved in the progression of lung cancer, but the underlying mechanism remains unclear. In this study, we investigated the effects of CXCL5 on proliferation and migration in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) using tissue microarrays from NSCLC patients and H460 cells transfected with a CXCL5-interfered lentivirus vector or stimulated with recombinant CXCL5. We observed that the expression of CXCL5 was significantly higher in lung cancer cell lines, and high CXCL5 was associated with high chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 2 expression and was significantly associated with poor differentiation. The high expression of CXCL5 was associated with poor NSCLC prognosis and was an independent predictive factor. Furthermore, downregulation of CXCL5 in H460 cells significantly reduced proliferation and migration. Recombinant CXCL5 promoted H460 cell proliferation and movement by activating MAPK/ERK1/2 and PI3K/AKT signaling. Our study elucidates the important role of CXCL5 in the progression and prognosis of NSCLC. These findings suggested that CXCL5 might be a potential biomarker and novel therapeutic target for lung cancer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arenberg DA, Keane MP, DiGiovine B, Kunkel SL, Morris SB, Xue YY, Burdick MD, Glass MC, Iannettoni MD, Strieter RM (1998) Epithelial-neutrophil activating peptide (ENA-78) is an important angiogenic factor in non-small cell lung cancer. J Clin Invest 102:465–472
Coco S, Truini A, Alama A, Dal Bello MG, Vene R, Garuti A, Carminati E, Rijavec E, Genova C, Barletta G, Sini C, Ballestrero A, Boccardo F, Grossi F (2014) Afatinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer involves the PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK signalling pathways and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Target Oncol 10:393-404
Desurmont T, Skrypek N, Duhamel A, Jonckheere N, Millet G, Leteurtre E, Gosset P, Duchene B, Ramdane N, Hebbar M, Van Seuningen I, Pruvot FR, Huet G, Truant S (2015) Overexpression of chemokine receptor CXCR2 and ligand CXCL7 in liver metastases from colon cancer is correlated to shorter disease-free and overall survival. Cancer Sci 106:262–269
Frick VO, Rubie C, Wagner M, Graeber S, Grimm H, Kopp B, Rau BM, Schilling MK (2008) Enhanced ENA-78 and IL-8 expression in patients with malignant pancreatic diseases. Pancreatology 8:488–497
Gao Y, Guan Z, Chen J, Xie H, Yang Z, Fan J, Wang X, Li L (2015) CXCL5/CXCR2 axis promotes bladder cancer cell migration and invasion by activating PI3K/AKT-induced upregulation of MMP2/MMP9. Int J Oncol 47:690–700
Germano G, Allavena P, Mantovani A (2008) Cytokines as a key component of cancer-related inflammation. Cytokine 43:374–379
Gu J, Ding JY, Lu CL, Lin ZW, Chu YW, Zhao GY, Guo J, Ge D (2013) Overexpression of CD88 predicts poor prognosis in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 81:259–265
Han N, Yuan X, Wu H, Xu H, Chu Q, Guo M, Yu S, Chen Y, Wu K (2015) DACH1 inhibits lung adenocarcinoma invasion and tumor growth by repressing CXCL5 signaling. Oncotarget 6:5877–5888
Hsu YL, Hou MF, Kuo PL, Huang YF, Tsai EM (2013) Breast tumor-associated osteoblast-derived CXCL5 increases cancer progression by ERK/MSK1/Elk-1/snail signaling pathway. Oncogene 32:4436–4447
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61:69–90
Kang X, Kong F, Wu X, Ren Y, Wu S, Wu K, Jiang Z, Zhang W (2015) High glucose promotes tumor invasion and increases metastasis-associated protein expression in human lung epithelial cells by upregulating heme oxygenase-1 via reactive oxygen species or the TGF-beta1/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem 35:1008–1022
Kasashima H, Yashiro M, Nakamae H, Kitayama K, Masuda G, Kinoshita H, Fukuoka T, Hasegawa T, Nakane T, Hino M, Hirakawa K, Ohira M (2016) CXCL1-chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 2 signaling stimulates the recruitment of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal cells into diffuse-type gastric cancer stroma. Am J Pathol 186:3028–3039
Kawamura M, Toiyama Y, Tanaka K, Saigusa S, Okugawa Y, Hiro J, Uchida K, Mohri Y, Inoue Y, Kusunoki M (2012) CXCL5, a promoter of cell proliferation, migration and invasion, is a novel serum prognostic marker in patients with colorectal cancer. Eur J Cancer 48:2244–2251
Khan MN, Wang B, Wei J, Zhang Y, Li Q, Luan X, Cheng JW, Gordon JR, Li F, Liu H (2015) CXCR1/2 antagonism with CXCL8/interleukin-8 analogue CXCL8(3-72)K11R/G31P restricts lung cancer growth by inhibiting tumor cell proliferation and suppressing angiogenesis. Oncotarget 6:21315–21327
Kim EJ, Juhnn YS (2015) Cyclic AMP signaling reduces sirtuin 6 expression in non-small cell lung cancer cells by promoting ubiquitin-proteasomal degradation via inhibition of the Raf-MEK-ERK (Raf/mitogen-activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase) pathway. J Biol Chem 290:9604–9613
Kowalczuk O, Burzykowski T, Niklinska WE, Kozlowski M, Chyczewski L, Niklinski J (2014) CXCL5 as a potential novel prognostic factor in early stage non-small cell lung cancer: results of a study of expression levels of 23 genes. Tumour Biol 35:4619–4628
Kuo PL, Huang MS, Hung JY, Chou SH, Chiang SY, Huang YF, Yang CJ, Tsai MJ, Chang WA, Hsu YL (2014) Synergistic effect of lung tumor-associated dendritic cell-derived HB-EGF and CXCL5 on cancer progression. Int J Cancer 135:96–108
Lee YC, Lin HH, Hsu CH, Wang CJ, Chiang TA, Chen JH (2010) Inhibitory effects of andrographolide on migration and invasion in human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells via down-regulation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 632:23–32
Liang JX, Gao W, Liang Y, Zhou XM (2015) Chemokine receptor CXCR4 expression and lung cancer prognosis: a meta-analysis. Int J Clin Exp Med 8:5163–5174
Morrison CD, Parvani JG, Schiemann WP (2013) The relevance of the TGF-beta paradox to EMT-MET programs. Cancer Lett 341:30–40
Pold M, Zhu LX, Sharma S, Burdick MD, Lin Y, Lee PP, Pold A, Luo J, Krysan K, Dohadwala M, Mao JT, Batra RK, Strieter RM, Dubinett SM (2004) Cyclooxygenase-2-dependent expression of angiogenic CXC chemokines ENA-78/CXC ligand (CXCL) 5 and interleukin-8/CXCL8 in human non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res 64:1853–1860
Saintigny P, Massarelli E, Lin S, Ahn YH, Chen Y, Goswami S, Erez B, O'Reilly MS, Liu D, Lee JJ, Zhang L, Ping Y, Behrens C, Solis SL, Heymach JV, Kim ES, Herbst RS, Lippman SM, Wistuba II, Hong WK, Kurie JM, Koo JS (2013) CXCR2 expression in tumor cells is a poor prognostic factor and promotes invasion and metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res 73:571–582
Shiels MS, Pfeiffer RM, Hildesheim A, Engels EA, Kemp TJ, Park JH, Katki HA, Koshiol J, Shelton G, Caporaso NE, Pinto LA, Chaturvedi AK (2013) Circulating inflammation markers and prospective risk for lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 105:1871–1880
Shrihari TG (2017) Dual role of inflammatory mediators in cancer. Ecancermedicalscience 11:721
Spaks A, Svirina D, Spaka I, Jaunalksne I, Breiva D, Tracums I, Krievins D (2016) CXC chemokine ligand 4 (CXCL4) is predictor of tumour angiogenic activity and prognostic biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients undergoing surgical treatment. Biomarkers 21:474–478
Sun JH, Fan N, Zhang Y (2016) Correlation between serum level of chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 18 and poor prognosis in breast cancer. Genet Mol Res 15
Takiguchi S, Korenaga N, Inoue K, Sugi E, Kataoka Y, Matsusue K, Futagami K, Li YJ, Kukita T, Teramoto N, Iguchi H (2014) Involvement of CXCL14 in osteolytic bone metastasis from lung cancer. Int J Oncol 44:1316–1324
Terlizzi M, Casolaro V, Pinto A, Sorrentino R (2014) Inflammasome: cancer’s friend or foe? Pharmacol Ther 143:24–33
Wu Y, Zhou BP (2010) TNF-alpha/NF-kappaB/Snail pathway in cancer cell migration and invasion. Br J Cancer 102:639–644
Yanagawa J, Walser TC, Zhu LX, Hong L, Fishbein MC, Mah V, Chia D, Goodglick L, Elashoff DA, Luo J, Magyar CE, Dohadwala M, Lee JM, St JM, Strieter RM, Sharma S, Dubinett SM (2009) Snail promotes CXCR2 ligand-dependent tumor progression in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 15:6820–6829
Youlden DR, Cramb SM, Baade PD (2008) The international epidemiology of lung cancer: geographical distribution and secular trends. J Thorac Oncol 3:819–831
Zheng J, Zhu X, Zhang J (2014) CXCL5 knockdown expression inhibits human bladder cancer T24 cells proliferation and migration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 446:18–24
Zhou SL, Dai Z, Zhou ZJ, Wang XY, Yang GH, Wang Z, Huang XW, Fan J, Zhou J (2012) Overexpression of CXCL5 mediates neutrophil infiltration and indicates poor prognosis for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 56:2242–2254
Zhou SL, Zhou ZJ, Hu ZQ, Li X, Huang XW, Wang Z, Fan J, Dai Z, Zhou J (2015) CXCR2/CXCL5 axis contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition of HCC cells through activating PI3K/Akt/GSK-3beta/Snail signaling. Cancer Lett 358:124–135
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 81372313) and Outstanding Youth Foundation of Zhongshan Hospital (grant number 2017ZSYQ28).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Shi, L., Gu, J. et al. CXCL5 regulation of proliferation and migration in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. J Physiol Biochem 74, 313–324 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-018-0619-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-018-0619-z