Abstract
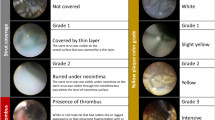
The ultrathin strut biodegradable polymer sirolimus-eluting stent (Orsiro, O-SES) exhibits satisfactory clinical outcomes. However, no report to date has documented the intravascular status of artery repair after O-SES implantation. We examined 5 O-SES placed in 4 patients (age 65 ± 12 years, male 75%) presenting with stable angina pectoris due to de novo lesions in native coronary arteries. Coronary angioscopy was performed immediately after percutaneous coronary intervention and 1 year later. Angioscopic images were analyzed to determine the following: (1) dominant grade of neointimal coverage (NIC) over the stent; (2) maximum yellow plaque grade; and (3) existence of thrombus. Yellow plaque grade was evaluated both immediately after stent implantation and at the time of follow-up observation. The other parameters were evaluated at the time of follow-up examination. NIC was graded as: grade 0, stent struts exposed; grade 1, struts bulging into the lumen, although covered; grade 2, struts embedded in the neointima, but translucent; grade 3, struts fully embedded and invisible. Yellow plaque severity was graded as: grade 0, white; grade 1, light yellow; grade 2, yellow; and grade 3, intensive yellow. Angioscopic findings at 1 year demonstrated the following: dominant NIC grade 1, grade 2, and grade 3 in 1, 2, and 2 stents, respectively; all stents were covered to some extent; focal thrombus adhesion was observed in only 1 stent. Yellow plaque grade did not change from immediately after stent implantation to follow-up. O-SES demonstrated satisfactory arterial repair 1 year after implantation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pilgrim T, Heg D, Roffi M, Tüller D, Muller O, Vuilliomenet A, et al. Ultrathin strut biodegradable polymer sirolimus-eluting stent versus durable polymer everolimus-eluting stent for percutaneous coronary revascularisation (BIOSCIENCE): a randomised, single-blind, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2014;384:2111–22.
Windecker S, Haude M, Neumann FJ, Stangl K, Witzenbichler B, Slagboom T, et al. Comparison of a novel biodegradable polymer sirolimus-eluting stent with a durable polymer everolimus-eluting stent: results of the randomized BIOFLOW-II trial. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2015;8:e001441.
von Birgelen C, Kok MM, van der Heijden LC, Danse PW, Schotborgh CE, Scholte M, et al. Very thin strut biodegradable polymer everolimus-eluting and sirolimus-eluting stents versus durable polymer zotarolimus-eluting stents in allcomers with coronary artery disease (BIO-RESORT): a three-arm, randomised, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2016;388:2607–17.
Sakai S, Mizuno K, Yokoyama S, Tanabe J, Shinada T, Seimiya K, et al. Morphologic changes in infarct-related plaque after coronary stent placement: a serial angioscopy study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;42:1558–65.
Takano M, Mizuno K, Yokoyama S, Seimiya K, Ishibashi F, Okamatsu K, et al. Changes in coronary plaque color and morphology by lipid-lowering therapy with atorvastatin: serial evaluation by coronary angioscopy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;42:680–6.
Kotani J, Awata M, Nanto S, Uematsu M, Oshima F, Minamiguchi H, et al. Incomplete neointimal coverage of sirolimus-eluting stents: angioscopic findings. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47:2108–11.
Awata M, Nanto S, Uematsu M, Morozumi T, Watanabe T, Onishi T, et al. Heterogeneous arterial healing in patients following paclitaxel-eluting stent implantation: comparison with sirolimus-eluting stents. J Am Coll Cardiol Interv. 2009;2:453–8.
den Heijer P, Foley DP, Hillege HL, Lablanche JM, van Dijk RB, Franzen D, et al. The ‘Ermenonville’ classification of observations at coronary angioscopy—evaluation of intra- and inter-observer agreement. European Working Group on Coronary Angioscopy. Eur Heart J. 1994;15:815–22.
Kurihara O, Okamatsu K, Mizuno K, Takano M, Yamamoto M, Kobayashi N, et al. Coronary atherosclerosis and risk of acute coronary syndromes in chronic kidney disease using angioscopy and the kidney disease: improving global outcomes (KDIGO) classification. Atherosclerosis. 2015;243:567–72.
Ueda Y, Asakura M, Yamaguchi O, Hirayama A, Hori M, Kodama K. The healing process of infarct-related plaques. Insights from 18 months of serial angioscopic follow-up. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001;38:1916–22.
Higo T, Ueda Y, Oyabu J, Okada K, Nishio M, Hirata A, et al. Atherosclerotic and thrombogenic neointima formed over sirolimus drug-eluting stent: an angioscopic study. J Am Coll Cardiol Imaging. 2009;2:616–24.
Awata M, Kotani J, Uematsu M, Morozumi T, Watanabe T, Onishi T, et al. Serial angioscopic evidence of incomplete neointimal coverage after sirolimus-eluting stent implantation: comparison with bare-metal stents. Circulation. 2007;116:910–6.
Awata M, Uematsu M, Sera F, Ishihara T, Watanabe T, Fujita M, et al. Angioscopic assessment of arterial repair following biodegradable polymer-coated biolimus A9-eluting stent implantation. Comparison with durable polymer-coated sirolimus-eluting stent. Circ J. 2011;75:1113–9.
Dai K, Matsuoka H, Kawakami H, Sato T, Watanabe K, Nakama Y, et al. Comparison of chronic angioscopic findings of bare metal stents, 1st-generation drug-eluting stents and 2nd-generation drug-eluting stents—Multicenter Study of Intra-coronary Angioscopy After Stent (MICASA). Circ J. 2016;80:1916–21.
Akazawa Y, Matsuo K, Ueda Y, Nishio M, Hirata A, Asai M, et al. Atherosclerotic change at one year after implantation of Endeavor zotarolimus-eluting stent vs. everolimus-eluting stent. Circ J. 2014;78:1428–36.
Karjalainen PP, Varho V, Nammas W, Mikkelsson J, Pietilä M, Ylitalo A, et al. Early neointimal coverage and vasodilator response following biodegradable polymer sirolimus-eluting vs. durable polymer zotarolimus-eluting stents in patients with acute coronary syndrome—HATTRICK-OCT trial. Circ J. 2015;79:360–7.
Schwartz RS. Pathophysiology of restenosis: interaction of thrombosis, hyperplasia, and/or remodeling. Am J Cardiol. 1998;81:14E–7E. http://www.ajconline.org/. Accessed 31 Oct 2016.
Foin N, Lee RD, Torii R, Guitierrez-Chico JL, Mattesini A, Nijjer S, et al. Impact of stent strut design in metallic stents and biodegradable scaffolds. Int J Cardiol. 2014;177:800–8.
Guagliumi G, Sirbu V, Musumeci G, Gerber R, Biondi-Zoccai G, Ikejima H, et al. Examination of the in vivo mechanisms of late drug-eluting stent thrombosis: findings from optical coherence tomography and intravascular ultrasound imaging. J Am Coll Cardiol Interv. 2012;5:12–20.
Finn AV, Joner M, Nakazawa G, Kolodgie F, Newell J, John MC, et al. Pathological correlates of late drug-eluting stent thrombosis: strut coverage as a marker of endothelialization. Circulation. 2007;115:2435–41.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
12928_2018_510_MOESM1_ESM.mpg
Angioscopic image of ultrathin strut biodegradable polymer sirolimus-eluting Stent (O-SES) 385 days after implantation (case number 1). Coronary angioscopic observation 1 year after O-SES (2.5 mm diameter by 18 mm length) implantation in the distal part of right coronary artery demonstrated that while stent struts were embedded in the neointima, but were translucently visible in the proximal segment, stent struts were fully embedded and invisible from middle to distal stented segment (MPG 4736 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishihara, T., Awata, M., Iida, O. et al. Satisfactory arterial repair 1 year after ultrathin strut biodegradable polymer sirolimus-eluting stent implantation: an angioscopic observation. Cardiovasc Interv and Ther 34, 34–39 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12928-018-0510-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12928-018-0510-4