Abstract
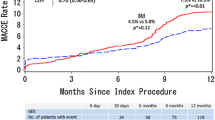
The impact of second-generation drug-eluting stent (G2-DES) implantations compared with first-generation drug-eluting stents (G1-DES) implantations on long-term clinical outcomes after percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with and without diabetes mellitus (DM) has not yet been adequately assessed. This pooled analysis compared 3-year clinical outcomes between G1- and G2-DES according to the presence or absence of DM, using individual patient-level data from the RESET and NEXT trials. Among 6431 patients, G1-DES and G2-DES were used in 713 and 2211 patients, respectively, in the DM stratum, and 887 and 2620 patients, respectively, in the non-DM stratum. Cumulative incidence of and adjusted hazard ratio (HR) for target-lesion revascularization (TLR) were not significantly different between G2- and G1-DES in both strata [DM, 8.7 versus 10.1%, adjusted HR: 0.80, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.59–1.10, P = 0.17; non-DM, 5.7 versus 6.2%, adjusted HR: 0.86, 95% CI 0.62–1.22, P = 0.38]. In the insulin-treated DM (ITDM), G2-DES had a significantly lower adjusted HR for TLR compared with G1-DES, although there was no significant difference in the non-ITDM (ITDM, adjusted HR: 0.54, 95% CI 0.32–0.96, P = 0.04; non-ITDM, adjusted HR: 0.95, 95% CI 0.66–1.42, P = 0.81). G2-DES provided similar risk for TLR in non-ITDM and non-DM patients compared with G1-DES. However, G2-DES compared with G1-DES had a lower risk for TLR among ITDM patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schofer J, Schlüter M, Rau T, Hammer F, Haag N, Mathey DG. Influence of treatment modality on angiographic outcome after coronary stenting in diabetic patients: a controlled study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;35:1554–9.
West NEJ. Clinical and angiographic predictors of restenosis after stent deployment in diabetic patients. Circulation. 2004;109:867–73.
Qin S, Zhou Y, Jiang H, Hu B, Tao L, Xie M. The association of diabetes mellitus with clinical outcomes after coronary stenting: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2013;8:e72710.
Machecourt J, Danchin N, Lablanche JM, Fauvel JM, Bonnet JL, Marliere S, et al. Risk factors for stent thrombosis after implantation of sirolimus-eluting stents in diabetic and nondiabetic patients. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;50:501–8.
Akin I, Bufe A, Eckardt L, Reinecke H, Senges J, Richardt G, et al. Comparison of outcomes in patients with insulin-dependent versus non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus receiving drug-eluting stents (from the first phase of the prospective Multicenter German DES.DE Registry)†. Am J Cardiol. 2010;106:1201–7.
Tada T, Kimura T, Morimoto T, Ono K, Furukawa Y, Nakagawa Y, et al. Comparison of three-year clinical outcomes after sirolimus-eluting stent implantation among insulin-treated diabetic, non–insulin-treated diabetic, and non-diabetic patients from J-Cypher registry. Am J Cardiol. 2011;107:1155–62.
Hillegass WB, Patel MR, Klein LW, Gurm HS, Brennan JM, Anstrom KJ, et al. Long-term outcomes of older diabetic patients after percutaneous coronary stenting in the US: a report from the national cardiovascular data registry, 2004–2008. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60:2280–9.
Moussa I. Impact of sirolimus-eluting stents on outcome in diabetic patients: a SIRIUS (SIRolImUS-coated Bx velocity balloon-expandable stent in the treatment of patients with de novo coronary artery lesions) substudy. Circulation. 2004;109:2273–8.
Stettler C, Allemann S, Wandel S, Kastrati A, Morice MC, Schomig A, et al. Drug eluting and bare metal stents in people with and without diabetes: collaborative network meta-analysis. BMJ. 2008;337:a1331.
Bangalore S, Kumar S, Fusaro M, Amoroso N, Kirtane AJ, Byrne RA, et al. Outcomes with various drug eluting or bare metal stents in patients with diabetes mellitus: mixed treatment comparison analysis of 22,844 patient years of follow-up from randomised trials. BMJ. 2012;345:e5170.
Kimura T, Morimoto T, Natsuaki M, Shiomi H, Igarashi K, Kadota K, et al. Comparison of everolimus-eluting and sirolimus-eluting coronary stents: 1-year outcomes from the randomized evaluation of sirolimus-eluting versus everolimus-eluting stent trial (RESET). Circulation. 2012;126:1225–36.
Shiomi H, Kozuma K, Morimoto T, Igarashi K, Kadota K, Tanabe K, et al. Long-term clinical outcomes after everolimus- and sirolimus-eluting coronary stent implantation: final 3-year follow-up of the randomized evaluation of sirolimus-eluting versus everolimus-eluting stent trial. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2014;7:343–54.
Natsuaki M, Kozuma K, Morimoto T, Kadota K, Muramatsu T, Nakagawa Y, et al. Biodegradable polymer biolimus-eluting stent versus durable polymer everolimus-eluting stent. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62:181–90.
Natsuaki M, Kozuma K, Morimoto T, Shiomi H, Kimura T. Two-year outcome of a randomized trial comparing second-generation drug-eluting stents using biodegradable or durable polymer. JAMA. 2014;311:2125.
Natsuaki M, Kozuma K, Morimoto T, Kadota K, Muramatsu T, Nakagawa Y, et al. Final 3-year outcome of a randomized trial comparing second-generation drug-eluting stents using either biodegradable polymer or durable polymer. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2015;8:e002817.
Mauri L, Hsieh W, Massaro JM, Ho KKL, D’Agostino R, Cutlip DE. Stent thrombosis in randomized clinical trials of drug-eluting stents. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:1020–9.
Kim W-J, Lee S-W, Park S-W, Kim Y-H, Yun S-C, Lee J-Y, et al. Randomized comparison of everolimus-eluting stent versus sirolimus-eluting stent implantation for de novo coronary artery disease in patients with diabetes mellitus (ESSENCE-DIABETES): results from the ESSENCE-DIABETES trial. Circulation. 2011;124:886–92.
Jensen LO, Thayssen P, Junker A, Maeng M, Tilsted H-H, Kaltoft A, et al. Comparison of outcomes in patients with versus without diabetes mellitus after revascularization with everolimus- and sirolimus-eluting stents (from the SORT OUT IV trial). Am J Cardiol. 2012;110:1585–91.
Christiansen EH, Jensen LO, Thayssen P, Tilsted H-H, Krusell LR, Hansen KN, et al. Biolimus-eluting biodegradable polymer-coated stent versus durable polymer-coated sirolimus-eluting stent in unselected patients receiving percutaneous coronary intervention (SORT OUT V): a randomised non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2013;381:661–9.
Kang S, Park KH, Ahn H, Park KW, Hong YJ, Koo B, et al. Everolimus-eluting versus sirolimus-eluting coronary stents in patients with and without diabetes mellitus. Eurointervention. 2014;10:74–82.
Johnstone MT, Creager SJ, Scales KM, Cusco JA, Lee BK, Creager MA. Impaired endothelium-dependent vasodilation in patients with insulin- dependent diabetes mellitus. Circulation. 1993;88:2510–6.
Hartge MM, Unger T, Kintscher U. The endothelium and vascular inflammation in diabetes. Diabetes Vasc Dis Res. 2007;4:84.
Acknowledgements
We appreciate the effort of the members of the cardiac catheterization laboratory and clinical research coordinators in the participating centers. A list of all RESET and NEXT Investigators is given in the Appendix in the Data Supplement (Supplemental Appendix A and B).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Sources of funding
The Abbott Vascular Japan (Tokyo, Japan) and Terumo (Tokyo, Japan).
Conflict of interest
Dr. Kozuma and Dr. Tanabe have served on the advisory boards of Abbott Vascular and Terumo; and have received lecture fees from Abbott Vascular and Terumo. Dr. Kadota has received honoraria from Abbott Vascular and Terumo; and has served on the advisory boards of Abbott Vascular. Dr. Morino has served on the advisory board of Abbott Vascular and Terumo. Dr. T. Kimura has served on the advisory board of Terumo and Abbott Vascular. The other authors report no conflicts.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakatsuma, K., Shiomi, H., Natsuaki, M. et al. Second-generation versus first-generation drug-eluting stents in patients with and without diabetes mellitus: pooled analysis from the RESET and NEXT trials. Cardiovasc Interv and Ther 33, 125–134 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12928-017-0458-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12928-017-0458-9